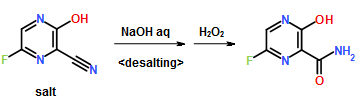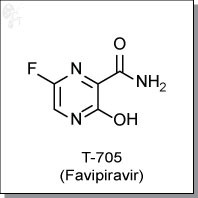
FAVIPIRAVIR
Toyama (Originator)
RNA-Directed RNA Polymerase (NS5B) Inhibitors
T-705 is an RNA-directed RNA polymerase (NS5B) inhibitor which has been filed for approval in Japan for the oral treatment of influenza A (including avian and H1N1 infections) and for the treatment of influenza B infection.
The compound is a unique viral RNA polymerase inhibitor, acting on viral genetic copying to prevent its reproduction, discovered by Toyama Chemical. In 2005, Utah State University carried out various studies under its contract with the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) and demonstrated that T-705 has exceptionally potent activity in mouse infection models of H5N1 avian influenza.
T-705 (Favipiravir) is an antiviral pyrazinecarboxamide-based, inhibitor of of the influenza virus with an EC90 of 1.3 to 7.7 uM (influenza A, H5N1). EC90 ranges for other influenza A subtypes are 0.19-1.3 uM, 0.063-1.9 uM, and 0.5-3.1 uM for H1N1, H2N2, and H3N2, respectively. T-705 also exhibits activity against type B and C viruses, with EC90s of 0.25-0.57 uM and 0.19-0.36 uM, respectively. (1) Additionally, T-705 has broad activity against arenavirus, bunyavirus, foot-and-mouth disease virus, and West Nile virus with EC50s ranging from 5 to 300 uM.
Studies show that T-705 ribofuranosyl triphosphate is the active form of T-705 and acts like purines or purine nucleosides in cells and does not inhibit DNA synthesis
In 2012, MediVector was awarded a contract from the U.S. Department of Defense’s (DOD) Joint Project Manager Transformational Medical Technologies (JPM-TMT) to further develop T-705 (favipiravir), a broad-spectrum therapeutic against multiple influenza viruses.
Several novel anti-influenza compounds are in various phases of clinical development. One of these, T-705 (favipiravir), has a mechanism of action that is not fully understood but is suggested to target influenza virus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. We investigated the mechanism of T-705 activity against influenza A (H1N1) viruses by applying selective drug pressure over multiple sequential passages in MDCK cells. We found that T-705 treatment did not select specific mutations in potential target proteins, including PB1, PB2, PA, and NP. Phenotypic assays based on cell viability confirmed that no T-705-resistant variants were selected. In the presence of T-705, titers of infectious virus decreased significantly (P < 0.0001) during serial passage in MDCK cells inoculated with seasonal influenza A (H1N1) viruses at a low multiplicity of infection (MOI; 0.0001 PFU/cell) or with 2009 pandemic H1N1 viruses at a high MOI (10 PFU/cell). There was no corresponding decrease in the number of viral RNA copies; therefore, specific virus infectivity (the ratio of infectious virus yield to viral RNA copy number) was reduced. Sequence analysis showed enrichment of G→A and C→T transversion mutations, increased mutation frequency, and a shift of the nucleotide profiles of individual NP gene clones under drug selection pressure. Our results demonstrate that T-705 induces a high rate of mutation that generates a nonviable viral phenotype and that lethal mutagenesis is a key antiviral mechanism of T-705. Our findings also explain the broad spectrum of activity of T-705 against viruses of multiple families.

favipiravir
Favipiravir also known as T-705 is an experimental anti-viral drug with activity against many RNA viruses. It, like some other experimental antiviraldrugs—T-1105 and T-1106, is apyrazinecarboxamide derivative. Favipiravir is active against influenza viruses, West Nile virus, yellow fever virus, foot-and-mouth disease virus as well as other flaviviruses, arenaviruses, bunyavirusesand alphaviruses.[1]
The mechanism of its actions is thought to be related to the selective inhibition of viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Favipiravir does not inhibit RNA of DNA synthesis in mammalian cells and is not toxic to them.[1]
- Furuta, Y.; Takahashi, K.; Shiraki, K.; Sakamoto, K.; Smee, D. F.; Barnard, D. L.; Gowen, B. B.; Julander, J. G.; Morrey, J. D. (2009). “T-705 (favipiravir) and related compounds: Novel broad-spectrum inhibitors of RNA viral infections”. Antiviral Research 82 (3): 95–102. doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2009.02.198. PMID 19428599. edit

