AMISELIMOD
UNII-358M5150LY; CAS 942399-20-4; 358M5150LY; MT-1303; Amiselimod, MT-1303
| Molecular Formula: | C19H30F3NO3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight: | 377.448 g/mol |
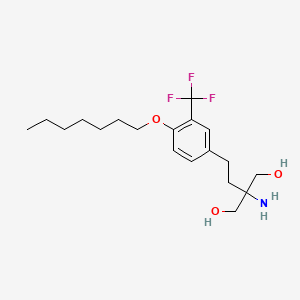
2-amino-2-[2-[4-heptoxy-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]ethyl]propane-1,3-diol
Phase II Crohn’s disease; Multiple sclerosis; Plaque psoriasis
AMISELIMOD HYDROCHLORIDE
- Molecular FormulaC19H31ClF3NO3
- Average mass413.902 Da
- Originator Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation
- Class Propylene glycols; Small molecules
- Mechanism of Action Immunosuppressants; Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor antagonist
Highest Development Phases
- Phase II Crohn’s disease; Multiple sclerosis; Plaque psoriasis
- Phase I Autoimmune disorders; Inflammation; Systemic lupus erythematosus
- No development reported Inflammatory bowel diseases
Most Recent Events
- 04 Nov 2017 No recent reports of development identified for phase-I development in Autoimmune-disorders in Japan (PO, Capsule)
- 04 Nov 2017 No recent reports of development identified for phase-I development in Autoimmune-disorders in USA (PO, Capsule)
- 04 Nov 2017 No recent reports of development identified for phase-I development in Inflammation in Japan (PO, Capsule)
Amiselimod, also known as MT1303, is a potent and selective immunosuppressant and sphingosine 1 phosphate receptor modulator. Amiselimod may be potentially useful for treatment of multiple sclerosis; inflammatory diseases; autoimmune diseases; psoriasis and inflammatory bowel diseases. Amiselimod is currently being developed by Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation
Mitsubishi Tanabe is developing amiselimod, an oral sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) receptor antagonist, for treating autoimmune diseases, primarily multiple sclerosis, psoriasis and inflammatory bowel diseases, including Crohn’s disease.
EU states expire 2026, and
Expire in the US in June 2030 with US154 extension.
| Inventors | Masatoshi Kiuchi, Kaoru Marukawa, Nobutaka Kobayashi, Kunio Sugahara |
| Applicant | Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation |
In recent years, calcineurin inhibitors such as cyclosporine FK 506 have been used to suppress rejection of patients receiving organ transplantation. While doing it, certain calcineurin inhibitors like cyclosporin can cause harmful side effects such as nephrotoxicity, hepatotoxicity, neurotoxicity, etc. For this reason, in order to suppress rejection reaction in transplant patients, development of drugs with higher safety and higher effectiveness is advanced.
[0003] Patent Documents 1 to 3 are useful as inhibitors of (acute or chronic) rejection in organ or bone marrow transplantation and also useful as therapeutic agents for various autoimmune diseases such as psoriasis and Behcet’s disease and rheumatic diseases 2 aminopropane 1, 3 dioly intermediates are disclosed.
[0004] One of these compounds, 2-amino-2- [2- (4-octylphenel) propane] 1, 3 diol hydrochloride (hereinafter sometimes referred to as FTY 720) is useful for renal transplantation It is currently under clinical development as an inhibitor of rejection reaction. FTY 720 is phosphorylated by sphingosine kinase in vivo in the form of phosphorylated FTY 720 [hereinafter sometimes referred to as FTY 720-P]. For example, 2 amino-2-phosphoryloxymethyl 4- (4-octafil-el) butanol. FTY720 – P has four types of S1 P receptors (hereinafter referred to as S1 P receptors) among five kinds of sphingosine – 1 – phosphate (hereinafter sometimes referred to as S1P) receptors It acts as an aggroove on the body (other than S1P2) (Non-Patent Document 1).
[0005] It has recently been reported that S1P1 among the S1P receptors is essential for the export of mature lymphocytes with thymus and secondary lymphoid tissue forces. FTY720 – P downregulates S1P1 on lymphocytes by acting as S1P1 ghost. As a result, the transfer of mature lymphocytes from the thymus and secondary lymphatic tissues is inhibited, and the circulating adult lymphocytes in the blood are isolated in the secondary lymphatic tissue to exert an immunosuppressive effect Has been suggested (
Non-Patent Document 2).
