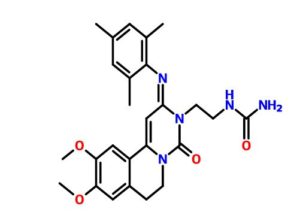
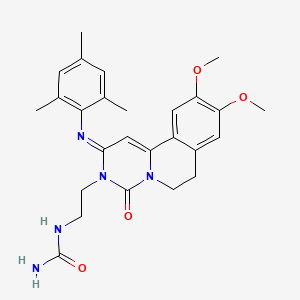
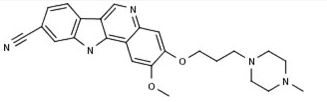
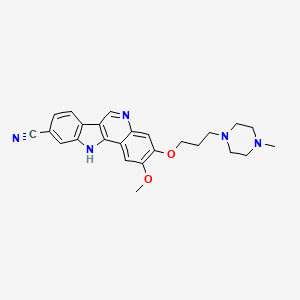
RPL-554
- MF C26H31N5O4
- MW 477.555
CFTR stimulator; PDE 3 inhibitor; PDE 4 inhibitor
RPL-554 is a mixed phosphodiesterase (PDE) III/IV inhibitor in phase II clinical development at Verona Pharma for the treatment of asthma, allergic rhinitis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and inflammation.
RPL-554 is expected to have long duration of action and will be administered nasally thereby preventing gastrointestinal problems often resulting from orally administered PDE4 antiinflammatory drugs.
The company is now seeking licensing agreements or partnerships for the further development and commercialization of the drug.
RPL-554 (LS-193,855) is a drug candidate for respiratory diseases. It is an analog of trequinsin, and like trequinsin, is a dual inhibitor of the phosphodiesterase enzymes PDE-3 and PDE-4.[1] As of October 2015, inhaled RPL-554 delivered via a nebulizer was in development for COPD and had been studied in asthma.[2]
PDE3 inhibitors act as bronchodilators, while PDE4 inhibitors have an anti-inflammatory effect.[1][3]
RPL554 was part of a family of compounds invented by Sir David Jack, former head of R&D for GlaxoSmithKline, and Alexander Oxford, a medicinal chemist; the patents on their work were assigned to Vernalis plc.[4][5]:19-20
In 2005, Rhinopharma Ltd, acquired the rights to the intellectual property from Vernalis.[5]:19-20 Rhinopharma was a startup founded in Vancouver, Canada in 2004 by Michael Walker, Clive Page, and David Saint, to discover and develop drugs for chronic respiratory diseases,[5]:16 and intended to develop RPL-554, delivered with an inhaler, first for allergic rhinitis, then asthma, then forCOPD.[5]:16-17 RPL554 was synthesized at Tocris, a contract research organization, under the supervision of Oxford, and was studied in collaboration with Page’s lab at King’s College, London.[1] In 2006 Rhinopharma recapitalized and was renamed Verona Pharma plc.[5]
This was first seen in April 2015 when it was published as a France national. Verona Pharma (formerly Rhinopharma), under license from Kings College via Vernalis, is developing the long-acting bronchodilator, RPL-554 the lead in a series dual inhibitor of multidrug resistant protein-4 and PDE 3 and 4 inhibiting trequinsin analogs which included RPL-565, for treating inflammatory respiratory diseases, such as allergic rhinitis, asthma, and COPD.
RPL554
Verona Pharma’s lead drug, RPL554, is a “first-in-class” inhaled drug under development for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma and cystic fibrosis. The drug is an inhibitor of the phosphodiesterase 3 (PDE3) and phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) enzymes, two enzymes known to be of importance in the development and progression of immunological respiratory diseases. The drug has the potential to act as both a bronchodilator and an anti-inflammatory which would significantly differentiate it from existing drugs.
RPL554 was selected from a class of compounds co-invented by Sir David Jack, the former Director of Research at Glaxo who led the team that discovered many of the commercially successful drugs in the respiratory market.
Verona Pharma has successfully completed two double-blind placebo controlled randomised Phase 2b studies of RPL554: one in mild to moderate asthma and another in mild to moderate COPD. The drug was found to be well tolerated, free from drug-related adverse effects (especially cardiovascular and gastro-intestinal effects) and generated significant bronchodilation. Additionally, double-blind placebo controlled exploratory studies in healthy volunteers challenged with an inhaled irritant also generated consistent, clinically meaningful anti-inflammatory effects.
