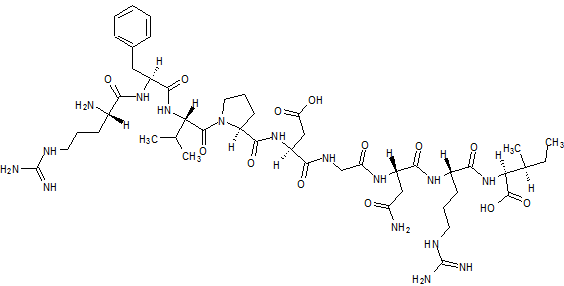
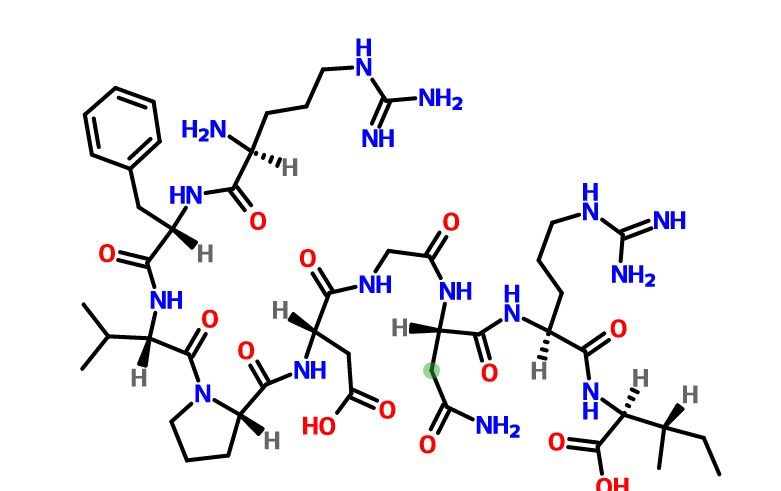
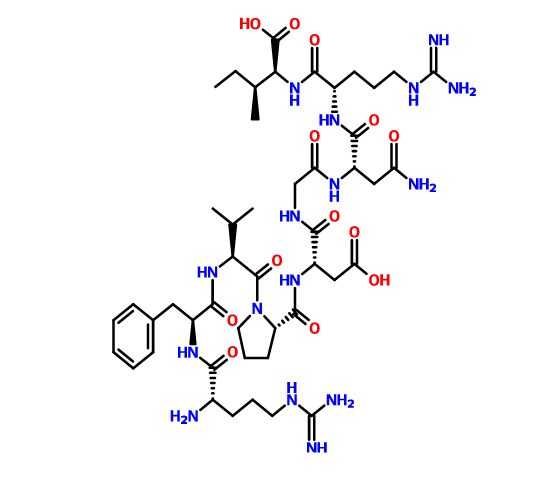
Elpamotide str drawn bt worlddrugtracker
Elpamotide
L-Arginyl-L-phenylalanyl-L-valyl-L-prolyl-L-alpha-aspartylglycyl-L-asparaginyl-L-arginyl-L-isoleucine human soluble (Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor) VEGFR2-(169-177)-peptide
- 10: PN: WO2008099908 SEQID: 10 claimed protein
- 14: PN: WO2009028150 SEQID: 1 claimed protein
- 18: PN: JP2013176368 SEQID: 18 claimed protein
- 1: PN: WO2009028150 SEQID: 1 claimed protein
- 2: PN: WO2010027107 TABLE: 1 claimed sequence
- 6: PN: WO2013133405 SEQID: 6 claimed protein
- 8: PN: US8574586 SEQID: 8 unclaimed protein
- 8: PN: WO2004024766 SEQID: 8 claimed sequence
- 8: PN: WO2010143435 SEQID: 8 claimed protein
Phase III
A neoangiogenesis antagonist potentially for the treatment of pancreatic cancer and biliary cancer.

