The bark of Nauclea latifolia contains tramadol at medicinal concentrations © imagebroker / Alamy
http://www.rsc.org/chemistryworld/2013/09/african-plant-natural-source-tramadol
In another example of nature beating chemists, the African plant Nauclea latifolia has been found to be a natural source of the synthetic opioid tramadol. First marketed in 1977, tramadol is frequently used to relive moderate to moderately-severe pain. While other synthetic drugs have later been found in nature, this is the first instance where the discovery involves clinically viable concentrations.
Colloquially known as the ‘African peach’ or ‘pin cushion tree’, N. latifolia is a flowering, sub-Saharan evergreen that grows widely across Central and West Africa and is used by local populations to treat a wide variety of ailments – including epilepsy, malaria, general pain and many infectious diseases………………………. READ ALL AT
http://www.rsc.org/chemistryworld/2013/09/african-plant-natural-source-tramadol
tramadol

tramadol hydrocloride
The chemical name for tramadol hydrochloride is (±)cis-2-[(dimethylamino)methyl]-1-(3methoxyphenyl) cyclohexanol hydrochloride
Tramadol (marketed as the hydrochloride salt by Janssen Pharmaceutica as Ultram in the United States, Ralivia by Biovail in Canada and many other companies throughout the world) is a centrally acting synthetic opioid analgesic used to treat moderate to moderately severe pain. The drug has a wide range of applications, including treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, restless legs syndrome, motor neurone disease and fibromyalgia.[citation needed] It was launched and marketed as Tramal by the German pharmaceutical company Grünenthal GmbH in 1977.
Tramadol is a weak μ-opioid receptor agonist, a serotonin releaser and a reuptake inhibitor of norepinephrine. Tramadol is metabolized to O-desmethyltramadol, a significantly more potent μ-opioid agonist. Tramadol and its major metabolite(s) are distinguished from other more potent opioid agonists by relative selectivity for μ-opioid receptors.
Chemistry
Characteristics
Structurally, tramadol closely resembles a stripped down version of codeine. Both codeine and tramadol share the 3-methyl ether group, and both compounds are metabolized along the same hepatic pathway and mechanism to the stronger opioid, phenol agonist analogs. For codeine, this is morphine, and for tramadol, it is the O-desmethyltramadol.
When administered through IV, patients notice very little clinical difference in subjective potency compared to morphine.
Comparison with related substances
Structurally, tapentadol is the closest chemical relative of tramadol in clinical use. Tapentadol is also an opioid, but unlike both tramadol and venlafaxine, tapentadol represents only one stereoisomer and is the weaker of the two, in terms of opioid effect. Both tramadol and venlafaxine are racemic mixtures. Structurally, tapentadol also differs from tramadol in being a phenol, and not an ether. Also, both tramadol and venlafaxine incorporate a cyclohexyl moiety, attached directly to the aromatic, while tapentadol lacks this feature.
Synthesis and stereoisomerism


(1R,2R)-Tramadol (1S,2S)-Tramadol


(1R,2S)-Tramadol (1S,2R)-Tramadol
The chemical synthesis of tramadol is described in the literature.[62] Tramadol [2-(dimethylaminomethyl)-1-(3-methoxyphenyl)cyclohexanol] has two stereogenic centers at the cyclohexane ring. Thus, 2-(dimethylaminomethyl)-1-(3-methoxyphenyl)cyclohexanol may exist in four different configurational forms:
- (1R,2R)-isomer
- (1S,2S)-isomer
- (1R,2S)-isomer
- (1S,2R)-isomer
The synthetic pathway leads to the racemate (1:1 mixture) of (1R,2R)-isomer and the (1S,2S)-isomer as the main products. Minor amounts of the racemic mixture of the (1R,2S)-isomer and the (1S,2R)-isomer are formed as well. The isolation of the (1R,2R)-isomer and the (1S,2S)-isomer from the diastereomeric minor racemate [(1R,2S)-isomer and (1S,2R)-isomer] is realized by the recrystallization of the hydrochlorides. The drug tramadol is a racemate of the hydrochlorides of the (1R,2R)-(+)- and the (1S,2S)-(–)-enantiomers. The resolution of the racemate [(1R,2R)-(+)-isomer / (1S,2S)-(–)-isomer] was described[63] employing (R)-(–)- or (S)-(+)-mandelic acid. This process does not find industrial application, since tramadol is used as a racemate, despite known different physiological effects[64] of the (1R,2R)- and (1S,2S)-isomers, because the racemate showed higher analgesic activity than either enantiomer in animals[65] and in humans.[66]
- 62…..Pharmaceutical Substances, Axel Kleemann, Jürgen Engel, Bernd Kutscher and Dieter Reichert, 4. ed. (2000) 2 volumes, Thieme-Verlag Stuttgart (Germany), p. 2085 bis 2086, ISBN 978-1-58890-031-9; since 2003 online with biannual actualizations.
- 63………Zynovy, Zinovy; Meckler, Harold (2000). “A Practical Procedure for the Resolution of (+)- and (−)-Tramadol”. Organic Process Research & Development 4 (4): 291–294. doi:10.1021/op000281v.
- 64……..Burke D, Henderson DJ (April 2002). “Chirality: a blueprint for the future”. British Journal of Anaesthesia 88 (4): 563–76. doi:10.1093/bja/88.4.563. PMID 12066734.
- 65…Raffa, R. B.; Friderichs, E.; Reimann, W.; Shank, R. P.; Codd, E. E.; Vaught, J. L.; Jacoby, H. I.; Selve, N. (1993). “Complementary and synergistic antinociceptive interaction between the enantiomers of tramadol”. The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 267 (1): 331–340. PMID 8229760.
- 66 ..Grond, S.; Meuser, T.; Zech, D.; Hennig, U.; Lehmann, K. A. (1995). “Analgesic efficacy and safety of tramadol enantiomers in comparison with the racemate: a randomised, double-blind study with gynaecological patients using intravenous patient-controlled analgesia”. Pain 62 (3): 313–320. doi:10.1016/0304-3959(94)00274-I. PMID 8657431.
-
tramadol hydrochloride, which is (RR, SS)-2-dimethylaminomethyl-1-(3-methoxyphenyl)cyclohexanol hydrochloride (trans), from a mixture of its (RS, SR) (cis) and trans bases, and to an improved process for the preparation of tramadol (base) monohydrate, sometimes used as an intermediate in the preparation of tramadol hydrochloride.
-
Tramadol is a well-established drug disclosed in US patent specification no. 3 652 589, which is used in the form of its hydrochloride salt as a non-narcotic analgesic drug. Tramadol is the pharmacologically active trans isomer of 2-dimethylaminomethyl-1-(3-methoxyphenyl)cyclohexanol, as opposed to the corresponding cis isomer, namely, (RS, SR)-2-dimethylaminomethyl-1-(3-methoxyphenyl)cyclohexanol.
-
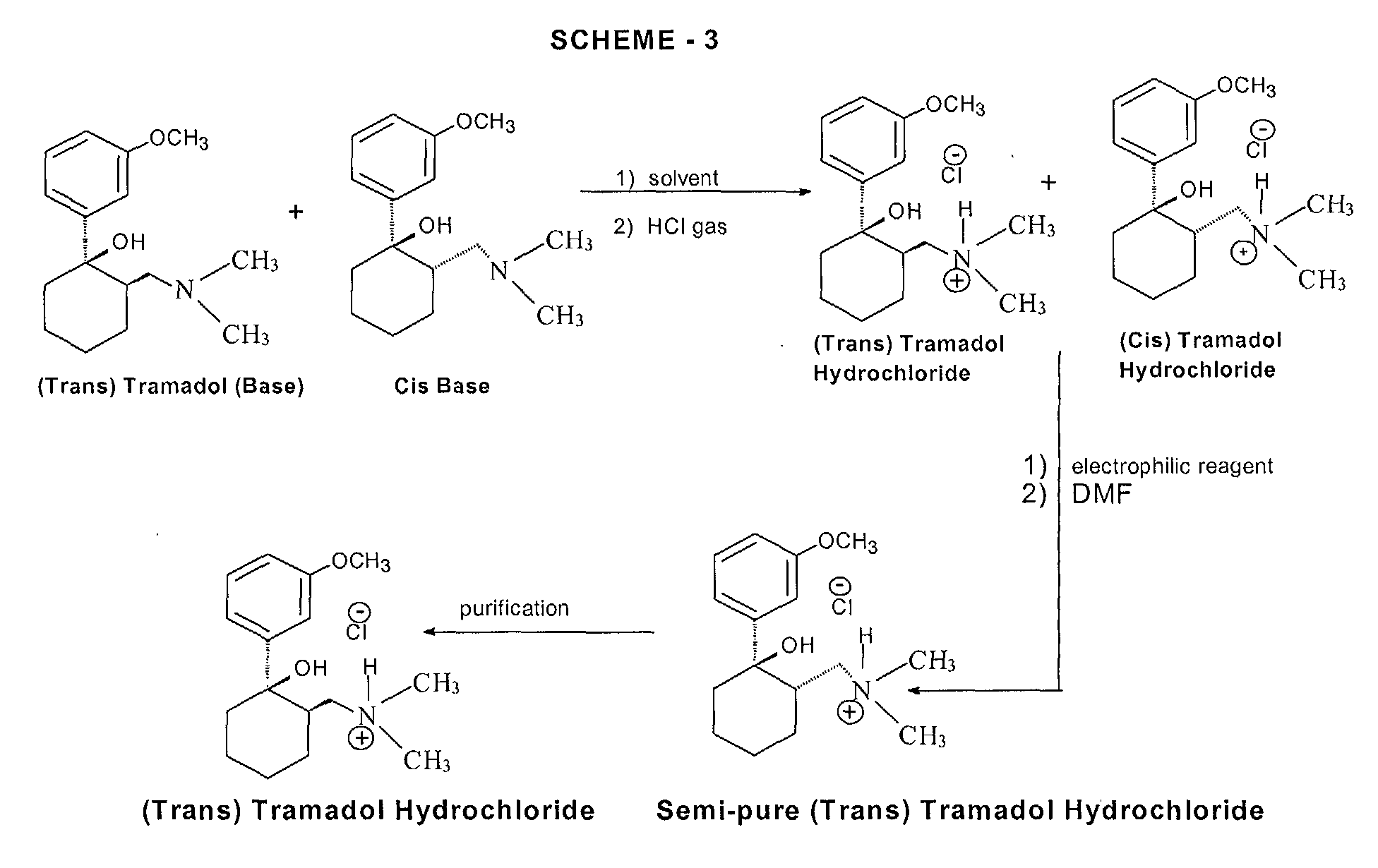
Various processes for the synthesis of tramadol hydrochloride have been described in the prior art. For example, US 3 652 589 and British patent specification no. 992 399 describe the preparation of tramadol hydrochloride. In this method, Grignard reaction of 2-dimethylaminomethyl cyclohexanone (Mannich base) with metabromo-anisole gives an oily mixture of tramadol and the corresponding cis isomer, along with Grignard impurities. This oily reaction mixture is subjected to high vacuum distillation at high temperature to give both the geometric isomers of the product base as an oil. This oil, on acidification with hydrogen chloride gas, furnishes insufficiently pure tramadol hydrochloride as a solid. This must then be purified, by using a halogenated solvent and 1,4-dioxane, to give sufficiently pure tramadol hydrochloride. The main drawback of this process is the use of large quantities of 1,4-dioxane and the need for multiple crystallizations to get sufficiently pure trans isomer hydrochloride (Scheme – 1).
-
The use of dioxane for the separation of tramadol hydrochloride from the corresponding cis isomer has many disadvantages, such as safety hazards by potentially forming explosive peroxides, and it is also a category 1 carcinogen (Kirk and Othmer, 3rd edition, 17, 48). Toxicological studies of dioxane show side effects such as CNS depression, and necrosis of the liver and kidneys. Furthermore, the content of dioxane in the final tramadol hydrochloride has been strictly limited; for example, the German Drug Codex (Deutscher Arzneimittel Codex, DAC (1991)) restricts the level of dioxane in tramadol hydrochloride to 0.5 parts per million (ppm).
-
In another process, disclosed in US patent specification no. 5 414 129, the purification and separation of tramadol hydrochloride is undertaken from a reaction mixture containing the trans and cis isomers, and Grignard reaction side products, in which the reaction mixture is diluted in isopropyl alcohol and acidified with gaseous hydrogen chloride to yield (trans) tramadol hydrochloride (97.8%) and its cis isomer (2.2%), which is itself crystallized twice with isopropyl alcohol to give pure (trans) tramadol hydrochloride (Scheme – 2). This process relies on the use of multiple solvents to separate the isomers (ie butylacetate, 1-butanol, 1-pentanol, primary amyl alcohol mixture, 1-hexanol, cyclohexanol, 1-octanol, 2-ethylhexanol and anisole). The main drawback of this process is therefore in using high boiling solvents; furthermore, the yields of tramadol hydrochloride are still relatively low and the yield of the corresponding cis hydrochloride is relatively high in most cases.
- PCT patent specification no. WO 99/03820 describes a method of preparation of tramadol (base) monohydrate, which involves the reaction of Mannich base with metabromo-anisole (Grignard reaction) to furnish a mixture of tramadol base with its corresponding cis isomer and Grignard impurities. This, on treatment with an equimolar quantity of water and cooling to 0 to -5°C, gives a mixture of tramadol (base) monohydrate with the corresponding cis isomer (crude). It is further purified with ethyl acetate to furnish pure (trans) tramadol (base) monohydrate, which is again treated with hydrochloric acid in the presence of a suitable solvent to give its hydrochloride salt (Scheme – 2). The drawback of this method is that, to get pure (trans) tramadol hydrochloride, first is prepared pure (trans) tramadol (base) monohydrate, involving a two-step process, and this is then converted to its hydrochloride salt. The overall yield is low because of the multiple steps and tedious process involved.
-
More recently, a process for the separation of tramadol hydrochloride from a mixture with its cis isomer, using an electrophilic reagent, has been described in US patent specification no. 5 874 620. The mixture of tramadol hydrochloride with the corresponding cis isomer is reacted with an electrophilic reagent, such as acetic anhydride, thionyl chloride or sodium azide, using an appropriate solvent (dimethylformamide or chlorobenzene) to furnish a mixture of tramadol hydrochloride (93.3 to 98.6%) with the corresponding cis isomer (1.4 to 6.66%), (Scheme – 3). The product thus obtained is further purified in isopropyl alcohol to give pure (trans) tramadol hydrochloride. However, the drawback of this process is that a mixture of tramadol base with its cis isomer is first converted into the hydrochloride salts, and this is further reacted with toxic, hazardous and expensive electrophilic reagents to get semi-pure (trans) tramadol hydrochloride. The content of the cis isomer is sufficiently high to require further purification, and this therefore results in a lower overall yield.


