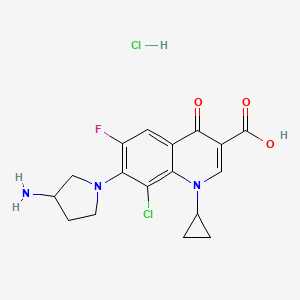
Clinafloxacin
7-(3-Aminopyrrolidin-1-yl)-8-chloro-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid
7-(3-Amino-1-pyrrolidinyl)-8-chloro-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-l,4-dihydro-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid
(±)-7-(3-Amino-1-pyrrolidinyl)-8-chloro-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid
105956-99-8 cas no
Clinafloxacin (INN) is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic. Its use is associated with phototoxicity and hypoglycaemia.[1]
Clinafloxacin is a novel quinolone with wide activity against the plethora of microorganisms encountered in intraabdominal infections.
Clinafloxacin is a chlorofluoroquinolone with excellent bioavailability and activity against gram-positive, gram-negative, and anaerobic pathogens . Typical MICs for α-streptococci are 0.06–0.12 µg/mL . MIC90 values for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) average 1.0 µg/mL. The MIC90 for enterococci is typically 0.5 µg/mL . Both intravenous and oral formulations have been developed . Several studies have demonstrated the efficacy of clinafloxacin monotherapy for serious infections Clinafloxacin was also active in animal models of endocarditis, including endocarditis due to ciprofloxacin-resistant S. aureus infection .


- Example 28 7-(3-Amino-1-pyrrolidinyl)-8-chloro-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-l,4-dihydro-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid
-
A mixture of 8-chloro-1-cyclopropyl-6,7-difluoro-1,4-di- hydro-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid (0.6 g), anhydrous acetonitrile (6 ml), 3-aminopyrrolidine (0.35 g) and DBU (0.31 g) was refluxed for an hour. Then, 3-aminopyrrolidine (0.2 g) was more added and further refluxed for 2 hours. After cooling, the resulting precipitate was collected by filtration, dissolved in water (9 ml) containing sodium hydroxide (0.12 g) and neutralized with acetic acid. The resulting precipitate was collected by filtration and washed with water and acetonitrile successively to give the title compound (0.52 g) as colorless powder, mp 237-238 °C (decompd.).
-
Analysis (%) for C17H17ClFN3O3·H2O, Calcd. (Found): C, 53.20 (52.97); H, 4.99 (4.62); N, 10.95 (10.83).
Example 29 7-(3-Amino-1-pyrrolidinyl)-8-chloro-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-l,4-dihydro-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid hydrochloride
-
To a suspension of 7-(3-amino-1-pyrrolidinyl)-8-chloro-1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid (100 mg) in ethanol (2 ml) was added 0.2 ml of ethanol solution of hydrogen chloride (7.0 mmol HC1/ml) and then the mixture was concentrated. The resulting residue was recrystallized from methanol to give the title compound (79 mg) as light yellow prisms, mp 263-265 °C (decompd.).
-
Analysis (%) for C17H17ClFN3O3.HCl, Calcd. (Found): C, 50.76 (50.50); H, 4.51 (4.44); N, 10.45 (10.38).
…………………..
J. Med. Chem., 23, 1358 (1980)
-
The compound wherein R3 is hydrogen, namely 3-pyrrolidinemethanamine, has been reported in J. Org. Chem., 26, 4955 (1961).
References
- Rubinstein, E. (2001). “History of quinolones and their side effects.”. Chemotherapy. 47 Suppl 3: 3–8; discussion 44–8.doi:10.1159/000057838. PMID 11549783.
| EP0106489A2 * | Sep 6, 1983 | Apr 25, 1984 | Warner-Lambert Company | Antibacterial agents |
| EP0153163A2 * | Feb 15, 1985 | Aug 28, 1985 | Warner-Lambert Company | 7-Substituted-1-cyclopropyl-6,8-difluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic acids; 7-substituted-1-cyclopropyl-1,4-dihydro-6-fluoro-4-oxo-1,8-naphthyridine-3-carboxylic acids; their derivatives; and a process for preparing the compounds |
| BE899399A1 * | Title not available | |||
| GB2057440A * | Title not available |
| Examples of | ||
| reported trade | ||
| names for products | ||
| containing the 6- | ||
| 6-Fluoroquinolin- | fluoroquinolin- | |
| 4(1H)-one | 4(1H)-one | Structure |
| amifloxacin | ||
| balofloxacin | ||
| ciprofloxacin | Cipro®, Ciprobay, & Ciproxin | |
| clinafloxacin | ||
| danofloxacin | Advocin & Advocid | |
| difloxacin | Dicural® & Vetequinon | |
| enrofloxacin | Baytril® | |
| fleroxacin | Megalone | |
| flumequine | Flubactin | |
| garenoxacin | ||
| gatifloxacin | Tequin® & Zymar® | |
| grepafloxacin | Raxar | |
| ibafloxacin | ||
| levofloxacin | Levaquin®, Gatigol, Tavanic, Lebact, Levox, & Cravit | |
| lomefloxacin | Maxaquin® | |
| marbofloxacin | Marbocyl® & Zenequin | |
| moxifloxacin | Avelox® & Vigamox® | |
| nadifloxacin | Acuatin, Nadoxia, & Nadixa | |
| norfloxacin | Noroxin®, Lexinor, Quinabic, & Janacin | |
| ofloxacin | Floxin®, Oxaldin, & Tarivid | |
| orbifloxacin | Orbax® & Victas | |
| pazufloxacin | ||
| pefloxacin | ||
| pradofloxacin | ||
| prulifloxacin | ||
| rufloxacin | Uroflox | |
| sarafloxacin | Floxasol, Saraflox, Sarafin | |
| sitafloxacin | ||
| sparfloxacin | Zagam | |
| temalioxacin | Omniflox | |
| enoxacin | Penetrex & Enroxil | |
| gemifloxacin | Factive | |
| tosufloxacin | ||
| trovafloxacin | Trovan | |