OTS-102
CAS No.673478-49-4, UNII: S68632MB2G
- Originator OncoTherapy Science
- Class Cancer vaccines; Peptide vaccines
- Mechanism of Action Cytotoxic T lymphocyte stimulants
- 16 Jun 2015 No recent reports on development identified – Phase-II/III for Pancreatic cancer (Combination therapy) and Phase-II for Biliary cancer in Japan (SC)
- 09 Jan 2015 Otsuka Pharmaceutical announces termination of its license agreement with Fuso Pharmaceutical for elpamotide in Japan
- 01 Feb 2013 OncoTherapy Science and Fuso Pharmaceutical Industries complete a Phase-II trial in unresectable advanced Biliary cancer and recurrent Biliary cancer (combination therapy) in Japan (UMIN000002500)
Elpamotide str drawn bt worlddrugtracker
Elpamotide , credit kegg
Elpamotide is a neoangiogenesis inhibitor in phase II clinical trials at OncoTherapy Science for the treatment of inoperable advanced or recurrent biliary cancer. Phase III clinical trials was also ongoing at the company for the treatment of pancreas cancer, but recent progress report for this indication are not available at present.
Consisting of VEGF-R2 protein, elpamotide is a neovascular inhibitor with a totally novel mechanism of action. Its antitumor effect is thought to work by inducing strong immunoreaction against new blood vessels which provide blood flow to tumors. The drug candidate only act against blood vessels involved in tumor growth and is associated with few adverse effects.
Gemcitabine is a key drug for the treatment of pancreatic cancer; however, with its limitation in clinical benefits, the development of another potent therapeutic is necessary. Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 is an essential target for tumor angiogenesis, and we have conducted a phase I clinical trial using gemcitabine and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 peptide (elpamotide). Based on the promising results of this phase I trial, a multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind phase II/III clinical trial has been carried out for pancreatic cancer. The eligibility criteria included locally advanced or metastatic pancreatic cancer. Patients were assigned to either the Active group (elpamotide + gemcitabine) or Placebo group (placebo + gemcitabine) in a 2:1 ratio by the dynamic allocation method. The primary endpoint was overall survival. The Harrington-Fleming test was applied to the statistical analysis in this study to evaluate the time-lagged effect of immunotherapy appropriately. A total of 153 patients (Active group, n = 100; Placebo group, n = 53) were included in the analysis. No statistically significant differences were found between the two groups in the prolongation of overall survival (Harrington-Fleming P-value, 0.918; log-rank P-value, 0.897; hazard ratio, 0.87, 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.486-1.557). Median survival time was 8.36 months (95% CI, 7.46-10.18) for the Active group and 8.54 months (95% CI, 7.33-10.84) for the Placebo group. The toxicity observed in both groups was manageable. Combination therapy of elpamotide with gemcitabine was well tolerated. Despite the lack of benefit in overall survival, subgroup analysis suggested that the patients who experienced severe injection site reaction, such as ulceration and erosion, might have better survival
The vaccine candidate was originally developed by OncoTherapy Science. In January 2010, Fuso Pharmaceutical, which was granted the exclusive rights to manufacture and commercialize elpamotide in Japan from OncoTherapy Science, sublicensed the manufacturing and commercialization rights to Otsuka Pharmaceutical. In 2015, the license agreement between Fuso Pharmaceutical and OncoTherapy Science, and the license agreement between Fuso Pharmaceutical and Otsuka Pharmaceutical terminated.

WO 2010143435
US 8574586
WO 2012044577
WO 2010027107
WO 2013133405
WO 2009028150
WO 2008099908
WO 2004024766
PATENT
In order to avoid difficulties in the formulation preparation, as described above, a vaccine formulation comprising one type of T-cell epitope peptides, methods for multiple types administered to the same patient is also contemplated. However, when administering plural kinds of vaccine preparation, it is necessary to vaccination of a plurality of locations of the body, burden on a patient is increased. Also peptide vaccine formulation, the DTH (Delayed Type Hypersensitivity) skin reactions are often caused called reaction after inoculation. Occurrence of skin reactions at a plurality of positions of the body, increases the discomfort of the patient. Therefore, in order to reduce the burden of patients in vaccination is preferably a vaccine formulation comprising a plurality of T-cell epitope peptide. Further, even when the plurality of kinds administering the vaccine formulation comprising a single type of epitope peptides, when manufacturing each peptide formulation is required the task of selecting an appropriate solvent for each peptide.
Patent Document 2: International Publication No. 2004/031413 Patent
Patent Document 3: The European Patent Publication No. 2111867
///////////Elpamotide, Phase III, A neoangiogenesis antagonist, pancreatic cancer and biliary cancer, OTS-102, OncoTherapy Science Inc, peptide
CC[C@H](C)