- (1R,2R)-isomer
- (1S,2S)-isomer
- (1R,2S)-isomer
- (1S,2R)-isomer
The first generic version of the oral chemotherapy drug Xeloda (capecitabine) has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to treat cancers of the colon/rectum or breast
capecitabine
154361-50-9
- R-340, Ro-09-1978, Xeloda
pentyl [1-(3,4-dihydroxy-5-methyltetrahydrofuran-2-yl)-5-fluoro-2-oxo-1H-pyrimidin-4-yl]carbamate

MONDAY Sept. 16, 2013 — The first generic version of the oral chemotherapy drug Xeloda (capecitabine) has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to treat cancers of the colon/rectum or breast, the agency said Monday in a news release.
This year, an estimated 142,820 people will be diagnosed with cancer of the colon/rectum, and 50,830 are predicted to die from the disease, the FDA said, citing the U.S. National Cancer Institute. An estimated 232,340 women will be diagnosed with cancer of the breast this year, and some 39,620 will die from it.
The most common side effects of the drug are diarrhea, vomiting; pain, redness, swelling or sores in the mouth; fever and infection, the FDA said.
The agency stressed that approved generics have the same high quality and strength as their brand-name counterparts.
License to produce the generic drug was given to Israel-based Teva Pharmaceuticals. The brand name drug is produced by the Swiss pharma firm Roche.
Capecitabine (INN) /keɪpˈsaɪtəbiːn/ (Xeloda, Roche) is an orally-administeredchemotherapeutic agent used in the treatment of metastatic breast andcolorectal cancers. Capecitabine is a prodrug, that is enzymatically converted to 5-fluorouracil in the tumor, where it inhibits DNA synthesis and slows growth of tumor tissue. The activation of capecitabine follows a pathway with three enzymatic steps and two intermediary metabolites, 5′-deoxy-5-fluorocytidine (5′-DFCR) and 5′-deoxy-5-fluorouridine (5′-DFUR), to form 5-fluorouracil

