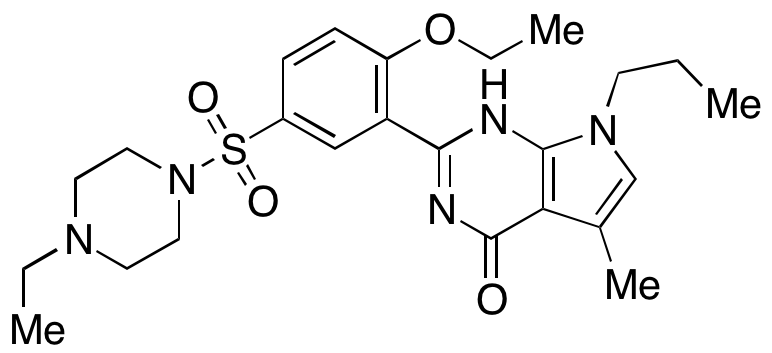
Yonkenafil
Mw 487.61, MF C₂₄H₃₃N₅O₄S,
Cas 804518-63-6
4H-Pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-one, 2-[2-ethoxy-5-[(4-ethyl-1-piperazinyl)sulfonyl]phenyl]-3,7-dihydro-5-methyl-7-propyl-,
2- [2-ethoxy –5- (4 – ethylpiperazine -1– sulfonyl) phenyl] -5 – methyl – 7 – n-Propyl-3 7 – PYRROLINE [2, 3 – d] pyrimidin – 4 – one
Phase2 Erectile dysfunction
扬子江药业 (Originator), 天士力制药 (Originator)
phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) inhibitor
- Originator Tasly Pharmaceutical Group; Yangtze River Pharmaceutical Group
- Class Erectile dysfunction therapies
- Mechanism of Action Type 5 cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase inhibitors



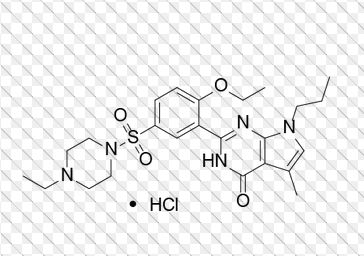
Yonkenafil Hydrochloride
| Molecular Weight | 524.08 | |
| Formula | C24H33N5O4S • HCl |
804518-63-6 (Yonkenafil);
804519-64-0 (Yonkenafil Hydrochloride);
4H-Pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-one, 2-[2-ethoxy-5-[(4-ethyl-1-piperazinyl)sulfonyl]phenyl]-3,7-dihydro-5-methyl-7-propyl-, hydrochloride (1:1)
2- [2-ethoxy –5- (4 – ethylpiperazine -1– sulfonyl) phenyl] -5 – methyl – 7 – n-Propyl-3 7 – PYRROLINE [2, 3 – d] pyrimidin – 4 – one
Yonkenafil hydrochloride, useful for treating erectile dysfunction and other PDE-5 mediated diseases eg female sexual dysfunction, benign prostatic hyperplasia, hypertension, allergic asthma, bronchitis, glaucoma, gastrointestinal motility disorders or Alzheimer’s Ydisease.
Yangtze River Pharmaceutical, under license from Jilin University, is developing yonkenafil (appears to be first disclosoed in WO2004108726), a PDE-5 inhibitor, for treating male erectile dysfunction.
In June 2016, yonkenafil was reported to be in phase 2 clinical development.
Yonkenafil hydrochloride is in phase II clinical trials for the treatment of erectile dysfunction (ED).
The compound was co-developed by Yangtze River Pharmaceutical and Tianjin Tasly Pharm.