Verona Pharma is also carrying out exploratory studies to investigate the potential of RPL554 as a novel treatement for cystic fibrosis. In November 2014, the Company received a Venture and Innovation Award from the UK Cystic Fibrosis Trust to further such studies.
For further information on the potential of RPL554 for the treatment of respiratory diseases, refer to the peer-reviewed paper available on-line in the highly-respected medication journal, The Lancet Respiratory Medicine, entitled “Efficacy and safety of RPL554, a dual PDE3 and PDE4 inhibitor, in healthy volunteers and in patients with asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: findings from four clinical trials”.
The competitive advantages of RPL554 include the following:
- combining bronchodilator (PDE 3) and anti-inflammatory actions (PDE 4) in a single drug, something that is currently only achieved with a combination LABA and glucocorticosteroid inhaler,
- unique in not using steroids or beta agonists, which have known side effects,
- planned to be administered by nasal inhalation, thereby reducing the unwanted gastrointestinal side effects of many orally administered drugs.
History of Clinical Trials
- Following completion in May 2008 of toxicological studies of RPL554, the Company commenced in February 2009 a Phase I/IIa clinical trial of the drug at the Centre for Human Drug Research (CHDR) at Leiden in the Netherlands. In September 2009, the Company announced that it had successfully completed the trial, demonstrating that RPL554 has a good safety profile and has beneficial effects in terms of bronchodilation and bronchoprotection in asthmatics and a reduction in the numbers of inflammatory cells in the nasal passages of allergic rhinitis patients.
- In November 2010, the Company successfully completed a further trial that examined the safety and bronchodilator effectiveness of the drug administered at higher doses.
- In August 2011, the Company demonstrated that bronchodilation is maintained over a period of 6 days with daily dosing of RPL554 in asthmatics.
- In November 2011, the Company successfully demonstrated safety and bronchodilation of RPL554 in patients with mild to moderate forms of COPD.
- In March 2013, the Company demonstrated positive airway anti-inflammatory activity with respect to COPD at a clinical trial carried out at the Medicines Evaluation Unit (MEU) in Manchester, UK.

Synthesis
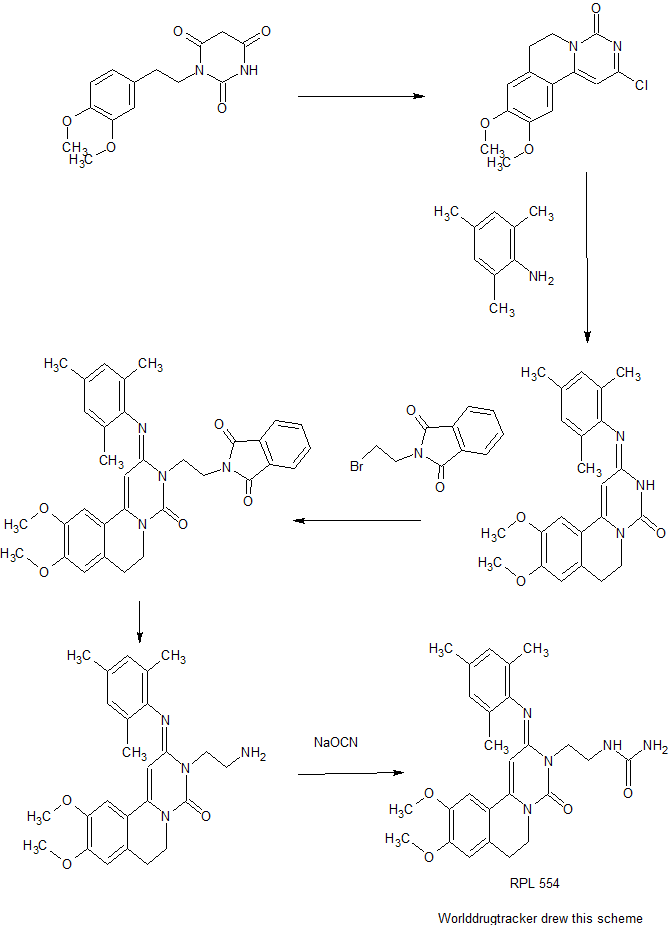
Cyclization of 1-(3,4-dimethoxyphenethyl)barbituric acid in refluxing POCl3 produces the pyrimidoisoquinolinone , which is further condensed with 2,4,6-trimethylaniline in boiling isopropanol to afford the trimethylphenylimino derivative . Subsequent alkylation of with N-(2-bromoethyl)phthalimide in the presence of K2CO3 and KI, followed by hydrazinolysis of the resulting phthalimidoethyl compound yields the primary amine . This is finally converted into the title urea RPL 554 by reaction with sodium cyanate in aqueous HCl.
