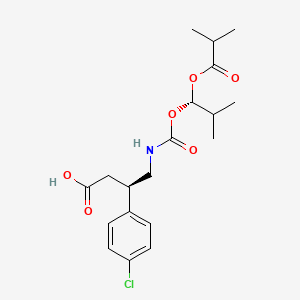
Arbaclofen placarbil
(3R)-3-(4-chlorophenyl)-4-[[(1S)-2-methyl-1-(2-methylpropanoyloxy)propoxy]carbonylamino]butanoic acid
NDA filed
A GABA (B) receptor agonist potentially for the treatment of muscle spasticity.

AGI-006; STX-209; OS-440
CAS No. 69308-37-8 free
847353-30-4 placarbil
Arbaclofen placarbil (ar-bac-loe-fen pla-kar-bil, also known as XP19986) is a prodrug of R–baclofen. Arbaclofen placarbil possesses more favorable pharmacokinetic profile than baclofen, with less fluctuations in plasma drug levels. It was being developed as a potential treatment for patients with GERD and spasticity due to multiple sclerosis; however, in May 2013 XenoPort announced the termination of development because of unsuccessful results in phase III clinical trials.[1]
Arbaclofen Placerbil is a prodrug of Arbaclofen, which is a selective gamma-amino-butyric acid type B receptor agonist and the R-enantiomer of baclofen. It was discovered, and has been patented by XenoPort as a new chemical entity with an improved pharmacokinetic profile compared to baclofen, which allows for sustained release properties. ArbaclofenPlacerbil was believed to have therapeutic potential in treating gastroesophogeal reflux disease (GERD) and plasticity; however due to discouraging clinical trial results, the drug was abandoned by XenoPort in 2011 for the treatment of GERD. On May 20th, 2013, XenoPort announced plans to terminate the development of Arbaclofen Placerbil for the treatment of multiple sclerosis.

Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a behaviorally defined disorder which has increased in prevalence over the last two decades. Despite decades of research, no effective treatment is currently available. Animal models, as well as other lines of evidence, point to abnormalities in the balance of cortical excitation to inhibition in individuals with ASD, with this imbalance resulting in an overall increase in cortical excitation. To reduce cortical excitatory glutamate pathways, arbaclofen, a selective agonist of the gamma aminobutyric acid receptor type B, has been developed. This article reviews the evidence for this treatment for ASD using a systematic review methodology. Overall, a systematic search of the literature revealed 148 relevant references with the majority of these being review papers or news items that mentioned the potential promise of arbaclofen. Five original studies were identified, four of which used STX209, a form of arbaclofen developed by Seaside Therapeutics, Inc., and one which used R-baclofen. In an animal model, treatment of Fragile X, a genetic disease with ASD features, demonstrated a reversal of behavioral, neurological, and neuropathological features associated with the disease. One double-blind, placebo-controlled study treated children and adults with Fragile X. Results from this study were promising, with signs of improvement in social function, especially in the most severely socially impaired. Two studies, one open-label and one double-blind, placebo-controlled, were conducted in children, adolescents, and young adults with ASD. These studies suggested some improvements in socialization, although the effects were limited and may have been driven by individuals with ASD that were higher-functioning. These studies and others that have used arbaclofen for the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux suggest that arbaclofen is safe and well-tolerated. Clearly, further clinical studies are needed in order to refine the symptoms and characteristics of children with ASD that are best treated with arbaclofen.
Fig. 1.
The Structures of R-baclofen (1), arbaclofen placarbil (2), R-baclofen lactam (3), and the potential γ-hydroxy metabolite of R-baclofen (4).
References
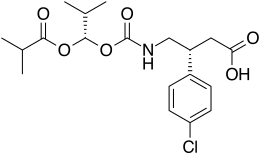 |
|
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
|---|---|
|
(3R)-3-(4-chlorophenyl)-4-[[[(1S)-2-methyl-1-[(2-methylpropanoyl)oxy]propoxy]carbonyl]amino]butanoic acid
|
|
| Clinical data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | 847353-30-4 |
| ATC code | none |
| PubChem | CID 11281011 |
| ChemSpider | 9456008 |
| KEGG | D08861 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL2107312 |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | C19H26ClNO6 |
| Molar mass | 399.86 g/mol |
///////AGI-006, STX-209, OS-440, Arbaclofen, autism spectrum disorder, Fragile X, gamma-aminobutyric acid, arbaclofen, R-baclofen, STX209
CC(C)[C@@H](OC(=O)C(C)C)OC(=O)NC[C@H](CC(=O)O)C1=CC=C(C=C1)Cl