Yonkenafil is a novel phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) inhibitor. Here we evaluated the effect of yonkenafil on ischemic injury and its possible mechanism of action. Male Sprague-Dawley rats underwent middle cerebral artery occlusion, followed by intraperitoneal or intravenous treatment with yonkenafil starting 2h later. Behavioral tests were carried out on day 1 or day 7 after reperfusion. Nissl staining, Fluoro-Jade B staining and electron microscopy studies were carried out 24h post-stroke, together with an analysis of infarct volume and severity of edema. Levels of cGMP-dependent Nogo-66 receptor (Nogo-R) pathway components, hsp70, apaf-1, caspase-3, caspase-9, synaptophysin, PSD-95/neuronal nitric oxide synthases (nNOS), brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF)/tropomyosin-related kinase B (TrkB) and nerve growth factor (NGF)/tropomyosin-related kinase A (TrkA) were also measured after 24h. Yonkenafil markedly inhibited infarction and edema, even when administration was delayed until 4h after stroke onset. This protection was associated with an improvement in neurological function and was sustained for 7d. Yonkenafil enlarged the range of penumbra, reduced ischemic cell apoptosis and the loss of neurons, and modulated the expression of proteins in the Nogo-R pathway. Moreover, yonkenafil protected the structure of synapses and increased the expression of synaptophysin, BDNF/TrkB and NGF/TrkA. In conclusion, yonkenafil protects neuronal networks from injury after stroke.

Erectile dysfunction (Erectile dysfunction, ED) refers to the duration can not be achieved, and (or) maintain an erection sufficient for satisfactory sexual life. ED can be divided according to different causes psychogenic, organic and mixed three categories, which are closely related to the aging process, but it is not inevitable disease with age.
The primary risk factors for ED include: high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, coronary and peripheral vascular disease, spinal cord injury or pelvic organs or surgery. According to statistics worldwide about 150 million men suffer from varying degrees of ED, 2025 the number of patients will double. More ED treatment options, such as oral medications phosphodiesterase 5 (PDE5) inhibitors, dopaminergic activator, a receptor blocker, intracavernous injection therapy, vacuum devices treatment, penile prosthesis treatment Wait. Wherein the selective phosphodiesterase 5 (PDE5) inhibitors are the most sophisticated study based on ED treatment, clinical treatment for ED is the first-line drugs. Has now approved the listing of these drugs were five sildenafil (Sildenafil), Tadalafil (Tadalafil), vardenafil (Vardenafil), to that of non-black (Udenafil) and Miro that non-( Mirodenafil).
In 2004 the Chinese patent CN03142399. X discloses a series pyrrolopyrimidine ketone compound of the structure and for the treatment of sexual dysfunction in animals, including humans, in particular male erectile dysfunction and TOE5 function-related diseases use; wherein the compound 1-HC1, i.e. 2- [2_ ethoxy-5- (4-ethyl-piperazine-1-sulfonyl) phenyl] -5-methyl-7-n-propyl -3 , 7-dihydro-pyrrolo [2, 3-d] pyrimidine-4-one monohydrochloride salt has been used as CN03142399. X Example features are disclosed compound named hydrochloride that non-gifted grams. This patent only to the preparation of the compounds have been described
PATENT
WO2004108726
http://www.google.co.in/patents/WO2004108726A1?cl=en
Example 1
Preparation of 2-[2-ethoxyl-5-(4-ethylpiperazinyl-1-sulfonyl)phenyl] -5-methyl-7-n-propyl-3,7-dihydropyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-one, its monohydrochloride and dihydrochloride
Route of synthesis
-
- (1a)2-amino-3-cyano-4-methylpyrrole;
- (1b)N-propyl-2-amino-3-cyano-4-methylpyrrole;
- (2)2-ethoxylbenzoyl chloride;
- (3a)N-(3-cyano-4-methyl-1H-pyrrol-2-yl)-2-ethoxylbenzamide;
- (3b)N-(3-cyano-4-methyl-1-n-propyl-1H-pyrrol-2-yl)-2-ethoxylbenzami de;
- (4a) 2-(2-ethoxylbenzamido)-4-methyl-1H-pyrrolo-3-formamide;
- (4b) 2-(2-ethoxylbenzamido)-4-methyl-1-n-propyl-1H-pyrrolo-3-formamide;
- (5) 2-(2-ethoxylphenyl)-5-methyl-3,7-dihydro-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin -4-one;
- (6)2-(2-ethoxylphenyl)-5-methyl-7-n-propyl-3,7-dihydropyrrolo[2,3-d ]pyrimidin-4-one;
- (7)4-ethoxyl-3-(5-methyl-4-oxy-7-n-propyl-3,7-dihydropyrrolo[2,3-d] pyrimidin-2-yl)benzenesulfonyl chloride;
- (8)2-[2-ethoxyl-5-(4-ethylpiperazinyl-1-sulfonyl)phenyl]-5-methyl-7 -n-propyl-3,7-dihydropyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-one.