[0006] On the other hand, conventional 2-aminopropane 1, 3 dioly compounds are concerned as transient bradycardia expression as a side effect, and in order to solve this problem, 2-aminopropane 1, 3 diiori Many new compounds have been reported by geometrically modifying compounds. Among them, as a compound having a substituent on the benzene ring possessed by FTY 720, Patent Document 4 discloses an aminopropenol derivative as a S1P receptor modulator with a phosphate group, Patent Documents 5 and 6 are both S1P Discloses an amino-propanol derivative as a receptor modulator. However, trihaloalkyl groups such as trifluoromethyl groups are not disclosed as substituents on the benzene ring among them. In any case, it is currently the case that it has not yet reached a satisfactory level of safety as a pharmaceutical.
Patent Document 1: International Publication Pamphlet WO 94 Z 08943
Patent Document 2: International Publication Pamphlet WO 96 Z 06068
Patent Document 3: International Publication Pamphlet W 0 98 z 45 429
Patent Document 4: International Publication Pamphlet WO 02 Z 076995
Patent document 5: International public non-fret WO 2004 Z 096752
Patent Document 6: International Publication Pamphlet WO 2004 Z 110979
Non-patent document 1: Science, 2002, 296, 346-349
Non-patent document 2: Nature, 2004, 427, 355-360
Reference Example 3
5 bromo 2 heptyloxybenzonitrile
(3- 1) 5 Synthesis of bromo-2 heptyloxybenzonitrile (Reference Example Compound 3- 1)
1-Heptanol (1.55 g) was dissolved in N, N dimethylformamide (24 ml) and sodium hydride (0.321 g) was added at room temperature. After stirring for 1 hour, 5 bromo-2 fluoborosyl-tolyl (2.43 g) was added and the mixture was further stirred for 50 minutes. The reaction solution was poured into water, extracted with ethyl acetate, washed with water, saturated brine, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and the solvent was distilled off under reduced pressure. After eliminating the 5 bromo 2 fluconate benzonitrile as a raw material, the reaction was carried out again under the same conditions and purification was carried out by silica gel column chromatography (hexane: ethyl acetate = 50: 1 to 5: 1) to obtain the desired product (3.10 g ) As a colorless oil.
– NMR (CDCl 3) δ (ppm): 0.89 (3H, t, J = 6.4 Hz), 1.24-1.35 (6H, m
J = 8.8 Hz), 1.48 (2H, quint, J = 7.2 Hz), 1.84 7.59 (1 H, dd, J = 8.8, 2.4 Hz), 7.65 (1 H, d, J = 2.4 Hz).
Example 1
2 Amino 2- [2- (4-heptyloxy-3 trifluoromethylph enyl) propane-1, 3-diol hydrochloride
(1 – 1) {2, 2 Dimethyl 5- [2- (4 hydroxy 3 trifluoromethylfuethyl) ethyl] 1,3 dioxane 5 mercaptothenylboronic acid t butyl ester (synthesis compound 1 1)
Reference Example Compound 2-5 (70.3 g) was dissolved in tetrahydrofuran (500 ml), t-butoxycallium (13.Og) was added, and the mixture was stirred for 1 hour. To the mixed solution was dropwise added a solution of the compound of Reference Example 1 (15.Og) in tetrahydrofuran (100 ml) under ice cooling, followed by stirring for 2 hours under ice cooling. Water was added to the reaction solution, the mixture was extracted with ethyl acetate, washed with water, saturated brine, dried with anhydrous magnesium sulfate, and the solvent was distilled off under reduced pressure. The residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (hexane: ethyl acetate = 3: D to obtain 31. Og of a pale yellow oily matter.) The geometric isomer ratio of the obtained product was (E : Z = 1: 6).
This pale yellow oil was dissolved in ethyl acetate (200 ml), 10% palladium carbon (3.00 g) was added, and the mixture was stirred under a hydrogen atmosphere at room temperature for 7 hours. After purging the inside of the reaction vessel with nitrogen, the solution was filtered and the filtrate was concentrated. The residue was washed with diisopropyl ether to obtain the desired product (2.2 g) as a colorless powder.
1 H-NMR (CDCl 3) δ (ppm): 1. 43 (3H, s), 1.44 (3H, s), 1. 47 (9H, s), 1
(2H, m), 91- 1. 98 (2H, m), 2. 50-2.66 (2H, m), 3. 69 (2H, d, J = Il. 6 Hz), 3. 89 J = 8.2 Hz), 7. 22 (1 H, dd J = 8 Hz), 5. 02 (1 H, brs), 5. 52 . 2, 1. 7 Hz), 7. 29 (1 H, d, J = l. 7 Hz).
(1-2) {2,2 Dimethyl-5- [2- (4heptyloxy-3 trifluoromethyl) ethyl] 1,3 dioxane 5-mercaptobutyric acid t-butyl ester Synthesis (compound 1 2)
Compound 1-1 (510 mg) was dissolved in N, N dimethylformamide (10 ml), potassium carbonate (506 mg) and n-heptyl bromide (0.235 ml) were added and stirred at 80 ° C. for 2 hours. Water was added to the reaction solution, the mixture was extracted with ethyl acetate, washed with water and saturated brine, dried with anhydrous sulfuric acid
The resultant was dried with GENSCHUM and the solvent was distilled off under reduced pressure to obtain the desired product (640 mg) as a colorless oil.