Indications
Capecitabine is FDA-approved for:
- Adjuvant in colorectal cancer Stage III Dukes’ C – used as first-line monotherapy.
- Metastatic colorectal cancer – used as first-line monotherapy, if appropriate.
- Metastatic breast cancer – used in combination with docetaxel, after failure of anthracycline-based treatment. Also as monotherapy, if the patient has failed paclitaxel-based treatment, and if anthracycline-based treatment has either failed or cannot be continued for other reasons (i.e., the patient has already received the maximum lifetime dose of an anthracycline).
In the UK, capecitabine is approved by the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) for colon and colorectal cancer, and locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer.[1] On March 29, 2007, the European Commission approved Capecitabine, in combination with platinum-based therapy (with or without epirubicin), for the first-line treatment of advanced stomach cancer.
Capecitabine is a cancer chemotherapeutic agent that interferes with the growth of cancer cells and slows their distribution in the body. Capecitabine is used to treat breast cancer and colon or rectum cancer that has spread to other parts of the body.
Formulation
Capecitabine (as brand-name Xeloda) is available in light peach 150 mg tablets and peach 500 mg tablets.
- Lacy, Charles F; Armstrong, Lora L; Goldman, Morton P; Lance, Leonard L (2004). Lexi-Comp’s Drug Information Handbook (12th Edition). Lexi-Comp Inc. ISBN 1-59195-083-X
- Fischer, David S; Knobf, M Tish; Durivage, Henry J; Beaulieu, Nancy J (2003). The Cancer Chemotherapy Handbook (6th Edition). Mosby. ISBN 0-323-01890-4
- Thomson Centerwatch: Drugs Approved by the FDA (Xeloda) Retrieved 6/05
- Mercier C, Ciccolini J (2007). “Severe or lethal toxicities upon capecitabine intake: is DPYD genetic polymorphism the ideal culprit?”. Trends in pharmacological sciences 28 (12): 597–598.doi:10.1016/j.tips.2007.09.009. PMID 18001850.
- “Subtopics”. Nice.org.uk. Retrieved 2012-08-15.
- Fingerprints May Vanish With Cancer Drug – US News and World Report
- Cancer Drug Erases Man’s Fingerprints – CNN
- “Stritch School of Medicine”. Stritch.luc.edu. Retrieved 2012-08-15.
- Xeloda.com (patient information, tools, and resources)
- OralChemo Advisor (patient information)
Capecitabine is an orally-administered anticancer agent widely used in the treatment of metastatic breast and colorectal cancers. Capecitabine is a ribofuranose-based nucleoside, and has the sterochemical structure of a ribofuranose having an β-oriented 5-fluorocytosine moiety at C-I position.
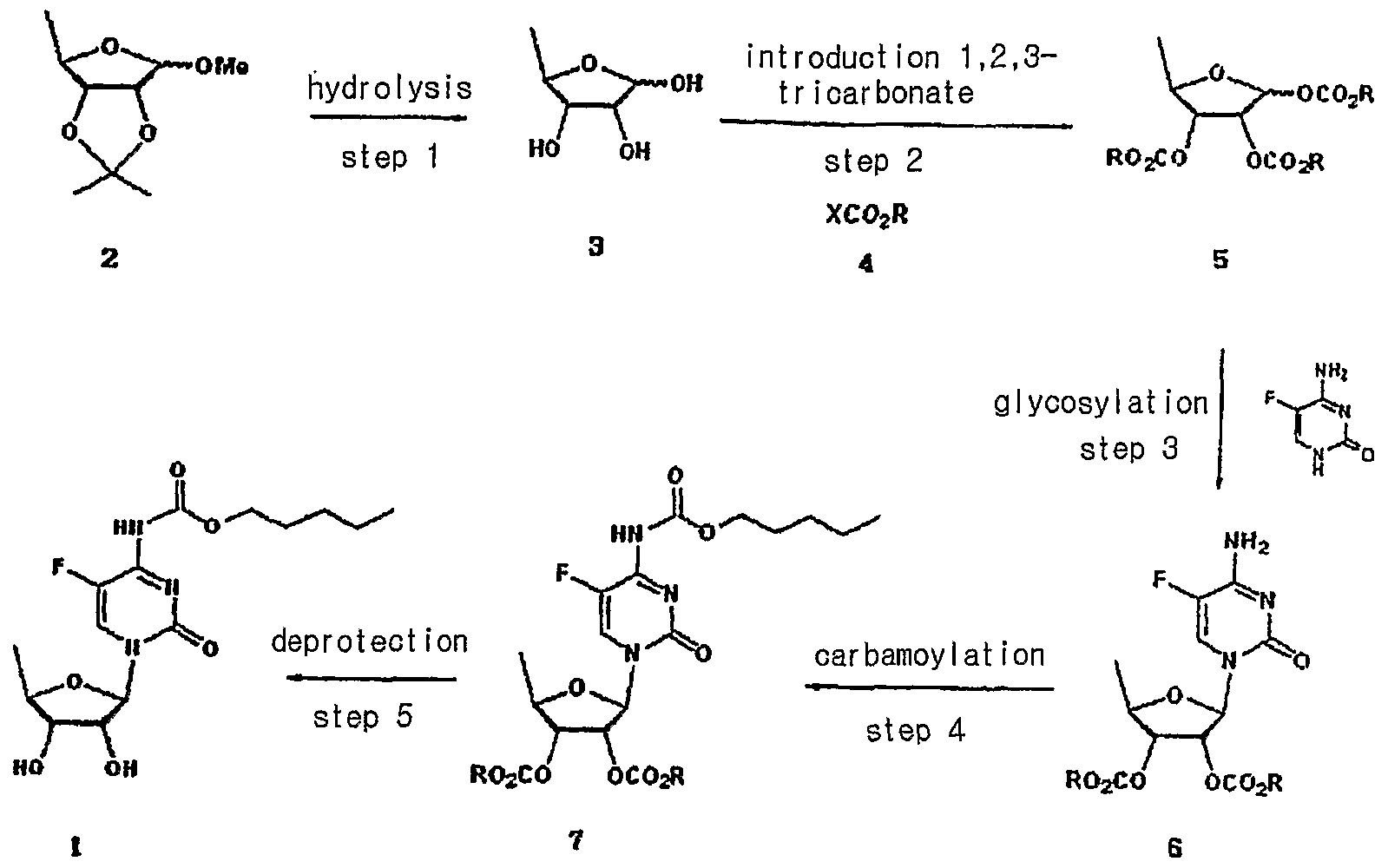
US Patent Nos. 5,472,949 and 5,453,497 disclose a method for preparing capecitabine by glycosylating tri-O-acetyl-5-deoxy-β-D-ribofuranose of formula I using 5-fluorocytosine to obtain cytidine of formula II; and carbamoylating and hydrolyzing the resulting compound, as shown in Reaction Scheme 1 :
Reaction Scheme 1
1
The compound of formula I employed as an intermediate in Reaction
Scheme 1 is the isomer having a β-oriented acetyl group at the 1 -position, for the reason that 5-fluorocytosine is more reactive toward the β-isomer than the α-isomer in the glycosylation reaction due to the occurrence of a significant neighboring group participation effect which takes place when the protecting group of the 2-hydroxy group is acyl.
Accordingly, β-oriented tri-O-acetyl-5-deoxy-β-D-ribofuranose (formula
I) has been regarded in the conventional art to the essential intermediate for the preparation of capecitabine. However, such a reaction gives a mixture of β- and α-isomers from which cytidine (formula II) must be isolated by an uneconomical step.
Meanwhile, US Patent No. 4,340,729 teaches a method for obtaining capecitabine by the procedure shown in Reaction Scheme 2, which comprises hydrolyzing 1-methyl-acetonide of formula III to obtain a triol of formula IV; acetylating the compound of formula IV using anhydrous acetic anhydride in pyridine to obtain a β-/α-anomeric mixture of tri-O-acetyl-5-deoxy-D-ribofuranose of formula V; conducting vacuum distillation to purify the β-/α-anomeric mixture; and isolating the β-anomer of formula I therefrom:
Reaction Scheme 2
III IV
However, the above method is also hampered by the requirement to perform an uneconomical and complicated recrystallization steps for isolating the β-anomer from the mixture of β-/α-anomers of formula V, which leads to a low yield of only about 35% to 40% (Guangyi Wang et al., J. Med. Chem., 2000, vol. 43, 2566-2574; Pothukuchi Sairam et al., Carbohydrate Research, 2003, vol. 338, 303-306; Xiangshu Fei et al., Nuclear Medicine and Biology, 2004, vol. 31, 1033-1041; and Henry M. Kissman et al., J. Am. Chem. Soc, 1957, vol. 79, 5534-5540).
Further, US Patent No. 5,476,932 discloses a method for preparing capecitabine by subjecting 5′-deoxy-5-fluorocytidine of formula VI to a reaction with pentylchloroformate to obtain the compound of formula VII having the amino group and the 2-,3-hydroxy groups protected with C5Hi1CO2 groups; and removing the hydroxy-protecting groups from the resulting compound, as shown in Reaction Scheme 3 :
Reaction Scheme 3
Vl VII 1
However, this method suffers from a high manufacturing cost and also requires several complicated steps for preparing the 5′-deoxy-5-fluorocytidine of formula VI: protecting the 2-,3-hydroxy groups; conducting a reaction thereof with 5-fluorocytosine; and deprotecting the 2-,3-hydroxy groups.
Accordingly, the present inventors have endeavored to develop an efficient method for preparing capecitabine, and have unexpectedly found an efficient, novel method for preparing highly pure capecitabine using a trialkyl carbonate intermediate, which does not require the uneconomical β-anomer isolation steps.
synthesis