- WO 2000010569
- WO 2008099874
- WO 201009504
- WO 2010104170
- WO 2012063931


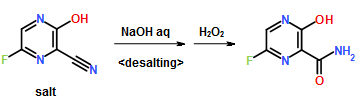
……………………………………………………………………………………
Influenza virus is a central virus of the cold syndrome, which has attacked human being periodically to cause many deaths amounting to tens millions. Although the number of deaths shows a tendency of decrease in the recent years owing to the improvement in hygienic and nutritive conditions, the prevalence of influenza is repeated every year, and it is apprehended that a new virus may appear to cause a wider prevalence.
For prevention of influenza virus, vaccine is used widely, in addition to which low molecular weight substances such as Amantadine and Ribavirin are also used
……………………………….

Synthesis of Favipiravir
ZHANG Tao1, KONG Lingjin1, LI Zongtao1,YUAN Hongyu1, XU Wenfang2*
(1. Shandong Qidu PharmaceuticalCo., Ltd., Linzi 255400; 2. School of Pharmacy, Shandong University, Jinan250012)
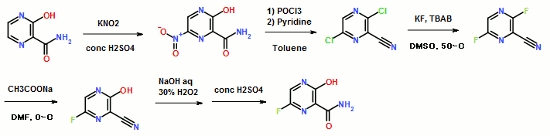
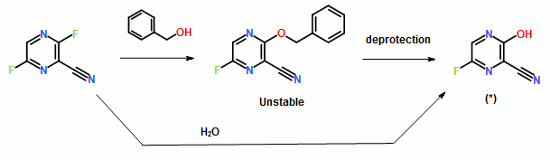
ABSTRACT: Favipiravir was synthesized from3-amino-2-pyrazinecarboxylic acid by esterification, bromination with NBS,diazotization and amination to give 6-bromo-3-hydroxypyrazine-2-carboxamide,which was subjected to chlorination with POCl3, fluorination with KF, andhydrolysis with an overall yield of about 22%.
………………………………..
US6787544

