picked up from a japanes site
Sams-Dodd F. Is poor research the cause of the declining productivity of the pharmaceutical industry? An industry in need of a paradigm shift.
Drug discovery today. 2012;00(00):1–7.
Available at:
http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1359644612003674過去20年の創薬パラダイムであるターゲットベースの創薬は、何千億円の投資の割にはそれほど効果的ではなかったと言われている。なぜこれほどまでに機能しなかったのか?ここでは従来の手法の失敗確率の高い理由を知り、生産性向上のための創薬手法の転換を提案する。たとえば、ターゲット選定の段階で、多くの研究者は選択的な化合物を目指そうとするが、癌のキナーゼ研究を見てもわかるように、薬効を示すのはマルチのターゲットによって複数のシグナルを同時に作用する事に発揮する場合も多い。また、製薬企業では薬効につながる明確なMOAを必要とする傾向にあるが、実際には精神疾患の薬剤のようにMOAが十分に説明できずに使,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,see below a translation
Available at: http:// linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1359644612003674
It is said that drug discovery of target-based drug discovery is a paradigm of the past 20 years, was not very effective in what percent of one hundred billion yen of investment. Why did not work so much? You know why a high failure probability of the conventional method, we propose the transformation of drug discovery techniques to improve productivity in this case.
For example, at the stage of target selection, many researchers trying to aim at compounds selective, but as can be seen from kinase cancer research, and shows a medicinal action at the same time a plurality of signals by the target multi- If you want to demonstrate to that you often. Further, it tends to require a clear MOA leading to efficacy in pharmaceutical companies, but the MOA is used to not be fully described as drug mental illness often actually in practice. Movement of proteins in vivo actually that it is not so simple many MOA to be described coherently At first glance also, also, may be used instead of different views depending on the specifications of interpretation in practice.
If you prove that it is selective for off-target of 100 kinds about the compound that is optimized in a single mechanism, if there is action on targets unknown other, it is that there is a clinically significant after we In some cases, it can be seen. Next is to evaluate and to build the flow of screening MOA and target Once you have decided, but it is also not necessarily the one that bridges the screening and clinical actually.
Case of cancer cells, and so extrapolate clinical efficacy in inhibition of proliferation activity, but are those far removed from the actual in vivo in most cases, the process itself is continuously evaluated by routine work ends as a waste of time not money. If you choose to use compound somehow, animal disease model is not possible to accurately predict clinical outcome. Uncertainties like this a lot, theme 97% never fail downright non-clinical. Rather than biology and disease clearly, feeling had focused on the process is undeniable drug discovery paradigm of current. Important thing originally, is to to centered on principles and appropriate science focused on disease in clinical, it is to re-build process on it.
Reorganization research and development are important, it is not able to change the nature of the disease where you have reorganized matter. Therefore, it is a secondary or if the organization. The new research paradigms consider the process to focus on the disease, it is necessary to apply the three principles. One of them is the process of science-based.Science is made up by systematic law, which is evidenced by the accumulation of observation and experiment without prejudice. It’s that you have to often is that is do we need to note here, discussions would begin while not to suspect the hypothesis and doctrine that are major premise.
For example, the earth if the major premise that it is a flat, what’s there in the flat world of another fall from the tip of the flat earth?Question that will come out. However, if you can dispel the assumption by the belief that there is no basis to recognize the shape of the earth, it is possible to pursue science in the right direction in a totally different perspective. This same is true for drug discovery research. For example, if a certain phenomenon is to work, it would no longer consider the direction of the other.
Cause of schizophrenia may be mentioned a theory that based on the excess dopamine hyperactivity as an example.May develop the symptoms of schizophrenia-like D amphetamine is allowed to release dopamine, this concept is the basis that it has a D2 antagonism dopamine psychotropic drugs many. However, it is said, not the D amphetamine contraindicated, psychotropic drugs long-term treatment is also lead to enhanced dopamine system schizophrenia many patients. However, the fact that you have these, never to be little consideration on the grounds that would be go against the doctrine of dopamine hypothesis. In other words, the doctrine would be to blind us to the alternative hypothesis essentially.