more info and description
Aspects of the present invention relate to capecitabine and processes for the preparation thereof.
The drug compound having the adopted name “capecitabine” has a chemical name 5′-deoxy-5-fluoro-N-[(pentyloxy) carbonyl] cytidine and has structural formula I.
H
OH OH I
This compound is a fluoropyrimidine carbamate with antineoplastic activity. The commercial product XELODA™ tablets from Roche Pharmaceuticals contains either 150 or 500 mg of capecitabine as the active ingredient.
U.S. Patent No. 4,966,891 describes capecitabine generically and a process for the preparation thereof. It also describes pharmaceutical compositions, and methods of treating of sarcoma and fibrosarcoma. This patent also discloses the use of ethyl acetate for recrystallization of capecitabine. The overall process is summarized in Scheme I.
Scheme I
U.S. Patent No. 5,453,497 discloses a process for producing capecitabine that comprises: coupling of th-O-acetyl-5-deoxy-β-D-hbofuranose with 5- fluorocytosine to obtain 2′,3′-di-O-acetyl-5′-deoxy-5-fluorocytidine; acylating a 2′, 3′- di-O-acetyl-5′-deoxy-5-fluorocytidine with n-pentyl chloroformate to form 5′-deoxy- 2′,3′-di-O-alkylcarbonyl-5-fluoro-N-alkyloxycarbonyl cytidine, and deacylating the 2′ and 3′ positions of the carbohydrate moiety to form capecitabine. The overall process is summarized in Scheme II.
Capecitabine
Scheme Il
The preparation of capecitabine is also disclosed by N. Shimma et al., “The Design and Synthesis of a New Tumor-Selective Fluoropyrimidine Carbamate, Capecitabine,” Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, Vol. 8, pp. 1697-1706 (2000). U.S. Patent No. 7,365,188 discloses a process for the production of capecitabine, comprising reacting 5-fluorocytosine with a first silylating agent in the presence of an acid catalyst under conditions sufficient to produce a first silylated compound; reacting the first silylated compound with 2,3-diprotected-5- deoxy-furanoside to produce a coupled product; reacting the coupled product with a second silylating agent to produce a second silylated product; acylating the second silylated product to produce an acylated product; and selectively removing the silyl moiety and hydroxyl protecting groups to produce capecitabine. The overall process is summarized in Scheme III. te
R: hydrocarbyl
Scheme III
Further, this patent discloses crystallization of capecitabine, using a solvent mixture of ethyl acetate and n-heptane. International Application Publication No. WO 2005/080351 A1 describes a process for the preparation of capecitabine that involves the refluxing N4– pentyloxycarbonyl-5-fluorocytosine with trimethylsiloxane, hexamethyl disilazanyl, or sodium iodide with trimethyl chlorosilane in anhydrous acetonitrile, dichloromethane, or toluene, and 5-deoxy-1 ,2,3-tri-O-acetyl-D-ribofuranose, followed by hydrolysis using ammonia/methanol to give capecitabine. The overall process is summarized in Scheme IV.
Scheme IV
International Application Publication No. WO 2007/009303 A1 discloses a method of synthesis for capecitabine, comprising reacting 5′-deoxy-5- fluorocytidine using double (trichloromethyl) carbonate in an inert organic solvent and organic alkali to introduce a protective lactone ring to the hydroxyl of the saccharide moiety; reacting the obtained compound with chloroformate in organic alkali; followed by selective hydrolysis of the sugar component hydrolytic group using an inorganic base to give capecitabine. The overall process is summarized in Scheme V.
Scheme V
Even though all the above documents collectively disclose various processes for the preparation of capecitabine, removal of process-related impurities in the final product has not been adequately addressed. Impurities in any active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) are undesirable, and, in extreme cases, might even be harmful to a patient. Furthermore, the existence of undesired as well as unknown impurities reduces the bioavailability of the API in pharmaceutical products and often decreases the stability and shelf life of a pharmaceutical dosage form.
nmr
1H NMR(CD3OD) δ 0.91(3H5 t), 1.36~1.40(4H, m), 1.41(3H, d), 1.68~1.73(2H, m), 3.72(1H, dd), 4.08(1H, dd), 4.13~4.21(3H, m), 5.7O(1H, s), 7.96(1H, d)

- The acetylation of 5′-deoxy-5-fluorocytidine (I) with acetic anhydride in dry pyridine gives 2′,3′-di-O-acetyl-5′-deoxy-5-fluorocytidine (II), which is condensed with pentyl chloroformate (III) by means of pyridine in dichromethane yielding 2′,3′-di-O-acetyl-5′-deoxy-5-fluoro-N4-(pentyloxycarbonyl)cytidine (IV). Finally, this compound is deacetylated with NaOH in dichloromethane/water. The diacetylated cytidine (II) can also be obtained by condensation of 5-fluorocytosine (V) with 1,2,3-tri-O-acetyl-5-deoxy-beta-D-ribofuranose (VI) by means of trimethylchlorosilane in acetonitrile or HMDS and SnCl4 in dichloromethane..
-
- EP 602454, JP 94211891, US 5472949.
- Capecitabine. Drugs Fut 1996, 21, 4, 358,
- Bioorg Med Chem Lett2000,8,(7):1697,
- Capecitabine. Drugs Fut 1996, 21, 4, 358,
- EP 602454, JP 94211891, US 5472949.
Novartis’ Breakthrough Therapy For A Rare Muscle-Wasting Disease
On August 20, 2013, Novartis announced in a press release that the FDA had granted breakthrough therapy designation to its experimental agent BYM338 (bimagrumab) for treatment of the rare muscle wasting disease sporadic inclusion body myositis (sIBM).
sIBM is a rare–but increasingly prevalent–disease. It is the most common cause of inflammatory myopathy in people over 50. sIBM has a yearly incidence of 2 to 5 per million adults with a peak at ages 50 to 70, with male predominance. Muscle wasting caused by sIBM is superimposed upon the sarcopenia (degenerative loss of muscle mass) that typically occurs with aging.
read all
bimagrumab
immunoglobulin G1-lambda2, anti-[Homo sapiens ACVR2B (activin
A receptor type IIB, ActR-IIB)], Homo sapiens monoclonal antibody;
gamma1 heavy chain (1-445) [Homo sapiens VH (IGHV1-2*02
(91.80%) -(IGHD)-IGHJ5*01 [8.8.8] (1-115) -IGHG1*03 (CH1 (116-
213), hinge (214-228), CH2 L1.3>A (232), L1.2>A (233) (229-338),
CH3 (339-443), CHS (444-445)) (116-445)], (218-216′)-disulfide with
lambda light chain (1′-217′) [Homo sapiens V-LAMBDA (IGLV2-
23*02 (90.90%) -IGLJ2*01) [9.3.11] (1′-111′) -IGLC2*01 (112′-217′)];
dimer (224-224”:227-227”)-bisdisulfide
myostatin inhibitor
bimagrumab immunoglobuline G1-lambda2, anti-[Homo sapiens ACVR2B
(récepteur type IIB de l’activine A, ActR-IIB)], Homo sapiens
anticorps monoclonal;
chaîne lourde gamma1 (1-445) [Homo sapiens VH (IGHV1-2*02
(91.80%) -(IGHD)-IGHJ5*01 [8.8.8] (1-115) -IGHG1*03 (CH1 (116-
213), charnière (214-228), CH2 L1.3>A (232), L1.2>A (233) (229-
338), CH3 (339-443), CHS (444-445)) (116-445)], (218-216′)-
disulfure avec la chaîne légère lambda (1′-217′) [Homo sapiens
V-LAMBDA (IGLV2-23*02 (90.90%) -IGLJ2*01) [9.3.11] (1′-111′) –
IGLC2*01 (112′-217′)]; dimère (224-224”:227-227”)-bisdisulfure
inhibiteur de la myostatine
inmunoglobulina G1-lambda2, anti-[Homo sapiens ACVR2B
(receptor tipo IIB de la activina A, ActR-IIB)], anticuerpo monoclonal
de Homo sapiens;
cadena pesada gamma1 (1-445) [Homo sapiens VH (IGHV1-2*02
(91.80%) -(IGHD)-IGHJ5*01 [8.8.8] (1-115) -IGHG1*03 (CH1 (116-
213), bisagra (214-228), CH2 L1.3>A (232), L1.2>A (233) (229-338),
CH3 (339-443), CHS (444-445)) (116-445)], (218-216′)-disulfuro con
la cadena ligera lambda (1′-217′) [Homo sapiens V-LAMBDA
(IGLV2-23*02 (90.90%) -IGLJ2*01) [9.3.11] (1′-111′) -IGLC2*01
(112′-217′)]; dímero (224-224”:227-227”)-bisdisulfuro
inhibidor de la miostatina
1356922-05-8
Heavy chain / Chaîne lourde / Cadena pesada
QVQLVQSGAE VKKPGASVKV SCKASGYTFT SSYINWVRQA PGQGLEWMGT 50
INPVSGSTSY AQKFQGRVTM TRDTSISTAY MELSRLRSDD TAVYYCARGG 100
WFDYWGQGTL VTVSSASTKG PSVFPLAPSS KSTSGGTAAL GCLVKDYFPE 150
PVTVSWNSGA LTSGVHTFPA VLQSSGLYSL SSVVTVPSSS LGTQTYICNV 200
NHKPSNTKVD KRVEPKSCDK THTCPPCPAP EAAGGPSVFL FPPKPKDTLM 250
ISRTPEVTCV VVDVSHEDPE VKFNWYVDGV EVHNAKTKPR EEQYNSTYRV 300
VSVLTVLHQD WLNGKEYKCK VSNKALPAPI EKTISKAKGQ PREPQVYTLP 350
PSREEMTKNQ VSLTCLVKGF YPSDIAVEWE SNGQPENNYK TTPPVLDSDG 400
SFFLYSKLTV DKSRWQQGNV FSCSVMHEAL HNHYTQKSLS LSPGK 445
Light chain / Chaîne légère / Cadena ligera
QSALTQPASV SGSPGQSITI SCTGTSSDVG SYNYVNWYQQ HPGKAPKLMI 50
YGVSKRPSGV SNRFSGSKSG NTASLTISGL QAEDEADYYC GTFAGGSYYG 100
VFGGGTKLTV LGQPKAAPSV TLFPPSSEEL QANKATLVCL ISDFYPGAVT 150
VAWKADSSPV KAGVETTTPS KQSNNKYAAS SYLSLTPEQW KSHRSYSCQV 200
THEGSTVEKT VAPTECS 217
Disulfide bridges location / Position des ponts disulfure / Posiciones de los puentes disulfuro
Intra-H 22-96 142-198 259-319 365-423
22”-96” 142”-198” 259”-319” 365”-423”
Intra-L 22′-90′ 139′-198′
22”’-90”’ 139”’-198”’
Inter-H-L 218-216′ 218”-216”’
Inter-H-H 224-224” 227-227”
N-glycosylation sites / Sites de N-glycosylation / Posiciones de N-glicosilación
H CH2 N84.4
Bimagrumab
http://www.who.int/medicines/publications/druginformation/innlists/PL108_Final.pdf
Novartis announced that the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted breakthrough therapy designation to BYM338 for sporadic inclusion body myositis (sIBM). This designation is based on the results of a phase 2 proof-of-concept study that showed BYM338 substantially benefited patients with sIBM compared to placebo.
read all at
Novartis receives FDA breakthrough therapy designation for BYM338 (bimagrumab) for sporadic inclusion body myositis (sIBM)
• Designation highlights potential of BYM338 to address an unmet medical need in a serious disease
• If approved, BYM338 has the potential to be the first treatment for sIBM patients
• BYM338 is the third Novartis investigational treatment this year to receive a breakthrough therapy designation by the FDA, highlighting Novartis’ leadership in the industry in breakthrough therapy designations
Bimagrumab (BYM338) is a human monoclonal antibody developed by Novartis to treat pathological muscle loss and weakness. On August 20, 2013 it was announced that bimagrumab was granted breakthrough therapy designation for sporadic inclusion body myositis(sIBM) by US Food and Drug Administration.[1]
- “Novartis receives FDA breakthrough therapy designation for BYM338 (bimagrumab) for sporadic inclusion body myositis (sIBM)”. Retrieved 20 August 2013.
World Health Organization (2012). “International Nonproprietary Names for Pharmaceutical Substances (INN). Proposed INN: List 108″ (PDF). WHO Drug Information 26(4)
LEVOCETRIZINE