Example 1 : 9 Λ 0-Dimethoxy-2-(2.4-6-trimethy-phen yliminoY-3-(N-carbamoyl-2- aminoethylV3.4.6.7-tetrahydro-2H-pyrimido[6.1-a]isoquinolin-4-one
Sodium cyanate (6.0g, 0.092 mol) in water (100 ml) was added dropwise to a stirred solution of 9,10-Dimethoxy-2-(2,4,6-trimethylphenylimino)-3-(2-aminoethyl)-3,4,6,7- tetrahydro-2H-pyrimido[6,l-a]isoquinolin-4-one, prepared according to Preparation 4 above (20.0g, 0.046 mol) in water (600 ml) and IN ΗC1 (92 ml) at 80°C. After stirring for 2h at 80°C the mixture was cooled in an ice-bath and basified with 2N NaOH. The mixture was extracted with dichloromethane (3 x 200 ml) and the combined extract was dried (MgSO- ) and evaporated in vacuo. The resulting yellow foam was purified by column chromatography on silica gel eluting with CH2CI2 / MeOH (97:3) and triturated with ether to obtain the title compound as a yellow solid, 11.9g, 54%.
M.p.: 234-236°C m/z: C26H31N5O4 requires M=477 found (M+l) = 478
HPLC: Area (%) 99.50 Column ODS (150 x 4.6 mm)
MP pH3 KH2PO4 / CH3CN (60/40)
FR (ml/min) 1.0 RT (min) 9.25 Detection 250 nm
lK NMR (300 MHz, CDCI3): δ 1.92 (1H, br s, NH), 2.06 (6H, s, 2xCH3), 2.29 (3H, s, CH3), 2.92 (2H, t, CH2), 3.53 (2H, m, CH2), 3.77 (3H, s, OCH3), 3.91 (3H, s, OCH3), 4.05 (2H, t, CH2), 4.40 (2H, t, CH2), 5.35 (2H, br s, NH2), 5.45 (1H, s, C=CH), 6.68 (1H, s, ArH), 6.70 (1H, s, ArH), 6.89 (2H, s, 2xArH).
Preparation 1 : Synthesis of 2-Chloro-6.7-d-hydro-9.10-Dimethoxy-4H-pyrimido- [6,l-a]isoquinoHn-4-one (shown as (1) in Figure 1
A mixture of l-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl) barbituric acid (70g, 0.24mol), prepared according to the method described in B. Lai et al. J.Med.Chem. 27 1470-1480 (1984), and phosphorus oxychloride (300ml, 3.22mol) was refluxed for 2.5h. The excess phosphorous oxychloride was removed by distillation (20mmHg) on wa ming. After cooling the residue was slurried in dioxan (100ml) and cautiously added to a vigorously stirred ice/water solution (11). Chloroform (11) was added and the resulting mixture was basified with 30% sodium hydroxide solution. The organic layer was separated and the aqueous phase further extracted with chloroform (2x750ml). The combined organic extracts were washed with water (1.51), dried over magnesium sulphate and concentrated in vacuo to leave a gummy material (90g). This was stirred in methanol for a few minutes, filtered and washed with methanol (200ml), diethyl ether (2x200ml) and dried in vacuo at 40°C to yield the title compound as a yellow/orange solid. 47g, 62%
(300MHz, CDCI3) 2.96(2H, t, C(7) H2); 3.96(6H, s, 2xOCH3; 4.20(2H, t, C(6) H2); 6.61(1H, s, C(1) H); 6.76(1H, s, Ar-H); 7.10(1H, s, Ar-H). Preparation 2: 9.10-Dimethoxy-2-(2.4.6-trimethylphenyliminoV3.4.6.7- tetrahydro-2H-pyrimido[6.1-a]isoquinolin-4-one (shown as (2) in Figure 1
2-Chloro-9,10-dimethoxy-6,7-dihydro-4H-pyrimido[6,l-a]isoquinolin-4-one, prepared according to Preparation 1, (38.5g, 0.13 mol) and 2,4,6-trimethylaniline (52.7g, 0.39 mol) in propan-2-ol (3 1) was stirred and heated at reflux, under nitrogen, for 24h. After cooling to room temperature, the solution was evaporated in vacuo and the residue was purified by column chromatography on silica gel, eluting with CΗ2CI2 /
MeOH, initially 98:2, changing to 96:4 once the product began to elute from the column. The title compound was obtained with a slight impurity, (just above the product on tic). Yield 34.6g, 67%.