– NMR (CDCl 3) δ (ppm): 0.89 (3H, t, J = 6.8 Hz), l.30-1.37 (6H, m
(2H, m), 1.91-1.98 (2H, m), 1.42-1.50 (2H, m), 1.42 (3H, s), 1.44 (3H, s), 1.47 J = 16.6 Hz), 4.00 (2H, t, J = 6.4 Hz), 4.9 8 (2H, d, J = 11.6 Hz), 3.69 1 H, brs), 6.88 (1 H, d, J = 8.5 Hz), 7.26 – 7.29 (1 H, m), 7.35 (1 H, d, J = 1.5 Hz).
(1-3) Synthesis of 2-amino-2- [2- (4heptyloxy 3 trifluoromethyl) ethyl] propane 1, 3 diol hydrochloride (Compound 1- 3)
Compound 12 (640 mg) was dissolved in ethanol (15 ml), concentrated hydrochloric acid (3 ml) was caught and stirred at 80 ° C. for 2 hours. The reaction solution was concentrated, and the residue was washed with ethyl ether to give the desired product (492 mg) as a white powder.
MS (ESI) m / z: 378 [M + H]
– NMR (DMSO-d) δ (ppm): 0.86 (3H,
6 t, J = 6.8 Hz), 1.24 – 1.39 (6
(4H, m), 3.51 (4H, d, J = 5. lHz), 4.06 (2H, m), 1.39-1.46 (2H, m), 1.68-1.78 (4H, m), 2.55-2.22 , 7.32 (2H, t, J = 5.1 Hz), 7.18 (1 H, d, J = 8.4 Hz), 7.42 – 7.45 (2 H, m), 7.76 (3 H, brs;).
PATENT
WO 2009119858
JP 2011136905
WO 2017188357
PATENT
WO-2018021517
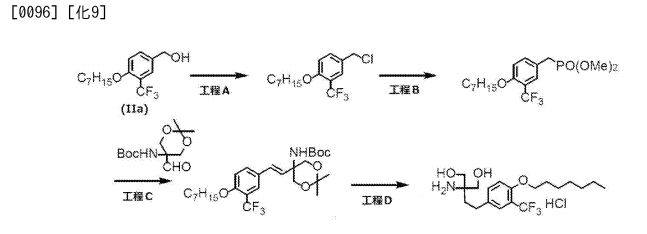
The production method includes the step of reducing 4-heptyloxy-3-trifluoromethylbenzoic acid (Ia) to 4-heptyloxy-3-trifluoromethylbenzyl alcohol (IIa). However, until now, there has been a problem such that the conversion is low and the by-product (IIa ‘) in which the trifluoromethyl group is reduced together with the compound (IIa) is generated in this step.

Patent Document 1: WO2007 / 069712
[Chemical formula 3]

the compound (IIa), the following scheme Based on the route, 2-amino-2- [2- (4-heptyloxy-3-trifluoromethylphenyl) ethyl] propane-1,3-diol hydrochloride was prepared.
Synthesis of 4-heptyloxy-3-trifluoromethylbenzyl chloride (Step A) A
few drops of N, N-dimethylformamide was added to a solution of compound (IIa) (26.8 g) in methylene chloride (107 mL), and 0 At 0 ° C., thionyl chloride (8.09 mL) was added dropwise. The mixture was stirred at the same temperature for 2 hours, and water (50 mL) was added to the reaction solution. The organic layer was separated and extracted, washed with water (50 mL), saturated aqueous sodium bicarbonate solution (70 mL), dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, and the solvent was distilled off under reduced pressure to give 4-heptyloxy-3-trifluoromethylbenzyl Chloride (28.3 g) as white crystals.
1H-NMR (CDCl 3) δ (ppm): 0.89 (3H, t, J = 6.5 Hz), 1.26-1.54 (8H, m), 1.77-1.86 (2H, m , 4.49 (2H, t, J = 6.4 Hz), 4.56 (2H, s), 6.96 (IH, d, J = 8.6 Hz), 7.49 (IH, dd, J = 2.0 Hz, 8.5 Hz), 7.58 (1 H, d, J = 1.9 Hz)
Synthesis of dimethyl (4-heptyloxy-3-trifluoromethylbenzyl) phosphonate (Step B) To
a solution of N, N (3-trifluoromethylbenzyl ) phosphonate of 4-heptyloxy-3-trifluoromethylbenzyl chloride (6.00 g, 19.4 mmol) (2.57 g, 23.3 mmol), cesium carbonate (7.60 g, 23.3 mmol) and tetrabutylammonium iodide (7.54 g, 20.4 mmol) were added to a dimethylformamide (36 mL) And the mixture was stirred at 25 ° C. for 1 day. Toluene (36 mL) and water (18 mL) were added for phase separation, and the resulting organic layer was washed twice with a mixture of N, N-dimethylformamide (18 mL) and water (18 mL). After concentration under reduced pressure, column purification using hexane and ethyl acetate gave 4.71 g of dimethyl (4-heptyloxy-3-trifluoromethylbenzyl) phosphonate.