LEVOCETRIZINE
History and formulations
Levocetirizine was first launched in 2001 by Belgian pharmaceutical company UCB. It is sold under the brand name Xyzal/ˈzaɪzæl/ in Australia, Czech Republic, Austria, Finland, France, Ireland, Netherlands, Portugal, Romania, Taiwan, Turkey, United States, South Africa and UK; Xuzal in Mexico; Xusal in Germany; and Xozal in Greece. In Hungary it is marketed by Richter Gedeon under the Zilola brand name.
Side effects
levocetirizine is called a non-sedating antihistamine as it does not enter the brain in significant amounts, and is therefore unlikely to cause drowsiness. However, some people may experience some slight sleepiness, headache, mouth dryness,lightheadedness, vision problems (mainly blurred vision), palpitations and fatigue.[3]
Research
latest research shows levocetirizine reduces asthma attacks by 70% in children.[4]
Availability]
- ^ Grant, JA; Riethuisen, JM; Moulaert, B; DeVos, C; Gamalero, C.; Descalzi, D.; Folli, C.; Passalacqua, G. et al. (2002-02). “A double-blind, randomized, single-dose, crossover comparison of levocetirizine with ebastine, fexofenadine, loratadine, mizolastine, and placebo: suppression of histamine-induced wheal-and-flare response during 24 hours in healthy male subjects.”. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 88 (2): 190–197. doi:10.1016/S1081-1206(10)61995-3. PMID 11868924.
- ^ http://www.beximco-pharma.com/allergic-disorders/147-curin.html
- ^ XOZAL technical specifications booklet.
- ^ Pasquali, M; Baiardini, I; Rogkakou, A; Riccio, AM; Gamalero, C; Descalzi, D; Folli, C; Passalacqua, G et al. (2006-09).“Levocetirizine in persistent allergic rhinitis and asthma: effects on symptoms, quality of life and inflammatory parameters.”.Clinical & Experimental Allergy 36 (9): 1161–7. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2222.2006.02548.x. PMID 16961716.
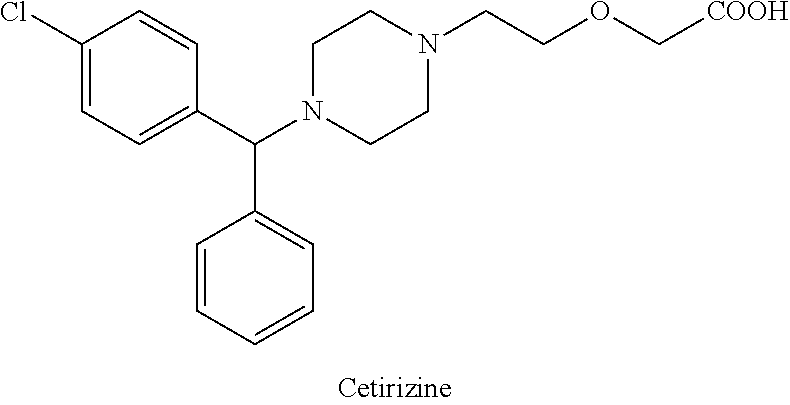
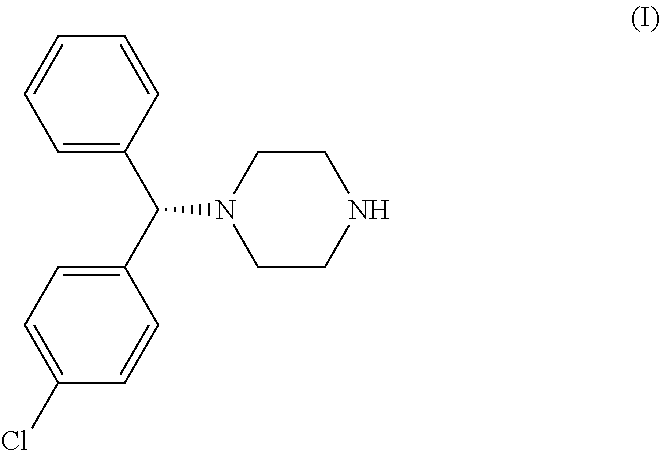
Figure 2 displays the synthesis of Cetirizine (Zyrtec). Levocetirizine, the R-enantiomer of cetirizine, is then formed from pyroglutamate salts in a synthesis that does not have attainable details.
 |
| (Figure 2) |
The synthesis of Cetrizine begins by reducing molecule 33 with a catecholborane. This reaction yields molecule 34, which is then treated with tetraflouroboric acid and reacted with an amine, compound 35. In order to remove the chromium group, the compound is refluxed in pyridine and undergoes an acid hydrolysis. This results in a yield of cetrizine.
Identification of all chirality centers:
Stereogenic centers are carbon atoms that are bonded to 4 groups. Tetrahedral stereogenic centers are stereogenic centers that are not only bonded to 4 groups but are more importantly bonded to 4 different groups. If a molecule contains 1 tetrahedral stereogenic center it is said to be chiral (nonsuperimposable on its mirror image).If a given compound contains more than 1 stereogenic center it must be further analyzed to determine if it is chiral or achiral(superimosable on its mirror image). The carbon atom bonded to the phenyl groups was found to be a tetrahedral stereogenic center. Therefore,xyzal,which was found to contain only 1 tetrahedral stereogenic center is generally considered a chiral compound because it meets the requirements of chirality and does not have a plane of symmetry that superimposes one half of the molecule on the other and is not super imposable on its mirror image.
Spectral data for Xyzal (IR and NMR):


– See more at: http://worlddrugtracker.blogspot.in/#sthash.6Ndn04WU.dpuf
ESCITALOPRAM