Preparation 1N-(3-cyano-4-methyl-1H-pyrrol-2-yl)-2-ethoxylbenzamide (3a) and N-(3-cyano-4-methyl-1-n-propyl-1H-pyrrol-2-yl)-2-ethoxylbenzamide (3b)
2-ethoxyl benzoic acid (10.0g, 60.2mmol) was added into thionyl chloride (20ml), and the mixture was refluxed with agitation for 40 minutes, and the excess amount of thionyl chloride was evaporated under reduced pressure. The residual was dissolved into dichloromethane (150ml). Within 30 minutes and being stirred on ice bath, the afore-obtained solution of 2-ethoxyl benzoyl chloride was dropped into the compound (1a) (7.0g, 56.8mmol) dissolved in tetrahydrofuran (80ml) and triethylamine (8.5ml, 61.0mmol). After completion, the mixture was stirred for 1 hour at 0°C . After being washed with water and filtrated with diatomaceous earth, the reaction solution was mixed with 20g of silica gel and evaporated to dryness. The resulting residual was eluted with dichloromethane by using silica gel(80g) column to obtain 7.5g of solid product (3a) with the yield of 48%. Furthermore, the sample for analysis was prepared by column chromatography (developing agent: dichloromethane: n-hexane=1:2) and recrystallization (dichloromethane: n-hexane=1:5).
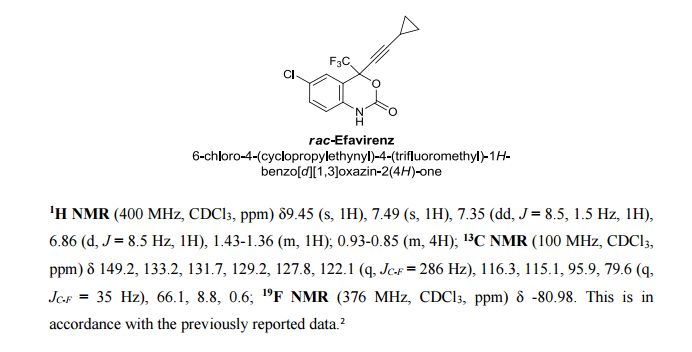
mp 183~184°C (sublimation 162°C);\
IR (cm-1) : 3326, 3309, 2981, 2938, 2915, 2854, 2208, 1647, 1593, 1471, 1309, 1302, 1232, 1039, 923, 727, 655, 648;1H NMR (CDCl3) : δ 1.70 (t, J=7.0Hz, 3H), 2.15 (s, 3H), 4.32 (q, J=7.0Hz, 2H), 6.24 (s, 1H), 7.04 (d, 1H), 7.10 (m, 1H), 7.51 (dd, 1H), 8.20 (dd, J=7.9 and 1.8Hz, 1H), 10.69 (brs, 1H), 10.80 (s, 1H);13CNMR (CDCl3) : δ (CH3) 10.6, 15.0; (CH2) 65.7; (CH) 110.3, 112.3, 121.4132.1, 134.2; (C) 78.7, 115.6, 119.2, 119.4, 136.7, 157.0, 163.2;
MS (ES+) : m/z 287 (M+NH4) .
Elemental analysis (C15H15N3O2) : C 66.90%; H 5.61%; N 15.60%; 0 11.88%. The compound (3b) was prepared from compound (1b) according to the above-mentioned method with the yield of 41%.
mp 58~61°C;
IR (cm-1) : 3596, 3336, 2969, 2937, 2877, 2216, 1676, 1658, 1603, 1571, 1537, 1475, 1431, 1292, 1232, 1122, 1037, 927, 789, 752, 577;1H NMR (CDCl3): δ 0.88 (t, J=7.4Hz, 3H), 1.58 (t, J=7.0Hz, 3H), 1.75(m, 2H), 2.16 (s, 3H), 3.73 (t, J=7.4Hz, 2H),4.30 (q, J=7.0Hz, 2H), 6.36 (s, 1H), 7.04 (d, 1H), 7.11 (m, 1H), 7.48 (dd, 1H), 8.23 (dd, J=7.9 and 1.8Hz, 1H), 9.62 (brs, 1H) ;13C NMR (CDCl3) : δ (CH3) 11.1, 14.8; (CH2) 23.6, 48.3, 65.2; (CH) 112.5,117.0, 121.3, 132.5, 134.1; (C) 89.2, 115.6, 119.8, 120.5, 131.2, 157.1, 165.0;MS (ES+): m/z 329 (M+NH4).