Preparation 3: 9.10-Dimethoxy-2-(2.4.6-trimethylphenyliminoV3-(2-N- phthalimidoethyπ-3.4.6.7-tetrahydro-2H-pyrimido[6.1-a]isoquinolin-4-one
(shown as (3 in Figure 1)
A mixture of 9,10-Dimethoxy-2-(2,4,6-trimethylphenylimino)-3,4,6,7-tetrahydro-2H- pyrimido[6,l-a]isoquinolin-4-one (which was prepared according to Preparation 2) (60.0g, 0.153 mol), potassium carbonate (191g, 1.38 mol), sodium iodide (137g, 0.92 mol) and N-(2-bromoethyl)phthalimide (234g, 0.92 mol) in 2-butanone (1500 ml) was stirred and heated at reflux, under nitrogen, for 4 days. After cooling to room temperature the mixture was filtered and the filtrate was evaporated in vacuo. The residue was treated with methanol (1000 ml) and the solid filtered off, washed with methanol and recrystallised from ethyl acetate to obtain the title compound as a pale yellow solid in yield 40. Og, 46%. Evaporation of the mother liquor and column chromatography of the residue on silica gel (CΗ2C-2 / MeOH 95:5) provided further product 11.7g, 13.5%. Preparation 4: 9.10-Dimethoxy-2-(2A6-trimethylphenylimino)-3-(2-arninoethyO- 3.4.6.7-tetrahydro-2H-pyrimido[6.1-a]isoquino-in-4-one (shown as (4) in Figure 1)
A mixture of 9,10-Dimethoxy-2-(2,4,6-trimethylphenylimino)-3-(2-N- phthalimidoethyl)-3,4,6,7-tetrahydro-2H-pyrimido[6,l-a]isoquinolin-4-one (22. Og, 0.039 mol), prepared according to Preparation 3, and hydrazine hydrate (11.3g, 0.195 mol) in chloroform (300 ml) and ethanol (460 ml) was stined at room temperature, under nitrogen, for 18h. Further hydrazine hydrate (2.9g, 0.05 mol) was added and the mixture was stirred a further 4h. After cooling in ice / water, the solid was removed by filtration and the filtrate evaporated in vacuo. The residue was dissolved in dichloromethane and the insoluble material was removed by filtration. The fitrate was dried (MgSO-i) and evaporated in vacuo to afford the title compound as a yellow foam in yield 16.2g, 96%.
PATENT
WO 2012020016
PATENT
Novel crystalline acid addition salts forms of RPL-554 are claimed, wherein the salts, such as ethane- 1,2-disulfonic acid, ethanesulfonic acid, methanesulfonic acid, benzenesulfonic acid, p-toluenesulfonic acid, hydrochloric acid, hydrobromic acid, phosphoric acid or sulfuric acid. .
RPL554 (9, 10-dimethoxy-2-(2,4,6-trimethylphenylimino)-3-(/V-carbamoyl-2-aminoethyl)-3,4,6,7-tetrahydro-2H-pyrimido[6, l-a]isoquinolin-4-one) is a dual PDE3/PDE4 inhibitor and is described in WO 00/58308. As a combined PDE3/PDE4 inhibitor, RPL554 has both antiinflammatory and bronchodilatory activity and is useful in the treatment of respiratory disorders such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The structure of RPL554 is shown below.

