Ridaforolimus
572924-54-0
(1R,2R,4S)-4-[(2R)-2-[(1R,9S,12S,15R,16E,18R,19R,21R,23S,24E,26E,28Z,30S,32S,35R)-1,18-dihydroxy-19,30-dimethoxy-15,17,21,23,29,35-hexamethyl-2,3,10,14,20-pentaoxo-11,36-dioxa-4-azatricyclo[30.3.1.04,9]hexatriaconta-16,24,26,28-tetraen-12-yl]propyl]-2-methoxycyclohexyl dimethylphosphinate
Dimethyl-phosphinic Acid C-43 Rapamycin Ester
42-(dimethylphosphinate) Rapamycin
- AP 23573
- AP23573
- Deforolimus
- MK 8669
- MK-8669
- MK8669
- Ridaforolimus
- Taltorvic
- UNII-48Z35KB15K
An mTOR inhibitor for the treatment of cancer.
Ridaforolimus (MK-8669; AP23573; formerly Deforolimus)
Merck, under exclusive worldwide license agreement with Ariad Pharmaceuticals
Method of Action: Oral inhibitor of mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor (mTOR)
Indications/Phase of Trial: Maintenance therapy for metastatic soft-tissue sarcoma and bone sarcomas after at least four chemotherapy cycles (under review after receiving Complete Response letter from FDA in June; NME)
Ridaforolimus is an investigational small-molecule inhibitor of the protein mTOR, a protein that acts as a central regulator of protein synthesis, cell proliferation, cell cycle progression and cell survival, integrating signals from proteins, such as PI3K, AKT and PTEN, known to be important to malignancy.
TARGET- mTOR
Ridaforolimus (also known as AP23573 and MK-8669; formerly known as Deforolimus[1]) is an investigational targeted and small-molecule inhibitor of the protein mTOR, a protein that acts as a central regulator of protein synthesis, cell proliferation, cell cycle progression and cell survival, integrating signals from proteins, such as PI3K, AKT and PTEN known to be important to malignancy. Blocking mTOR creates a starvation-like effect in cancer cells by interfering with cell growth, division, metabolism, and angiogenesis.
It has had promising results in a clinical trial for advanced soft tissue and bone sarcoma.
RIDAFOROLIMUS
NMR….http://file.selleckchem.com/downloads/nmr/S102201-Deforolimus-HNMR-Selleck.pdf
HPLC . http://file.selleckchem.com/downloads/hplc/S102201-Deforolimus-HPLC-Selleck.pdf
MSDS..http://www.selleckchem.com/msds/Deforolimus-MSDS.html
| Commercial arrangements |
Ridaforolimus is being co-developed by Merck and ARIAD Pharmaceuticals. On May 5, 2010, Ariad Pharmaceuticals and Merck & Company announced a clinical development and marketing agreement. With this agreement, Ariad received $125 million in upfront payments from Merck and $53 million in milestone payments. Future payments are triggered upon acceptance of the NDA by the FDA with another payment when the drug receives marketing approval. There are similar milestones for acceptance and approval in both Europe and Japan. Other milestone payments are tied to revenue goals for the drug.[2] ARIAD has opted to co-promote ridaforolimus in the U.S. Merck plans to submit a New Drug Application (NDA) for ridaforolimus to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and a marketing application in the European Union in 2011.[3]
Clinical trials
Phase III SUCCEED
On June 6, 2011, Ariad and Merck announced detailed results from the largest randomized study ever in the soft tissue and bone sarcoma population, the Phase III SUCCEED clinical trial. SUCCEED evaluated oral ridaforolimus, in patients with metastatic soft-tissue or bone sarcomas who previously had a favorable response to chemotherapy. In this patient population, ridaforolimus improved progression-free survival (PFS) compared to placebo, the primary endpoint of the study. The complete study results were presented by Sant P. Chawla, M.D., director, Sarcoma Oncology Center, Santa Monica, CA, during the 2011 American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) annual meeting.
The SUCCEED (Sarcoma Multi-Center Clinical Evaluation of the Efficacy of Ridaforolimus) trial was a randomized (1:1), placebo-controlled, double-blind study of oral ridaforolimus administered at 40 mg/day (five of seven days per week) in patients with metastatic soft-tissue or bone sarcomas who previously had a favorable response to chemotherapy. Oral ridaforolimus was granted a Special Protocol Assessment (SPA) by the FDA for the SUCCEED trial.
Based on 552 progression-free survival (PFS) events in 711 patients, (ridaforolimus (N=347), placebo (N=364) determined by an independent radiological review committee, the study achieved its primary endpoint of improvement in PFS, with a statistically significant (p=0.0001) 28 percent reduction in the risk of progression or death observed in those treated with ridaforolimus compared to placebo (hazard ratio=0.72).
