Catal. Sci. Technol., 2016, Advance Article
DOI: 10.1039/C6CY00855K, Communication
DOI: 10.1039/C6CY00855K, Communication
Nicholas J. Weise, Syed T. Ahmed, Fabio Parmeggiani, Elina Siirola, Ahir Pushpanath, Ursula Schell, Nicholas J. Turner
An industrial-scale method employing a phenylalanine ammonia lyase enzyme
An industrial-scale method employing a phenylalanine ammonia lyase enzyme
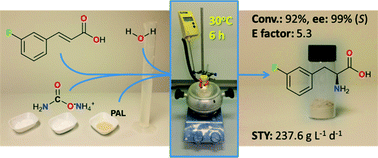
Intensified biocatalytic production of enantiomerically pure halophenylalanines from acrylic acids using ammonium carbamate as the ammonia source
*Corresponding authors
aManchester Institute of Biotechnology & School of Chemistry, University of Manchester, 131 Princess Street, Manchester, UK
E-mail: nicholas.turner@manchester.ac.uk
E-mail: nicholas.turner@manchester.ac.uk
bJohnson Matthey Catalysts and Chiral Technologies, 28 Cambridge Science Park, Milton Road, Cambridge, UK
Catal. Sci. Technol., 2016, Advance Article
DOI: 10.1039/C6CY00855K
SEE
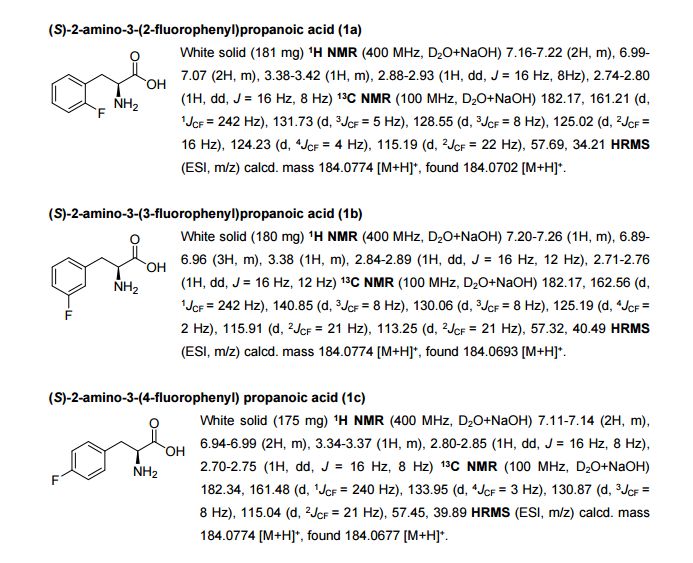
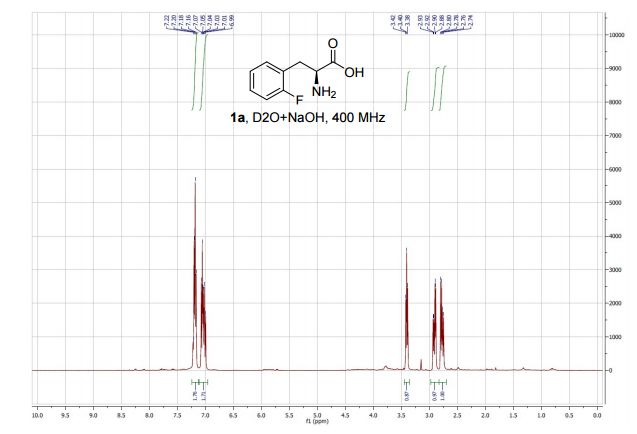
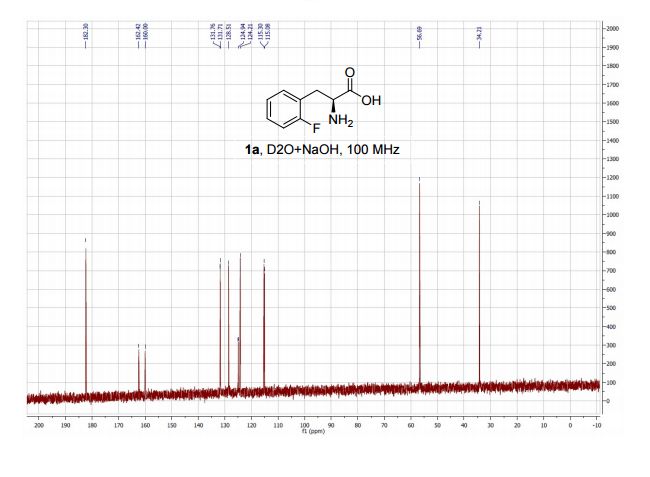
An intensified, industrially-relevant strategy for the production of enantiopure halophenylalanines has been developed using the novel combination of a cyanobacterial phenylalanine ammonia lyase (PAL) and ammonium carbamate reaction buffer. The process boasts STYs up to >200 g L−1 d−1, ees ≥ 98% and simplified catalyst/reaction buffer preparation and work up.
///////Intensified, biocatalytic production, enantiomerically pure, halophenylalanines, acrylic acids, ammonium carbamate, ammonia source