128196-01-0 ESCITALOPRAM
Escitalopram (also known under various trade names) is an antidepressant of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) class. It is approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of adults and children over 12 years of age with major depressive disorder and generalized anxiety disorder. Escitalopram is the (S)-stereoisomer (enantiomer) of the earlier Lundbeck drug citalopram, hence the name escitalopram. Escitalopram is noted for its high selectivity with serotonin reuptake inhibition. The similarity between escitalopram and citalopram has led to accusations of “evergreening“, an accusation that Lundbeck has rejected.[1]
Escitalopram has FDA approval for the treatment of major depressive disorder and generalized anxiety disorder in adults.[2]
Off-label uses
Escitalopram is sometimes prescribed off-label for the treatment of other conditions: social anxiety disorder,[3] panic disorder[4]and obsessive-compulsive disorder.[5] There is some evidence favouring escitalopram over the antidepressants citalopram andfluoxetine in the first two weeks of major depression.[6] Concerns of sponsorship bias with the studies are however noted.[6] In another review escitalopram and sertraline had the highest rate of efficacy and acceptability among adults receiving treatment for major depression with second-generation antidepressants.[7]
Efficacy
There is some controversy over selective publishing of SSRI clinical trials.[8] A meta-analysis analyzing published as well as unpublished trials found placebos to be similarly effective to SSRIs in treating mild depression, although SSRIs were more effective than placebo in more severe cases, with the magnitude of SSRI superiority increasing with increasing depression severity.[9]
A series of randomized, double-blind trials have found Escitalopram to be more efficacious and have fewer adverse effects than Citalopram.[10][11][12][13] Meta-analysis show a “small” but statistically significant improvement in effect strength [14][15] and some dispute these findings.[16]
Pharmacology
Escitalopram increases intrasynaptic levels of the neurotransmitter serotonin by blocking the reuptake of the neurotransmitter into the presynaptic neuron. Of the SSRIs currently on the market, escitalopram has the highest affinity for the human serotonin transporter (SERT). The enantiomer of escitalopram ((R)-citalopram) counteracts to a certain degree the serotonin-enhancing action of escitalopram. As a result, escitalopram has been claimed to be a more potent antidepressant than citalopram, which is a mixture of escitalopram and (R)-citalopram. In order to explain this phenomenon, researchers from Lundbeck proposed that escitalopram enhances its own binding via an additional interaction with another allosteric site on the transporter.[42] Further research by the same group showed that (R)-citalopram also enhances binding of escitalopram,[43] and therefore the allosteric interaction cannot explain the observed counteracting effect. In the most recent paper, however, the same authors again reversed their findings and reported that R-citalopram decreases binding of escitalopram to the transporter.[44] Although allosteric binding of escitalopram to the serotonin transporter is of unquestionable research interest, its clinical relevance is unclear since the binding of escitalopram to the allosteric site is at least 1000 times weaker than to the primary binding site.
In vitro studies using human liver microsomes indicated that CYP3A4 and CYP2C19 are the primary isozymes involved in the N-demethylation of escitalopram. The resulting metabolites, desmethylescitalopram and didesmethylescitalopram, are significantly less active and their contribution to the overall action of escitalopram is negligible.
History
Escitalopram was developed in close cooperation between Lundbeck and Forest Laboratories. Its development was initiated in the summer of 1997, and the resulting new drug application was submitted to the U.S. FDA in March 2001. The short time (3.5 years) it took to develop escitalopram can be attributed to the previous extensive experience of Lundbeck and Forest with citalopram, which has similar pharmacology.[45] The FDA issued the approval of escitalopram for major depression in August 2002 and for generalized anxiety disorder in December 2003. Escitalopram can be considered an example of “evergreening“[46] (also called “lifecycle management”[47])– the long-term strategy pharmaceutical companies use in order to extend the lifetime of a drug, in this case of the citalopram franchise. Escitalopram is an enantiopure compound of theracemic mixture citalopram, used for the same indication, and for that reason it required less investment and less time to develop. Two years after escitalopram’s launch, when the patent on citalopram expired, the escitalopram sales successfully made up for the loss. On May 23, 2006, the FDA approved a generic version of escitalopram by Teva.[48]On July 14 of that year, however, the U.S. District Court of Delaware decided in favor of Lundbeck regarding the patent infringement dispute and ruled the patent on escitalopram valid.[49]
In 2006 Forest Laboratories was granted an 828 day (2 years and 3 months) extension on its US patent for escitalopram.[50] This pushed the patent expiration date from December 7, 2009 to September 14, 2011. Together with the 6-month pediatric exclusivity, the final expiration date was March 14, 2012.
Brand names
Escitalopram is sold under the following brand names:
- Animaxen (Colombia)
- Anxiset-E (India)
- Cipralex
- Escital (Nigeria)
- Citalin
- Citram (Croatia)
- Ecytara (Slovenia)
- Elicea
- Entact (Greece)
- Escitalopram Actavis (Finland)
- Escitil (Czech Republic)
- Esitalo (Australia)
- Esopram, by Actavis (Iceland)
- Esto (Israel)
- Escitalopram Teva (Israel)
- Exodus (Brazil)
- Lexam
- Lexamil (South Africa)
- Lexapro
- Losita (Bangladesh)
- Nexito
- Reposil (Chile)
- Selectra (Russia)
- Selpram (Pakistan)
- Seroplex
- Sipralexa (Belgium)
References
- ^ a b c NHS pays millions of pounds more than it needs to for drugs, The Independent. Retrieved 05/10/2011.
- ^ “Escitalopram Oxalate”. The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Retrieved 3 April 2011.
- ^ Kasper, S; Stein, DJ; Loft, H; Nil, R (2005). “Escitalopram in the treatment of social anxiety disorder: Randomised, placebo-controlled, flexible-dosage study”. The British journal of psychiatry : the journal of mental science 186 (3): 222–6.doi:10.1192/bjp.186.3.222. PMID 15738503.
- ^ Stahl, SM; Gergel, I; Li, D (2003). “Escitalopram in the treatment of panic disorder: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial”. The Journal of clinical psychiatry 64(11): 1322–7. PMID 14658946.
- ^ Stein, DJ; Andersen, EW; Tonnoir, B; Fineberg, N (2007). “Escitalopram in obsessive-compulsive disorder: A randomized, placebo-controlled, paroxetine-referenced, fixed-dose, 24-week study”. Current medical research and opinion 23 (4): 701–11. doi:10.1185/030079907X178838. PMID 17407626.
- ^ a b Cipriani, A; Santilli C; Furukawa TA; Signoretti A; Nakagawa A; McGuire H; Churchill R; Barbui C (2009 April 15). “Escitalopram versus other antidepressant agents for depression”. In Cipriani, Andrea. Cochrane database of systematic reviews(2): CD006532. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006532.pub2. PMID 19370639. CD006532.
- ^ Cipriani, A; Furukawa TA; Salanti G; Geddes JR; Higgins JP; Churchill R; Watanabe N; Nakagawa A; Omori IM; McGuire H; Tansella M; Barbui C (2009 February 28). “Comparative efficacy and acceptability of 12 new-generation antidepressants: a multiple-treatments meta-analysis”. Lancet 373 (9665): 746–58. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60046-5. PMID 19185342.
- ^ Ioannidis JP (2008). “Effectiveness of antidepressants: an evidence myth constructed from a thousand randomized trials?”. Philos Ethics Humanit Med 3: 14.doi:10.1186/1747-5341-3-14. PMC 2412901. PMID 18505564.
- ^ Fournier JC, DeRubeis RJ, Hollon SD, Dimidjian S, Amsterdam JD, Shelton RC, Fawcett J (January 2010). “Antidepressant drug effects and depression severity: a patient-level meta-analysis”. JAMA 303 (1): 47–53. doi:10.1001/jama.2009.1943.PMID 20051569.
- ^ Ou, JJ; Xun, GL; Wu, RR; Li, LH; Fang, MS; Zhang, HG; Xie, SP; Shi, JG; Du, B; Yuan, XQ; Zhao, JP (2011 Feb). “Efficacy and safety of escitalopram versus citalopram in major depressive disorder: a 6-week, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, flexible-dose study.”. Psychopharmacology 213 (2-3): 639–46. doi:10.1007/s00213-010-1822-y. PMID 20340011.
|accessdate=requires|url=(help) - ^ Yevtushenko, VY; Belous, AI; Yevtushenko, YG; Gusinin, SE; Buzik, OJ; Agibalova, TV (2007 Nov). “Efficacy and tolerability of escitalopram versus citalopram in major depressive disorder: a 6-week, multicenter, prospective, randomized, double-blind, active-controlled study in adult outpatients.”. Clinical therapeutics 29 (11): 2319–32.PMID 18158074.
- ^ Colonna, L; Andersen, HF; Reines, EH (2005 Oct). “A randomized, double-blind, 24-week study of escitalopram (10 mg/day) versus citalopram (20 mg/day) in primary care patients with major depressive disorder.”. Current medical research and opinion 21(10): 1659–68. PMID 16238906.