1
H-NMR (CDCl 3) δ (ppm): 0.89 (3 H, t, J = 6.9 Hz), 1.20 – 1.41 (6 H, m) , 1.43-1.49 (2H, m), 1.72-1.83 (2H, m), 3.09 (IH, s), 3.14 (IH, s), 3.68 (3H , 7.41 – 7.44 (2 H, t, J = 6.4 Hz), 6.94 (1 H, d, J = 8.4 Hz), 3.70 (3 H, s), 4.02 (2H, m)
tert-Butyl (E) – {2,2-dimethyl-5- [2- (4-heptyloxy-3-trifluoromethylphenyl) vinyl] -1, 3-dioxan-5- yl} carbamate Ester synthesis (Step C) A
solution of dimethyl (1.18 g, 3.09 mmol ) (4-heptyloxy-3-trifluoromethylbenzyl) phosphonate in 1.25 mL of N, N- dimethylformamide and (2, -dimethyl-5-formyl-1,3-dioxan-5-yl) carbamic acid tert-butyl ester (961 mg, 3.71 mmol) in tetrahydrofuran (4 mL) was treated with potassium tert-butoxide (1.28 g, 4 mmol) in tetrahydrofuran (7 mL), and the mixture was stirred at 0 ° C. for 6 hours. Heptane (7 mL) and water (3 mL) were added and the layers were separated, and the obtained organic layer was washed twice with water (3 mL) and concentrated. Heptane was added and the mixture was cooled in an ice bath. The precipitated crystals were collected by filtration and dried under reduced pressure to give (E) – {2,2-dimethyl-5- [2- (4-heptyloxy- Phenyl) vinyl] -1, 3-dioxan-5-yl} carbamic acid tert-butyl ester.
1
H-NMR (CDCl 3) δ (ppm): 0.89 (3 H, t, J = 6.9 Hz), 1.29 – 1.38 (6 H, m) , 1.44 – 1.59 (17 H, m), 1.77 – 1.83 (2 H, m), 3.83 – 3.93 (2 H, m), 3.93 – 4.08 (4 H, J = 16.5 Hz), 6.48 (1 H, d, J = 16.5 Hz), 6.91 (1 H, d, J), 5.21 (1 H, brs), 6.10 J = 8.5 Hz), 7.44 (1 H, dd, J = 8.6, 2.1 Hz), 7.55 (1 H, d, J = 2.0 Hz)
Synthesis of 2-amino-2- [2- (4-heptyloxy-3-trifluoromethylphenyl) ethyl] propane-1,3-diol hydrochloride (Step D)
(E) – {2, -dimethyl-5- [2- (4-heptyloxy-3-trifluoromethylphenyl) vinyl] -1,3-dioxan- 5-yl} carbamic acid tert-butyl ester (6.50 g, 12.6 mmol) Methanol (65 mL) solution was heated to 50 ° C., a solution of concentrated hydrochloric acid (2.55 g) in methanol (5.3 mL) was added dropwise, and the mixture was stirred at 60 ° C. for 6 hours. The mixture was cooled to around room temperature, 5% palladium carbon (0.33 g) was added thereto, and the mixture was stirred under a hydrogen gas atmosphere for 3 hours. After filtration and washing the residue with methanol (39 mL), the filtrate was concentrated and stirred at 5 ° C. for 1 hour. Water (32.5 mL) was added and the mixture was stirred at 5 ° C for 1 hour, and the precipitated crystals were collected by filtration. Washed with water (13 mL) and dried under reduced pressure to obtain 4.83 g of 2-amino-2- [2- (4-heptyloxy-3-trifluoromethylphenyl) ethyl] propane-1,3-diol hydrochloride .
MS (ESI) m / z: 378 [M + H]
PATENTS
////////////AMISELIMOD, Phase II, Crohn’s disease, Multiple sclerosis, Plaque psoriasis, MT-1303, MT1303, MT 1303, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation, Mitsubishi , JAPAN, PHASE 2
CCCCCCCOC1=C(C=C(C=C1)CCC(CO)(CO)N)C(F)(F)F