Owing to its applicability in the treatment of respiratory disorders, it is often preferable to administer RPL554 by inhalation. Franciosi et al. disclose a solution of RPL554 in a citrate-phosphate buffer at pH 3.2 (The Lancet: Respiratory Medicine 11/2013; l(9):714-27. DOI: 10.1016/S2213-2600(13)70187-5). The preparation of salts of RPL554 has not been described.
PATENT
http://www.google.ch/patents/WO2000058308A1?cl=en&hl=de
PATENT
http://www.google.ch/patents/WO2012020016A1?cl=en
U.S. Pat. No. 6,794,391, 7,378,424, and 7,105,663, which are each incorporated herein by reference, discloses compound RPL-554 (N-{2-[(2iT)-2-(mesityiimino)-9,10- dimethoxy-4-oxo-6,7-dihydro-2H-pyrimido[6,l-a]-isoquinolin-3 4H)-yl]ethyl}urea).
It would be beneficial to provide a composition of a stable polymorph of RPL-554, that has advanrtages over less stable polymorphs or amorphous forms, including
stability, compressibility, density, dissolution rates, increased potency or. lack toxicity.
| WO2000058308A1 * | Mar 29, 2000 | Oct 5, 2000 | Vernalis Limited | DERIVATIVES OF PYRIMIDO[6,1-a]ISOQUINOLIN-4-ONE |
| US6794391 | Sep 26, 2001 | Sep 21, 2004 | Vernalis Limited | Derivatives of pyrimido[6.1-a]isoquinolin-4-one |
| US7105663 | Feb 24, 2004 | Sep 12, 2006 | Rhinopharma Limited | Derivatives of pyrimido[6,1-a]isoquinolin-4-one |
| US7378424 | Feb 24, 2004 | May 27, 2008 | Verona Pharma Plc | Derivatives of pyrimido[6, 1-A]isoquinolin-4-one |
| WO2012020016A1 * | 9. Aug. 2011 | 16. Febr. 2012 | Verona Pharma Plc | Crystalline form of pyrimidio[6,1-a]isoquinolin-4-one compound |
| WO2014140647A1 | 17. März 2014 | 18. Sept. 2014 | Verona Pharma Plc | Drug combination |
| WO2014140648A1 | 17. März 2014 | 18. Sept. 2014 | Verona Pharma Plc | Drug combination |
| WO2015173551A1 * | 11. Mai 2015 | 19. Nov. 2015 | Verona Pharma Plc | New treatment |
| US8883857 | 8. März 2013 | 11. Nov. 2014 | Baylor College Of Medicine | Small molecule xanthine oxidase inhibitors and methods of use |
| US8883858 | 23. Juli 2014 | 11. Nov. 2014 | Baylor College Of Medicine | Small molecule xanthine oxidase inhibitors and methods of use |
| US8895626 | 23. Juli 2014 | 25. Nov. 2014 | Baylor College Of Medicine | Small molecule xanthine oxidase inhibitors and methods of use |
| US8987337 | 23. Juli 2014 | 24. März 2015 | Baylor College Of Medicine | Small molecule xanthine oxidase inhibitors and methods of use |
| US9061983 | 23. Juli 2014 | 23. Juni 2015 | Baylor College Of Medicine | Methods of inhibiting xanthine oxidase activity in a cell |
| US9062047 | 9. Aug. 2011 | 23. Juni 2015 | Verona Pharma Plc | Crystalline form of pyrimido[6,1-A] isoquinolin-4-one compound |
References
- Boswell-Smith V et al. The pharmacology of two novel long-acting phosphodiesterase 3/4 inhibitors, RPL554 [9,10-dimethoxy-2(2,4,6-trimethylphenylimino)-3-(n-carbamoyl-2-aminoethyl)-3,4,6,7-tetrahydro-2H-pyrimido[6,1-a]isoquinolin-4-one] and RPL565 [6,7-dihydro-2-(2,6-diisopropylphenoxy)-9,10-dimethoxy-4H-pyrimido[6,1-a]isoquinolin-4-one]. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006 Aug;318(2):840-8. PMID 16682455
- Nick Paul Taylor for FierceBiotech. October 1, 2015 Verona sets sights on PhIIb after COPD drug comes through early trial
- Turner MJ et al. The dual phosphodiesterase 3 and 4 inhibitor RPL554 stimulates CFTR and ciliary beating in primary cultures of bronchial epithelia. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2016 Jan 1;310(1):L59-70. PMID 26545902
- Jump up^ see US20040171828, identified in the citations of PMID 16682455
- ISIS Resources, PLC. August 23, 2006 Proposed Acquisition of Rhinopharma
REFERENCES
1: Calzetta L, Cazzola M, Page CP, Rogliani P, Facciolo F, Matera MG. Pharmacological characterization of the interaction between the dual phosphodiesterase (PDE) 3/4 inhibitor RPL554 and glycopyrronium on human isolated bronchi and small airways. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2015 Jun;32:15-23. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2015.03.007. Epub 2015 Apr 18. PubMed PMID: 25899618.