- ^ Moore, N; Verdoux, H; Fantino, B (2005 May). “Prospective, multicentre, randomized, double-blind study of the efficacy of escitalopram versus citalopram in outpatient treatment of major depressive disorder.”. International clinical psychopharmacology 20 (3): 131–7. PMID 15812262.
- ^ Montgomery, Stuart; Hansen, Thomas; Kasper, Siegfried (28 September 2010). “Efficacy of escitalopram compared to citalopram: a meta-analysis”. The International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology 14 (02): 261–268.doi:10.1017/S146114571000115X. PMID 20875220.
- ^ Gorman, JM; Korotzer, A; Su, G (2002 Apr). “Efficacy comparison of escitalopram and citalopram in the treatment of major depressive disorder: pooled analysis of placebo-controlled trials.”. CNS spectrums 7 (4 Suppl 1): 40–4. PMID 15131492.
- ^ Trkulja, V (2010 Feb). “Is escitalopram really relevantly superior to citalopram in treatment of major depressive disorder? A meta-analysis of head-to-head randomized trials.”. Croatian medical journal 51 (1): 61–73. PMID 20162747.
- ^ “Citalopram and escitalopram: QT interval prolongation—new maximum daily dose restrictions (including in elderly patients), contraindications, and warnings”.Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency. December 2011. Retrieved March 5, 2013.
- ^ Van Gorp, Freek; Whyte, Ian M.; Isbister, Geoffrey K. (2009). “Clinical and ECG Effects of Escitalopram Overdose”. Annals of Emergency Medicine 54 (3): 404–8.doi:10.1016/j.annemergmed.2009.04.016. PMID 19556032.
- ^ FDA Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (2001). “Review and evaluation of clinical data for application 21-323”. Retrieved 2009-12-03.
- ^ Bolton JM, Sareen J, Reiss JP (2006). “Genital anesthesia persisting six years after sertraline discontinuation”. J Sex Marital Ther 32 (4): 327–30.doi:10.1080/00926230600666410. PMID 16709553.
- ^ Clayton A, Keller A, McGarvey EL (2006). “Burden of phase-specific sexual dysfunction with SSRIs”. Journal of Affective Disorders 91 (1): 27–32.doi:10.1016/j.jad.2005.12.007. PMID 16430968.
- ^ Lexapro prescribing information
- ^ Csoka AB, Bahrick AS, Mehtonen O-P (2008). “Persistent Sexual Dysfunction after Discontinuation of Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs)”. J Sex Med. 5 (1): 227–33. doi:10.1111/j.1743-6109.2007.00630.x. PMID 18173768.
- ^ Baldwin DS, Reines EH, Guiton C, Weiller E (2007). “Escitalopram therapy for major depression and anxiety disorders”. Ann Pharmacother 41 (10): 1583–92.doi:10.1345/aph.1K089. PMID 17848424.
- ^ Pigott TA, Prakash A, Arnold LM, Aaronson ST, Mallinckrodt CH, Wohlreich MM (2007). “Duloxetine versus escitalopram and placebo: an 8-month, double-blind trial in patients with major depressive disorder”. Curr Med Res Opin 23 (6): 1303–18.doi:10.1185/030079907X188107. PMID 17559729.
- ^ Davidson JR, Bose A, Wang Q (2005). “Safety and efficacy of escitalopram in the long-term treatment of generalized anxiety disorder”. J Clin Psychiatry 66 (11): 1441–6.doi:10.4088/JCP.v66n1115. PMID 16420082.
- ^ Kasper S, Lemming OM, de Swart H (2006). “Escitalopram in the long-term treatment of major depressive disorder in elderly patients”. Neuropsychobiology 54 (3): 152–9. doi:10.1159/000098650. PMID 17230032.
- ^ Guerdjikova, AI; McElroy SL, Kotwal R, et al. (January 2008). “High-dose escitalopram in the treatment of binge-eating disorder with obesity: a placebo-controlled monotherapy trial”. Human Psychopharmacology: Clinical and Experimental23 (1): 1–11. doi:10.1002/hup.899. PMID 18058852.
- ^ Levenson M, Holland C. “Antidepressants and Suicidality in Adults: Statistical Evaluation. (Presentation at Psychopharmacologic Drugs Advisory Committee; December 13, 2006)”. Retrieved 2007-05-13.
- ^ Stone MB, Jones ML (2006-11-17). “Clinical Review: Relationship Between Antidepressant Drugs and Suicidality in Adults” (PDF). Overview for December 13 Meeting of Pharmacological Drugs Advisory Committee (PDAC). FDA. pp. 11–74. Retrieved 2007-09-22.
- ^ Levenson M; Holland C (2006-11-17). “Statistical Evaluation of Suicidality in Adults Treated with Antidepressants” (PDF). Overview for December 13 Meeting of Pharmacological Drugs Advisory Committee (PDAC). FDA. pp. 75–140. Retrieved 2007-09-22.
- ^ Gunnell D, Saperia J, Ashby D (2005). “Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and suicide in adults: meta-analysis of drug company data from placebo controlled, randomized controlled trials submitted to the MHRA’s safety review”. BMJ330 (7488): 385. doi:10.1136/bmj.330.7488.385. PMC 549105. PMID 15718537.
- ^ Khan A, Schwartz K (2007). “Suicide risk and symptom reduction in patients assigned to placebo in duloxetine and escitalopram clinical trials: analysis of the FDA summary basis of approval reports”. Ann Clin Psychiatry 19 (1): 31–6.doi:10.1080/10401230601163550. PMID 17453659.
- ^ Budur, Kumar; Hutzler, Jeffrey (June 2004). “Severe suicidal ideation with escitalopram (Lexapro): a case report”. Primary Care Psychiatry 9 (2): 67–68.doi:10.1185/135525704125004222.
- ^ Karch, Amy (2006). 2006 Lippincott’s Nursing Drug Guide. Philadelphia, Baltimore, New York, London, Buenos Aires, Hong Kong, Sydney, Tokyo: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 1-58255-436-6.
- ^ Malling, D.; Poulsen, M.; Søgaard, B. (2005). “The effect of cimetidine or omeprazole on the pharmacokinetics of escitalopram in healthy subjects”. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 60 (3): 287–290. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2125.2005.02423.x.PMC 1884771. PMID 16120067. edit
- ^ “Lexapro – Warnings”. RxList. 12/08/2004. Retrieved 2006-10-22.
- ^ Alwan S, Reefhuis J, Rasmussen SA, Olney RS, Friedman JM, for the National Birth Defects Prevention Study. Use of selective serotonin-reuptake inhibitors in pregnancy and the risk of birth defects. N Engl J Med 2007;356:2684–92.
- ^ van Gorp F, Whyte IM, Isbister GK. Clinical and ECG effects of escitalopram overdose. Ann. Emer. Med. 54: 404-408, 2009.
- ^ Haupt D. Determination of citalopram enantiomers in human plasma by liquid chromatographic separation on a Chiral-AGP column. J. Chrom. B 685: 299-305, 1996.
- ^ R. Baselt, Disposition of Toxic Drugs and Chemicals in Man, 8th edition, Biomedical Publications, Foster City, CA, 2008, pp. 552-553.
- ^ For an overview of supporting data, see Sánchez C, Bøgesø KP, Ebert B, Reines EH, Braestrup C (2004). “Escitalopram versus citalopram: the surprising role of the R-enantiomer”. Psychopharmacology (Berl.) 174 (2): 163–76. doi:10.1007/s00213-004-1865-z. PMID 15160261.
- ^ Chen F, Larsen MB, Sánchez C, Wiborg O (2005). “The (S)-enantiomer of (R,S)-citalopram, increases inhibitor binding to the human serotonin transporter by an allosteric mechanism. Comparison with other serotonin transporter inhibitors”.European Neuropsychopharmacology 15 (2): 193–198.doi:10.1016/j.euroneuro.2004.08.008. PMID 15695064.
- ^ Mansari ME, Wiborg O, Mnie-Filali O, Benturquia N, Sánchez C, Haddjeri N (2007). “Allosteric modulation of the effect of escitalopram, paroxetine and fluoxetine: in-vitro and in-vivo studies”. The International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology 10 (1): 31–40. doi:10.1017/S1461145705006462. PMID 16448580.
- ^ “2000 Annual Report. p 28 and 33” (PDF). Lundbeck. 2000. Retrieved 2007-04-07.
- ^ “”New drugs from old”. Presented at the Medical Journal Club, Morriston Hospital, by Scott Pegler, pharmacist at the National Health Service, UK, on November 20, 2006.” (PPT). Retrieved 2007-04-07.
- ^ “New drugs from old”. Drug and Therapeutics Bulletin (BMJ Publishing Group Ltd.)44 (10): 73–77. 2006. doi:10.1136/dtb.2006.441073. PMID 17067118.
- ^ Miranda Hitti. “FDA OKs Generic Depression Drug – Generic Version of Lexapro Gets Green Light”. WebMD. Retrieved 2007-10-10.
- ^ Marie-Eve Laforte (2006-07-14). “US court upholds Lexapro patent”. FirstWord. Retrieved 2007-10-10.
- ^ “Forest Laboratories Receives Patent Term Extension for Lexapro” (Press release). PRNewswire-FirstCall. 2006-03-02. Retrieved 2009-01-19.
- ^ Harris, “A Drug Maker’s Playbook Reveals a Marketing Strategy”
- ^ Lexapro Fiscal 2004 Marketing Plan
- ^ “Forest Laboratories: A Tale of Two Whistleblowers” article by Alison Frankel inThe American Lawyer February 27, 2009
- ^ United States of America v. Forest Laboratories Full text of the federal complaint filed in the US District Court for the district of Massachusetts
- ^ “Drug Maker Is Accused of Fraud” article by Barry Meier and Benedict Carey inThe New York Times February 25, 2009
- ^ “Forest Laboratories, Inc. Provides Statement in Response to Complaint Filed by U.S. Government” Forest press-release. February 26, 2009.
- “A Drug Maker’s Playbook Reveals a Marketing Strategy” article in The New York Times by Gardiner Harris, September 1, 2009
- Royal Pharmaceutical Society of Great Britain (September 2009). British National Formulary (BNF 58). UK: BMJ Group and RPS Publishing. ISBN 978-0-85369-778-7.
- U.S. National Library of Medicine: Drug Information Portal — Escitalopram
- Lexapro (Forest Laboratories) Official Lexapro homepage
- Cipralex (Lundbeck) Official Cipralex homepage
- Pharmacological information Lexapro
- Cipla Medpro Official Cipla Medpro homepage