Preparation 2
2-(2-ethoxylbenzamido)-4-methyl-1H-pyrrolo-3-formamide (4a) and 2-(2-ethoxylbenzamido)-4-methyl-1-n-propyl-1H-pyrrolo-3-formamide(4 b);
A mixture of N-(3-cyano-4-methyl-1H-pyrrol-2-yl)-2-ethoxylbenzamide(3a) (2.00g, 7.44mmol) or N-(3-cyano-4-methyl-1-n-propyl-1H-pyrrol-2-yl)-2 -ethoxylbenzamide(3b) (2.30g, 7.44mmol) of preparation 1 and 85% phosphoric acid (14.8ml) was stirred for 20 minutes at 130°C, cooled and poured into crushed ice (80g). The precipitations were filtrated and dried to give dark red solid of compound (3a) or (3b) with the yield of 80%. The product(3a) and (3b) of this step may be directly used for the next step without further purification.
Preparation 32-(2-ethxoylphenyl)-5-methyl-3,7-dihydropyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-one(5) and 2-(2-ethoxylphenyl)-5-methyl-7-n-propyl -3,7-dihydropyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-one(6)
A mixture of 2-(2-ethoxylbenzamido)-4-methyl-1H-pyrrolo-3-formamide (4a) (7.0g, 25.5mmol) of preparation 2 and dimethyl cyclohexylamine (20ml) was refluxed with agitation for 11 hours in N,N-dimethyl formamide (100ml). After evaporation the solvent by distillation under reduced pressure, the residual was extracted with dichloromethane, and the dichloromethane extraction was washed with water. the resultant extraction was dried with anhydrous sodium sulfate. n-hexane (80ml) was added into the residual and ground to give product (5) (6.0g) by filtration with the yield of 91%.
mp 219~221°C
IR (cm-1) : 3187, 3114, 3062, 2978, 2923, 1658, 1587, 1460, 1321, 1292, 1250, 1044, 771, 763;
1H NMR (DMSO-d6) : δ 1.35 (t, J=6.9Hz, 3H), 2.29 (s, 3H), 4.13 (q, J=7.0Hz, 2H), 6.79 (s, 1H), 7.05 (t, 1H), 7.14 (d, 1H), 7.45 (dd, 1H), 7.76 (dd, 1H), 11.35 (brs, 1H), 11.54 (brs, 1H);
13C NMR (DMSO-d6) : δ (CH3) 11.2, 14.5; (CH2) 64.2; (CH) 113.0, 118.0, 120.6, 130.1, 131.9, (C) 105.0, 113.6, 121.9, 148.5, 149.8, 156.5, 159.2; MS(ES+) : m/z 287 (M+NH4) .
The compound (6) was prepared from compound(4b) according to the above-mentioned method with the yield of 85%
mp 124~127°C
IR (cm-1) : 3234, 3184, 3141, 3103, 3056, 2956, 2943, 2869, 1654, 1595, 1567, 1468, 1311, 1267, 1243, 1191, 1118, 1047, 758;
1H NMR (CDCl3) : δ 0.88 (t, J=7.5Hz, 3H), 1.23 (t, 3H), 1 . 80 (q, 2H), 2. 42 (s, 3H), 4.08 (t, J=7.2Hz, 2H), 4.22 (q, 2H), 6.60 (s, 1H), 7.01 (d, J=8.3Hz, 1H), 7.08 (t, 1H), 7.40 (m, 1H), 8.35 (dd, J=8.0 and 1.9 Hz, 1H), 11.02 (brs, 1H).
Preparation 42-(2-ethxoylphenyl)-5-methyl-7-n-propyl-3,7-dihydro-pyrrolo[2,3-d] pyrimidin-4-one(6):
A mixture of compound (5) (1.5g, 5.57mmol) of preparation 3, n-propyl bromide (2.0g, 16.3mmol) and potassium carbonate (5g, 36.2mmol) was dissolved in acetone (15ml), refluxed with agitation by heating for 15 hours, after the solids were filtrated out, the filtrate was dried under reduced pressure. The resultant was developed by column chromatography, using dichloromethane as mobile phase to obtain 0.6g of product (6) with yield of 35%. The physical/chemical data were identical with that of the above-mentioned.