…………………
EP2192117

Example 1-1
To a 17.5 ml N,N-dimethylformamide solution of 5.0 g of 3,6-difluoro-2-pyrazinecarbonitrile, a 3.8 ml water solution of 7.83 g of potassium acetate was added dropwise at 25 to 35° C., and the solution was stirred at the same temperature for 2 hours. 0.38 ml of ammonia water was added to the reaction mixture, and then 15 ml of water and 0.38 g of active carbon were added. The insolubles were filtered off and the filter cake was washed with 11 ml of water. The filtrate and the washing were joined, the pH of this solution was adjusted to 9.4 with ammonia water, and 15 ml of acetone and 7.5 ml of toluene were added. Then 7.71 g of dicyclohexylamine was added dropwise and the solution was stirred at 20 to 30° C. for 45 minutes. Then 15 ml of water was added dropwise, the solution was cooled to 10° C., and the precipitate was filtered and collected to give 9.44 g of dicyclohexylamine salt of 6-fluoro-3-hydroxy-2-pyradinecarbonitrile as a lightly yellowish white solid product.
1H-NMR (DMSO-d6) δ values: 1.00-1.36 (10H, m), 1.56-1.67 (2H, m), 1.67-1.81 (4H, m), 1.91-2.07 (4H, m), 3.01-3.18 (2H, m), 8.03-8.06 (1H, m), 8.18-8.89 (1H, broad)
Example 1-2
4.11 ml of acetic acid was added at 5 to 15° C. to a 17.5 ml N,N-dimethylformamide solution of 5.0 g of 3,6-difluoro-2-pyrazinecarbonitrile. Then 7.27 g of triethylamine was added dropwise and the solution was stirred for 2 hours. 3.8 ml of water and 0.38 ml of ammonia water were added to the reaction mixture, and then 15 ml of water and 0.38 g of active carbon were added. The insolubles were filtered off and the filter cake was washed with 11 ml of water. The filtrate and the washing were joined, the pH of the joined solution was adjusted to 9.2 with ammonia water, and 15 ml of acetone and 7.5 ml of toluene were added to the solution, followed by dropwise addition of 7.71 g of dicyclohexylamine. Then 15 ml of water was added dropwise, the solution was cooled to 5° C., and the precipitate was filtered and collected to give 9.68 g of dicyclohexylamine salt of 6-fluoro-3-hydroxy-2-pyrazinecarbonitrile as a slightly yellowish white solid product.
Examples 2 to 5
The compounds shown in Table 1 were obtained in the same way as in Example 1-1.
| TABLE 1 |
|
|
|
|
| Example No. |
Organic amine |
Example No. |
Organic amine |
|
| 2 |
Dipropylamine |
4 |
Dibenzylamine |
| 3 |
Dibutylamine |
5 |
N-benzylmethylamine |
|
Dipropylamine salt of 6-fluoro-3-hydroxy-2-pyrazinecarbonitrile
1H-NMR (DMSO-d6) 6 values: 0.39 (6H, t, J=7.5 Hz), 1.10 (4H, sex, J=7.5 Hz), 2.30-2.38 (4H, m), 7.54 (1H, d, J=8.3 Hz)
Dibutylamine salt of 6-fluoro-3-hydroxy-2-pyrazinecarbonitrile
1H-NMR (DMSO-d6) 6 values: 0.36 (6H, t, J=7.3 Hz), 0.81 (4H, sex, J=7.3 Hz), 0.99-1.10 (4H, m), 2.32-2.41 (4H, m), 7.53 (1H, d, J=8.3 Hz)
Dibenzylamine salt of 6-fluoro-3-hydroxy-2-pyrazinecarbonitrile
1H-NMR (DMSO-d6) δ values: 4.17 (4H, s), 7.34-7.56 (10H, m), 8.07 (1H, d, J=8.3 Hz)
N-benzylmethylamine salt of 6-fluoro-3-hydroxy-2-pyrazinecarbonitrile
1H-NMR (DMSO-d6) δ values: 2.57 (3H, s), 4.14 (2H, s), 7.37-7.53 (5H, m), 8.02-8.08 (1H, m)
Preparation Example 1
300 ml of toluene was added to a 600 ml water solution of 37.5 g of sodium hydroxide. Then 150 g of dicyclohexylamine salt of 6-fluoro-3-hydroxy-2-pyrazinecarbonitrile was added at 15 to 25° C. and the solution was stirred at the same temperature for 30 minutes. The water layer was separated and washed with toluene, and then 150 ml of water was added, followed by dropwise addition of 106 g of a 30% hydrogen peroxide solution at 15 to 30° C. and one-hour stirring at 20 to 30° C. Then 39 ml of hydrochloric acid was added, the seed crystals were added at 40 to 50° C., and 39 ml of hydrochloric acid was further added dropwise at the same temperature. The solution was cooled to 10° C. the precipitate was filtered and collected to give 65.6 g of 6-fluoro-3-hydroxy-2-pyrazinecarboxamide as a slightly yellowish white solid.
1H-NMR (DMSO-d6) δ values: 8.50 (1H, s), 8.51 (1H, d, J=7.8 Hz), 8.75 (1H, s), 13.41 (1H, s)
………………….
jan 2014
Investigational flu treatment drug has broad-spectrum potential to fight multiple viruses
First patient enrolled in the North American Phase 3 clinical trials for investigational flu treatment drug