2: Franciosi LG, Diamant Z, Banner KH, Zuiker R, Morelli N, Kamerling IM, de Kam ML, Burggraaf J, Cohen AF, Cazzola M, Calzetta L, Singh D, Spina D, Walker MJ, Page CP. Efficacy and safety of RPL554, a dual PDE3 and PDE4 inhibitor, in healthy volunteers and in patients with asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: findings from four clinical trials. Lancet Respir Med. 2013 Nov;1(9):714-27. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(13)70187-5. Epub 2013 Oct 25. PubMed PMID: 24429275.
3: Wedzicha JA. Dual PDE 3/4 inhibition: a novel approach to airway disease? Lancet Respir Med. 2013 Nov;1(9):669-70. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(13)70211-X. Epub 2013 Oct 25. PubMed PMID: 24429260.
4: Calzetta L, Page CP, Spina D, Cazzola M, Rogliani P, Facciolo F, Matera MG. Effect of the mixed phosphodiesterase 3/4 inhibitor RPL554 on human isolated bronchial smooth muscle tone. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2013 Sep;346(3):414-23. doi: 10.1124/jpet.113.204644. Epub 2013 Jun 13. PubMed PMID: 23766543.
5: Gross N. The COPD pipeline XX. COPD. 2013 Feb;10(1):104-6. doi: 10.3109/15412555.2013.766103. PubMed PMID: 23413896.
6: Gross NJ. The COPD Pipeline XIV. COPD. 2012 Feb;9(1):81-3. doi: 10.3109/15412555.2012.646587. PubMed PMID: 22292600.
7: Boswell-Smith V, Spina D, Oxford AW, Comer MB, Seeds EA, Page CP. The pharmacology of two novel long-acting phosphodiesterase 3/4 inhibitors, RPL554 [9,10-dimethoxy-2(2,4,6-trimethylphenylimino)-3-(n-carbamoyl-2-aminoethyl)-3,4,6, 7-tetrahydro-2H-pyrimido[6,1-a]isoquinolin-4-one] and RPL565 [6,7-dihydro-2-(2,6-diisopropylphenoxy)-9,10-dimethoxy-4H-pyrimido[6,1-a]isoquino lin-4-one]. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006 Aug;318(2):840-8. Epub 2006 May 8. PubMed PMID: 16682455.
 |
|
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
|---|---|
|
N-{2-[(2E)-2-(mesitylimino)-9,10-dimethoxy-4-oxo-6,7-dihydro-2H-pyrimido[6,1-a]-isoquinolin-3(4H)-yl]ethyl}urea
|
|
| Identifiers | |
| PubChem | CID 9934746 |
| ChemSpider | 8110374 |
| Synonyms | 9,10-Dimethoxy-2-(2,4,6-trimethylphenylimino)-3-(N-carbamoyl-2-aminoethyl)-3,4,6,7-tetrahydro-2H-pyrimido[6,1-a]isoquinolin-4-one |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | C26H31N5O4 |
| Molar mass | 477.554 g/mol |
///////////RPL-554, LS-193,855, 298680-25-8, UNII:3E3D8T1GIX, RPL554, RPL 554, phase 2,
Cc3cc(C)cc(C)c3N=c2cc1-c(cc4OC)c(cc4OC)CCn1c(=O)n2CCNC(N)=O
P V SINDHU OF INDIA WINS BADMINTON GOLD IN RIO 2016 OLYMPICS