Preparation 54-ethoxyl-3-(5-methyl-4-oxy-7-n-propyl-4,7-dihydropyrrolo[2,3-d] pyrimidin-2-yl)benzenesulfonyl chloride(7):
2-(2-ethxoylphenyl)-5-methyl-7-n-propyl-3,7-dihydropyrrolo[2,3-d] pyrimidin-4-one(6) (1.25g, 4.01mmol) of preparation 4 was added into chlorosulfonic acid (4ml) that was dissolved in acetic ether (20ml), stirred at 0°C by two batches. The obtained solution was stirred at 0 °C for 30 minutes, and then reacted with agitation at room temperature for 3 hours. The resultant solution was poured into the a mixture of icy water (50ml) and acetic ether (50ml) . The organic layer was separated, washed with cold water (5ml), desiccated with anhydrous sodium sulfate and concentrated to dryness to afford 1.33g of product as yellow foam. The yield was 81%. The product was used directly for the next reaction.
Compound 1:
BASE
2-[2-ethoxyl-5-(4-ethyl-piperazinyl-1-sulfonyl)phenyl]-5-methyl-7-n -propyl-3,7-dihydropyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-one (8):
4-ethoxyl-3-(5-methyl-4-oxy-7-n-propyl-4,7-dihydro-3H-pyrrolo[2,3-d ]pyrimidin-2-yl)benzenesulfonyl chloride(7) (1.00g, 2.44mmol) of Preparation 5 was dissolved into dichloromethane (20ml), stirred at 0 °C, into which 