BioDefense Therapeutics (BD Tx)—a Joint Product Management office within the U.S. Department of Defense (DoD)—announced the first patient enrolled in the North American Phase 3 clinical trials for favipiravir (T-705a). The drug is an investigational flu treatment candidate with broad-spectrum potential being developed by BD Tx through a contract with Boston-based MediVector, Inc.
Favipiravir is a novel, antiviral compound that works differently than anti-flu drugs currently on the market. The novelty lies in the drug’s selective disruption of the viralRNA replication and transcription process within the infected cell to stop the infection cycle.
“Favipiravir has proven safe and well tolerated in previous studies,” said LTC Eric G. Midboe, Joint Product Manager for BD Tx. “This first patient signifies the start of an important phase in favipiravir’s path to U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval for flu and lays the groundwork for future testing against other viruses of interest to the DoD.”
In providing therapeutic solutions to counter traditional, emerging, and engineered biological threats, BD Tx chose favipiravir not only because of its potential effectiveness against flu viruses, but also because of its demonstrated broad-spectrum potential against multiple viruses. In addition to testing favipiravir in the ongoing influenzaprogram, BD Tx is testing the drug’s efficacy against the Ebola virus and other viruses considered threats to service members. In laboratory testing, favipiravir was found to be effective against a wide variety of RNA viruses in infected cells and animals.
“FDA-approved, broad-spectrum therapeutics offer the fastest way to respond to dangerous and potentially lethal viruses,” said Dr. Tyler Bennett, Assistant Product Manager for BD Tx.
MediVector is overseeing the clinical trials required by the FDA to obtain drug licensure. The process requires safety data from at least 1,500 patients treated for flu at the dose and duration proposed for marketing of the drug. Currently, 150 trial sites are planned throughout the U.S.
SOURCE BioDefense Therapeutics
Efficient synthesis of 3H,3’H-spiro[benzofuran-2,1′-isobenzofuran]-3,3′-dione as novel skeletons specifically for influenza virus type B inhibition.
Malpani Y, Achary R, Kim SY, Jeong HC, Kim P, Han SB, Kim M, Lee CK, Kim JN, Jung YS.
Eur J Med Chem. 2013 Apr;62:534-44. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2013.01.015. Epub 2013 Jan 29.
| US3631036 * |
Nov 4, 1969 |
Dec 28, 1971 |
American Home Prod |
5-amino-2 6-substituted-7h-pyrrolo(2 3-d) pyrimidines and related compounds |
| US3745161 * |
Apr 20, 1970 |
Jul 10, 1973 |
Merck & Co Inc |
Phenyl-hydroxy-pyrazine carboxylic acids and derivatives |
| US4404203 * |
May 14, 1981 |
Sep 13, 1983 |
Warner-Lambert Company |
Substituted 6-phenyl-3(2H)-pyridazinones useful as cardiotonic agents |
| US4545810 * |
Mar 25, 1983 |
Oct 8, 1985 |
Sds Biotech Corporation |
Herbicidal and plant growth regulant diphenylpyridazinones |
| US4565814 * |
Jan 18, 1984 |
Jan 21, 1986 |
Sanofi |
Pyridazine derivatives having a psychotropic action and compositions |
| US4661145 * |
Sep 20, 1984 |
Apr 28, 1987 |
Rohm And Haas Company |
Plant growth regulating 1-aryl-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo(thio)-pyridazines |
| US5420130 |
May 16, 1994 |
May 30, 1995 |
Synthelabo |
2-aminopyrazine-5-carboxamide derivatives, their preparation and their application in therapeutics |
| US5459142 * |
Aug 23, 1993 |
Oct 17, 1995 |
Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. |
Pyrazinyl and piperazinyl substituted pyrazine compounds |
| US5597823 |
Jun 5, 1995 |
Jan 28, 1997 |
Abbott Laboratories |
Tricyclic substituted hexahydrobenz [e]isoindole alpha-1 adrenergic antagonists |
| US6159980 * |
Sep 15, 1997 |
Dec 12, 2000 |
Dupont Pharmaceuticals Company |
Pyrazinones and triazinones and their derivatives thereof |
| EP0023358A1 * |
Jul 28, 1980 |
Feb 4, 1981 |
Rohm And Haas Company |
Process for the preparation of pyridazine derivatives |
| GB1198688A |
|
|
|
Title not available |
| HU9401512A |
|
|
|
Title not available |
| JPH09216883A * |
|
|
|
Title not available |
| JPS5620576A |
|
|
|
Title not available |

THANKS AND REGARD’S
DR ANTHONY MELVIN CRASTO Ph.D
GLENMARK SCIENTIST , NAVIMUMBAI, INDIA
did you feel happy, a head to toe paralysed man’s soul in action for you round the clock
need help, email or call me
web link
I was paralysed in dec2007, Posts dedicated to my family, my organisation Glenmark, Your readership keeps me going and brings smiles to my family