Median PFS was 17.7 weeks for those treated with ridaforolimus compared to 14.6 weeks in the placebo group. Furthermore, based on the full analysis of PFS determined by investigator assessment, there was a statistically significant (p<0.0001) 31 percent reduction by ridaforolimus in the risk of progression or death compared to placebo (hazard ratio=0.69). In the investigator assessment analysis, median PFS was 22.4 weeks for those treated with ridaforolimus compared to 14.7 weeks in the placebo group [4
EU WITHDRAWAL IN NOV 2012
Merck, known as MSD outside the U.S. and Canada, announced today that it has formally notified the European Medicines Agency (EMA) of Merck’s decision to withdraw the Marketing Authorisation Application (MAA) for ridaforolimus.
The application for Marketing Authorisation for ridaforolimus was accepted by the EMA in August 2011. At the time of the withdrawal it was under review by the Agency’s Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP). In its letter to the EMA, Merck said that the withdrawal of ridaforolimus was based on the provisional view of the CHMP that the data available to date and provided in the Marketing Authorisation Application were not sufficient to permit licensure of ridaforolimus in the European Union for the maintenance treatment of patients with soft tissue sarcoma or primary malignant bone tumor.
Although the application for these uses was withdrawn, Merck is studying ridaforolimus in combination with other drugs in other tumor types. The withdrawal of the European application of ridaforolimus for the maintenance treatment of patients with soft tissue sarcoma or primary malignant bone tumor does not change Merck’s commitment to the ongoing clinical trials with ridaforolimus.
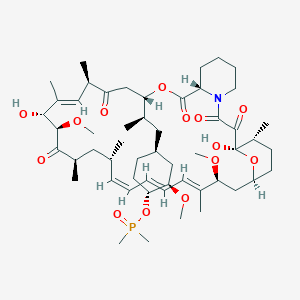
Description
42-(dimethylphosphinate) Rapamycin (Ridaforolimus) represented by the following formula I:
2. Description of RelatedArt
The mammalian target of Rapamycin (mTOR) is known as a mechanistic target of Rapamycin (H), which is found in the studies of Rapamycin. On the other hand, 42-(dimethylphosphinate) Rapamycin (Ridaforolimus) (I) is a derivative of Rapamycin (II), which is also a kind of mTOR inhibitor. Ridaforolimus (I) can inhibit cell division and possibly lead to tumor cell death. Hence, there are many studies related to solid tumor treatments and blood cancer treatments using Ridaforolimus (I). In addition, in 2011, Merck also applied a certification of this compound against soft tissue and bone cancer.
U.S. Pat. No. 7,091,213 discloses a process for preparing 42-(dimethylphosphinate) Rapamycin (Ridaforolimus) (I), and the process thereof is shown in the following Scheme I.
In this process, a solution of Rapamycin (II) in dichloromethane (DCM) was respectively added with 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-methylpyridine or 3,5-lutidine as a base, and followed by the addition of a solution of dimethylphosphinic chloride (DMP-Cl) to perform a phosphorylation reaction at 0° C., under a stream of N2(g). The crude product was purified by flash chromatography (eluted with MeOH/DCM/EtOAc/hexane=1:10:3:3) to provide 42-(dimethyl- phosphinate) Rapamycin (Ridaforolimus) (I), which is a phosphorylated compound at 42-hydroxyl position of Rapamycin (II). In addition, this patent also disclosed a side product of 31,42-bis(dimethyl phosphinate) Rapamycin (III), which is a phosphorylated compound at both 31- hydroxyl position and 42- hydroxyl position of Rapamycin (II).
…………………..
SYNTHESIS
Some additional transformations of potential interest to the practitioner are shown below, including the preparation of reagents for generating the described C-43 phosphorus-containing rapalogs:
Preparation of Diakyl/diaryl Chlorophoshates
Preparation of Alkyl Halide Phosphonates
Illustrative routes for using the foregoing sorts of reagents to prepare certain rapalogs of this invention are shown below.
The synthesis of compounds of this invention often involves preparation of an activated form of the desired moiety “J”, such as a phosphoryl chloride as shown above (e.g. (R)(RO)P—Cl or RR′P(═O)—Cl, etc), and reaction of that reagent with rapamycin (or the appropriate rapalog) under conditions yielding the desired product, which may then be recovered from residual reactants and any undesired side products. Protecting groups may be chosen, added and removed as appropriate using conventional methods and materials.
Purification of Compounds of the Invention
A variety of materials and methods for purifying rapamycin and various rapalogs have been reported in the scientific and patent literatures and may be adapted to purification of the rapalogs disclosed herein. Flash chromatography using a BIOTAGE prepacked cartridge system has been particularly effective. A typical protocol is disclosed in the Examples which follow.