1-ethyl piperazine (0.78ml, 6.10mmol) was added slowly. Reactant solution was stirred at 0°C for 5 minutes, and then sequentially stirred at room temperature for 5 hours. The crude product was washed with water and dried with anhydrous sodium sulfate to give 1. 2g of product as yellow foam. Continuously, the product was refined by column chromatography (acetic ether: methanol=20:1) to afford 0.89g of product as a yellow solid with yield of 75%.
mp: 174~176°C (EtOAc);
IR (cm-1) : 3324, 2960, 2923, 2869, 2862, 2767, 1682, 1560, 1458, 1355, 1282, 1247, 1172, 1149, 739, 615, 588, 555;
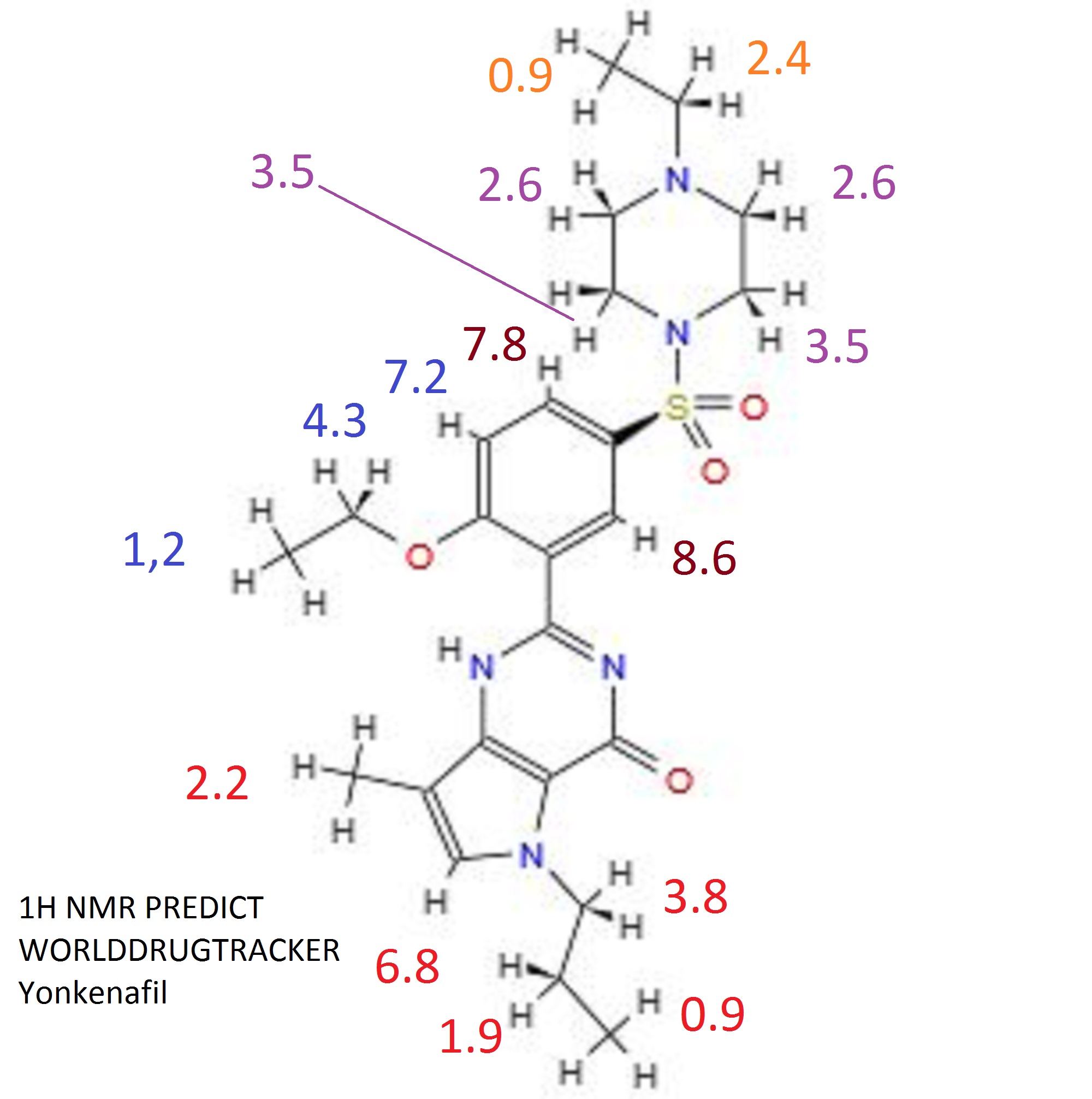
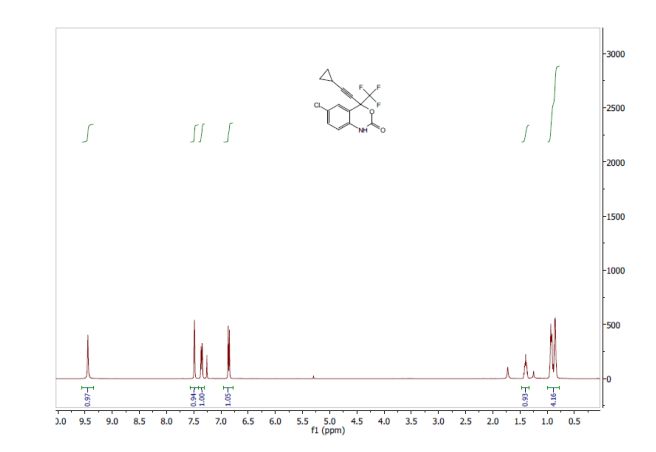
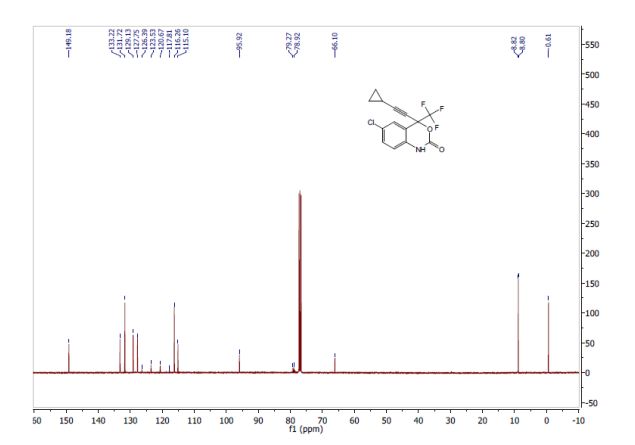
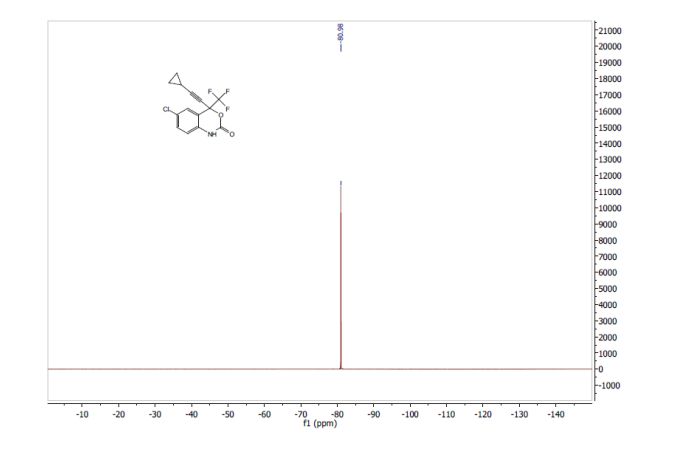
1H NMR(CDCl3) : δ 0.89(t,J=7.4Hz, 3H), 0.99(t, J=7.2Hz, 3H), 1.61(t,J=7.0Hz,3H),1.77-1.86(m, 2H), 2.35(m, 2H), 2.41(s, 3H), 2.50(brs, 4H), 3.05(brs,4H), 4.08(t, J=7.0Hz, 2H), 4.29-4.37(q, 2H), 6.61(s, 1H), 7.11(d, J=8.8Hz,1H), 7.77(dd, J=8.7 and2.2Hz, 1H), 8.74(d, J=2.2, 1H), 10.63(brs, 1H);
13C NMR(CDCl3) : δ (CH3) 11.0, 11.3, 11.8, 14.3; (CH2)23.8, 45.9, 46.1, 51.6, 51.7, 65.8; (CH)112.9, 121.1, 130.6, 131.3;(C)105.7,114.6, 121.4, 127.8, 146.8, 147.3, 159.3, 159.6;MS(ES+): m/z 505(M+NH4).