http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0040402011015249

http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0040402011015249
AstraZeneca pays $50 million upfront for Merck & Co cancer drug
AstraZeneca has licensed a drug which is in mid-stage studies for ovarian cancer from Merck & Co.
The pact centres around the US drug major’s MK-1775, an oral small molecule inhibitor of WEE1 kinase, a cell cycle checkpoint protein regulator. Preclinical data indicate that disruption of WEE1 may enhance the cell killing effects of some anticancer agents and the compound is in Phase IIa studies in combination with standard of care therapies for the treatment of patients with certain types of ovarian cancer………….read all at
http://www.pharmatimes.com/Article/13-09-11/AZ_pays_50_million_upfront_for_Merck_Co_cancer_drug.aspx
MK-1775
MK-1775 is a potent and selective Wee1 inhibitor with IC50 of 5.2 nM; hinders G2 DNA damage checkpoint. Phase 2. IC50 of 5.2 nM
Chemical Name: 1,2-dihydro-1-[6-(1-hydroxy-1-methylethyl)-2-pyridinyl]-6-[[4-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)phenyl]amino]-2-(2-propen-1-yl)-3H-Pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-3-one
Elemental Analysis: C, 64.78; H, 6.44; N, 22.38; O, 6.39
CAS 955365-80-7
C27H32N8O2
MW 500.61
| Biological Activity: |
A potent and selective Wee1 kinase inhibitor in vitro and in vivo.
MK 1775 abolishes cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (CDC2) activity by phosphorylation of the Tyr15 residue. It abrogates a DNA damage checkpoint (G2-phase), leading to apoptosis in combination with several DNA-damaging agents selectively in p53-deficient tumor cell lines. It is under clinical trial for advanced solid tumors.
References:
H. Hirai et al. Small-molecule inhibition of Wee1 kinase by MK-1775 selectively sensitizes p53-deficient tumor cells to DNA-damaging agents. Mol. Cancer. Ther. 2009, 8(11), 2992-3000. [online]
S. Schellens et al. A Phase I and pharmacological study of MK-1775, a Wee1 tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in both monotherapy and in combination with gemcitabine, cisplatin, or carboplatin in patients with advanced solid tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27(15s), abstr 3510.
H. Hirai et al. MK-1775, a small molecule Wee1 inhibitor, enhances anti-tumor efficacy of various DNA-damaging agents, including 5-fluorouracil. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2010, 9(7), 523-525. [online]
CC Porter et al. Integrated genomic analyses identify WEE1 as a critical mediator of cell fate and a novel therapeutic target in acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2012, 26, 1266-1276. [online]
MK-1775 is an inhibitor of Wee1, a kinase that phosphorylates CDC2 to inactivate the CDC2/cyclin B complex (regulating the G2 checkpoint). Since most human cancers harbor p53-dependent G1 checkpoint abnormalities, they are dependent on the G2 checkpoint. G2 checkpoint abrogation may therefore sensitize p53 deficient tumor cells to anti-cancer agents
MK-1775 inhibits phosphorylation of CDC2 at Tyr15 (CDC2Y15), a direct substrate of Wee1 kinase in cells. MK-1775 abrogates G2 DNA damage checkpoint, leading to apoptosis in combination with DNA-damaging chemotherapeutic agents such as gemcitabine, carboplatin, and cisplatin selectively in p53-deficient cells. In vivo, MK-1775 potentiates tumor growth inhibition by these agents, and cotreatment does not significantly increase toxicity. The enhancement of antitumor effect by MK-1775 was well correlated with inhibition of CDC2Y15 phosphorylation in tumor tissue and skin hair follicles. Our data indicate that Wee1 inhibition provides a new approach for treatment of multiple human malignancies. [Mol Cancer Ther 2009;8(11):2992-3000].
MK-1775 is a first in class Wee1 inhibitor that is well tolerated and shows promising anti-tumor activity in previously treated pts. for detail see: http://meeting.ascopubs.org/cgi/content/abstract/27/15S/3510.
Drug in Focus: Abiraterone Acetate (Zytiga) New drug for the treatment of advanced prostate cancer

Abiraterone Acetate (Zytiga)
When prostate cancer spreads to another location in the body, it is considered to have metastasised, and surgery to remove the prostate and pelvic lymph nodes cannot eliminate the cancer. As a result, most men with metastatic prostate cancer (PCa) receive hormonal therapy which is also known as androgen ablation or androgen-deprivation therapy (ADT). ADT is used to reduce the levels of circulating androgens (male hormones) in the body (a process known as castration) or to keep them from reaching PCa cells. After sometime, however, the PCa no longer responds to hormone therapy, including LHRH analogues and anti-androgens, andis considered to be castration-resistant. At this stage, so-called metastatic castration-resistant PCa (mCRPC) becomes increasingly difficult to treat……………full article
READ ALL AT
http://www.medicalgrapevineasia.com/mg/2013/07/09/drug-in-focus-abiraterone-acetate-zytiga/
by
Dr Tan Yew Oo, Medical Oncologist and Hematologist in private practice at Gleneagles Hospital, to tell us more about AA.
Dr Tan Yew Oo is currently a Consultant Medical Oncologist and Hematologist in private practice at Gleneagles Hospital, Singapore. After graduating with MBBS from University of Singapore in 1971, he did his postgraduate training in Internal Medicine, Hematology and Medical Oncology in the United States and Canada. Upon his return to Singapore, he joined the Faculty of Medicine of the National University of Singapore in 1978 as Lecturer. He rapidly rose to be Chief of Medicine at National University Hospital (NUH) and Head, Division of Hematology-Oncology at NUH in 1988 and Professor of Medicine in 1991. He resigned and went into private practice since 1993. Dr Tan has been active in post-graduate education and has published many papers and has been an invited speaker for numerous meetings. He has participated in several international phase III clinical trials using novel drugs, and he has special interests in multiple myeloma, breast, thoracic and GI/GU oncology.
Chemical synthesis of Abiraterone acetate
The following synthetic route of Abiraterone acetate was from J Med Chem. 1995 Jun 23;38(13):2463-71. Novel steroidal inhibitors of human cytochrome P45017 alpha (17 alpha-hydroxylase-C17,20-lyase): potential agents for the treatment of prostatic cancer. Potter GA, Barrie SE, Jarman M, Rowlands MG. Cancer Research Campaign Centre for Cancer Therapeutics, Institute of Cancer Research, Sutton, Surrey, U.K.

CAS#: 154229-18-2.
Synonym: CB 7630;CB-7630.
Chemical Formula: C26H33NO2
Exact Mass: 391.25113
Molecular Weight: 391.54
Elemental Analysis: C, 79.76; H, 8.50; N, 3.58; O, 8.17
IUPAC: [(3S,10R,13S)-10,13-dimethyl-17-pyridin-3-yl-2,3,4,7,8,9,11,12,14,15-decahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-yl] acetate.
ZYTIGA™ (abiraterone acetate) received FDA Approval in May 2011 for Treatment of Metastatic Prostate Cancer After Priority Review; First Once-Daily, Oral Treatment for Metastatic Prostate Cancer Inhibits Androgen Production. ZYTIGA™ (abiraterone acetate) in combination with prednisone is indicated for the treatment of patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) who have received prior chemotherapy containing docetaxel.
According to Wikipedia, Abiraterone (tradename Zytiga) is a drug currently under investigation for use in castration-resistant prostate cancer (formerly hormone-resistant or hormone-refractory prostate cancer) (prostate cancer not responding to androgen deprivation or treatment with antiandrogens). After an expedited six-month review, the drug has been approved for use by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). This drug was initially discovered in the Cancer Research UK Centre for Cancer Therapeutics at the Institute of Cancer Research in London. Rights for commercialization of the drug were assigned to BTG plc, a UK company that manages commercialization activity in pharmaceuticals. BTG then licensed the product to Cougar Biotechnology which began development of the commercial product. In 2009, Cougar was acquired by Johnson & Johnson which is currently conducting clinical trials on abiraterone. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Abiraterone).
Abiraterone acetate is an FDA approved drug, and is an orally active acetate ester of the steroidal compound abiraterone with antiandrogen activity. Abiraterone acetate was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in April 2011. Abiraterone inhibits the enzymatic activity of steroid 17alpha-monooxygenase (17alpha-hydrolase/C17,20 lyase complex), a member of the cytochrome p450 family that catalyzes the 17alpha-hydroxylation of steroid intermediates involved in testosterone synthesis. Administration of this agent may suppress testosterone production by both the testes and the adrenals to castrate-range levels. Check for active clinical trials or closed clinical trials using this agent.
Current developer: Cougar Biotechnology Inc, and Johnson & Johnson。
By Jim Zhang, Ph.D., JZMed, Inc.

The pharmaceutical markets of China and India have been experiencing such rapid growth in the past decade that they are widely recognized as two of the world’s most dynamic emerging markets. Consequently, they have attracted many drug companies around the world…………FULL ARTICLE
READ ALL AT
Jim Zhang, Ph.D., is president and managing director of JZMed, Inc., a market research company specializing in research on the Chinese pharmaceutical outsourcing industry. The company also provides consulting services for pharmaceutical outsourcing in China.

Melatonin: It’s Not Just for Bedtime Anymore – Part 1
Melatonin is a neurohormone that is produced in the brain, primarily by the pineal gland, from the amino acid tryptophan. Its most well known functions include helping to regulate sleep and the body’s circadian rhythm.
The amount of melatonin we produce is determined by how dark or light our surroundings are. Our eyes have specialized light-sensitive receptors that relay this message to a cluster of nerves in the brain called the suprachiasmatic nucleus, or SCN. The SCN sets our internal biological clock (circadian rhythm) while also regulating sleep. When our surroundings are dark, the SCN tells the pineal gland to produce melatonin, which is thought to trigger sleep. Some melatonin is also made in the stomach and intestines.