Physicochemical Characterization of Compounds of the Invention
The identity, purity and chemical/physical properties of the rapalogs may be determined or confirmed using known methods and materials, including HPLC, mass spectral analysis, X ray crystallography and NMR spectroscopy. High resolution 1D 1H and 31P NMR spectra acquired using a typical relaxation delay of 3 seconds have proved useful, as has reverse phase HPLC analysis (analytical column, 3 micron particle size, 120 ansgstrom pore size, thermostatted to 50° C. with a mobile phase of 50% acetonitrile, 5% methanol and 45% water (all % s by volume), for example, in an isocratic elution system, with elution of product and impurity peaks followed by UV detection at 280 nanometers). Normal phase HPLC may also be used, especially to evaluate the level of residual rapamycin or rapalog by-products. The presence of residual solvent, heavy metals, moisture and bioburden may be assessed using conventional methods.
Example 9
Dimethyl-phosphinic Acid C-43 Rapamycin Ester
Dimethyl-phosphinic Acid C-43 Rapamycin Ester
To a cooled (0° C.) solution of rapamycin (0.1 g, 0.109 mmol) in 1.8 mL of dichloromethane was added 0.168 g (0.82 mmol) of 2,6-di-t-butyl-4-methyl pyridine, under a stream of N2, followed immediately by a solution of dimethylphosphinic chloride (0.062 g, 0.547 mmol) in 0.2 mL of dichloromethane. The slightly yellow reaction solution was stirred at 0° C., under an atmosphere of N2, for 3.5 h (reaction monitored by TLC). The cold (0° C.) reaction solution was diluted with ˜20 mL EtOAc then transferred to a separatory funnel containing EtOAc (150 mL) and saturated NaHCO3 (100 mL). Upon removing the aqueous layer, the organic layer was washed successively with ice cold 1N HCl (1×100 mL), saturated NaHCO3 (1×100 mL), and brine (1×100 mL), then dried over MgSO4 and concentrated. The crude product was purified by silica gel flash chromatography (eluted with 1:10:3:3 MeOH/DCM/EtOAc/hexane) to provide 0.092 g of a white solid:
1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3) d 4.18 (m, 1H), 4.10 (m, 1H), 3.05 (m, 1H), 1.51 (m, 6H);
31P NMR (121 MHz, CDCl3) d 53.6; 1013 m/z (M+Na).
Example 9
Alternative Synthesis
Rapamycin and dichloromethane are charged into a nitrogen-purged reaction flask. The stirred solution is cooled to approximately 0° C. (an external temperature of −5±5° C. is maintained throughout the reaction). A solution of dimethylphosphinic chloride (2.0 molar equivalents) in dichloromethane is then added over a period of approximately 8–13 minutes.
This is followed immediately by the addition of a solution of 3,5-lutidine (2.2 molar equivalents) in dichloromethane over a period of approximately 15–20 minutes. Throughout both additions, the internal temperature of the reaction sssstays below 0° C. The cooled reaction solution is stirred for 1 hour and then transferred, while still cold, to an extractor containing saturated aqueous NaHCO3 and methyl-t-butyl ether (MTBE), ethyl acetate or diethyl ether. In-process samples are removed at 30 and 60 minute time points.
Samples are prepared in a similar fashion to that described for the reaction workup. Reaction progress is monitored by TLC (1:10:3:3 MeOH/DCM/EtOAc/hexanes) and reverse-phase HPLC analyses. The isolated organic layer is successively washed with ice cold 1N HCl, saturated aqueous NaHCO3 (2×), saturated aqueous NaCl, and dried over sodium sulfate. Upon filtration and solvent removal, the residue undergoes solvent exchange with acetone followed by concentration in vacuo to provide crude product, which may be analyzed for purity by normal- and reversed-phase HPLC.
…………………….
SYNTHESIS
The process of the present invention is shown in the following Scheme II.
- “ARIAD Reports First Quarter 2009 Development Progress and Financial Results- Ridaforolimus New USAN Name to Replace Deforolimus”. ARIAD Pharmaceuticals. 2009. Retrieved 2009-05-07.
- “ARIAD – News release”. Phx.corporate-ir.net. Retrieved 2012-10-07.
- “ARIAD – News release”. Phx.corporate-ir.net. 2011-03-17. Retrieved 2012-10-07.
- “ARIAD – News release”. Phx.corporate-ir.net. 2011-06-06. Retrieved 2012-10-07.
| US8216571 | 7-11-2012 | FULLY HUMAN ANTI-VEGF ANTIBODIES AND METHODS OF USING |
| US2011262525 | 10-28-2011 | METHODS OF TREATMENT |
| US2011014117 | 1-21-2011 | ANTI-IGF1R |
| US2007004767 | 1-5-2007 | Methods for treating neurofibromatosis 1 |
| US2004073024 | 4-16-2004 | Phosphorus-containing compounds and uses thereof |




