Elemental analysis (C24H33N5O4S) : theoretical value C 59.12%; H 6.82%; N 14.36%; practically measured value C59.38%; H 7.10%; N 14.12%.
Compound 1-HCl:
2-[2-ethoxyl-5-(4-ethylpiperazinyl-1-sulfonyl)phenyl]-5-methyl-7-n-propyl-3,7-dihydropyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-one monohydrochloride (9) :
The free alkali (compound 1) (1.00g, 2.05mmol) was dissolved into ether (10ml) and dichloromethane (10ml), into which the solution of 4M hydrochloric acid (HC1)- dioxane (0.51ml, 2.04mmol) diluted with ethyl ether (10ml) was dropped with agitation. After completion, the resulting solution was continued to stir at room temperature for 20 minutes, filtrated and dried to give 1.01g of monohydrochloride with yield of 94%.
mp: 147~150°C;
IR(cm-1): 2964, 2931, 2675, 2599, 2462, 1668, 1574, 1456, 1348, 1167, 933, 588;
1H NMR(D2O): δ 0.72(m, 3H),1.24(t, J=7.3Hz, 3H), 1.45(m, 3H), 1.59(m, 2H), 2.04(s, 3H), 2.77-3.81(all brs, 8H), 3.20(q, 2H), 3.75(m, 2H), 4.20(m, 2H), 6.62(m, 1H), 7.17(m, 1H), 7.73(m, 1H), 8.22(s, 1H).
Elemental analysis (C24H33N5O4S. HCl) : theoretical value C 55.00%; H 6.54%; N 13.36%; practically measured value C55.28%; H 6.41%; N 13.07%.