This same is true with respect to Alzheimer’s.When the doctrine of a certain hypothesis is treated as the principles, facts that go against the doctrine is ignored, hypothesis another is neglected, progress of science’s delayed in order to look away from the truth. Hypothesis became a doctrine becomes absolute only and is deified as the Bible. Fact defeat the hypothesis that even came out after another, the cause interpreted as another factor, never wake up until push forward until you collapse in clinical late as a result. Hypothesis that build on doctrine the wrong does not lead only in the wrong direction all.
Simply because I admit to know that the earth is a sphere, a new way of science he is cut open. In addition, reductionism approach dominant also should be noted in the discussion of science. Element has a plurality of by influencing the complex in vivo, originally, it is not possible to understand the living body to focus on a single element. For example, to understand the engine of the car, there is a need to disconnect the engine from the mirror and the door, however, they are not able to understand the engine itself and accidentally disconnect without knowing the function of important and bolts cylinder engine. Multi-target has been spotlighted in the drug synergy effect by the action of more than one is because the expected effect even insufficient for single target. That it kept asking the research many times, to re-examine the design of the experiment is important in decision-making, but is in surprisingly poor. Schizophrenia negative symptoms model of phencyclidine-induced and model of cerebral infarction has become a problem much that there is no reproducibility by the lab.
In the process of science-based, it will continue to refine while obtaining conclusive evidence to do the practice and discussion is important. Clinical success rate is low, it sifted the hypothesis as much as possible in the process of advancing the research, better should remain. The second principle is that the customers know. Be patient with the customer for the pharmaceutical companies. It is not possible to produce products that are competitive by knowing the limit disease, condition, existing drugs. Even on the researchers know the needs of the patient, taking into closer contact with the doctor is important. Principles of the third, is to understand the risks. The acceptable risk, it is not what we deal with the risk, that is, whether to undertake the corresponding risk, the only pass to avoid the discussion if not. First of all drug discovery are those difficult, many programs to fail in the mid-way is typical for the pharmaceutical companies.
However, it should be avoided risk, such as notice and a predictable if you even care, because he turn away the failure of such a future, because it should not be happening that failure waiting to happen after we some. A few years ago, pharmaceutical companies some had considered mGluR5 antagonists as an anti-anxiety drug. This MOA was expected as much anti-anxiety drug, but the side effects of psychotic disorders such as hallucinations and delusions has been concern on the other hand. However, was never to be fully verified until the compound drop in its side effects in Phase 1 this concern. Many pharmaceutical companies are in was not able to deal with known risks.
Any pharmaceutical company, and the last would complete the study because of the common “because other companies are doing” and, nobody did not want to press the stop button. Pharmaceutical companies had been wiped out by the results of the problem banzai charge of pharmaceutical companies which can be called reckless risk-taking took place waiting to happen in clinical trials. To avoid this situation, the practice of the process of due diligence scientific is the essential. Inspection with no bias due to opposition support and opinion is carried out in this process. And verified by experiment hypothesis that there is sufficient scientific reason to support (1) project, if you can dispel the uncertain surface with a (2) simple additional experiments, and (3) key in this process it is determined Uruka about, you can reduce the risk of later on in (4) checkpoint. Researchers lament “factor of the disease is too complex” and the “because there is no way of doing the other”, the researchers would start the research been sticking to the one target.
However, you should know that a little time, to discuss the clinical symptoms of the disease, you only need to discuss the screening method of Japan before, and there is also a problem that can be resolved














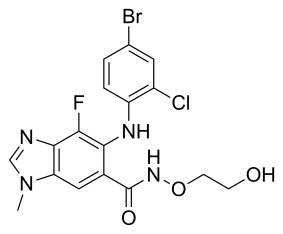




 LX4211
LX4211

















 LinkedIn
LinkedIn Facebook
Facebook Twitter
Twitter GooglePlus
GooglePlus