PATENT
WO 2016095650
https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/detail.jsf?docId=WO2016095650&redirectedID=true
SEE
https://www.google.com/patents/CN1552714A?cl=en
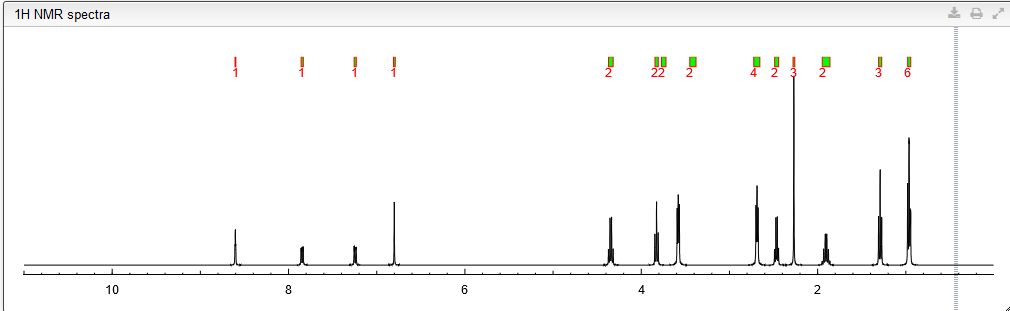
Spectral Analysis
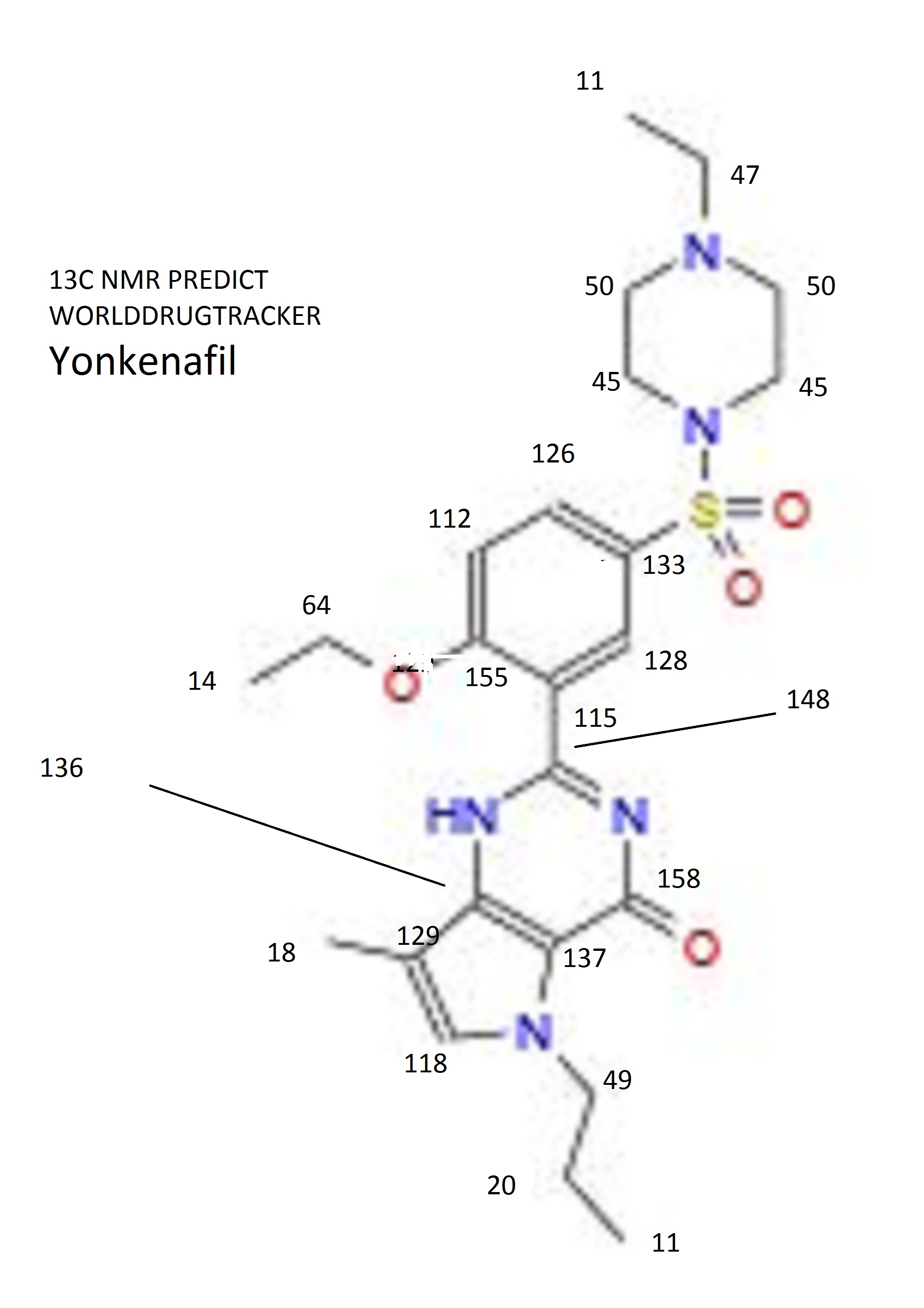
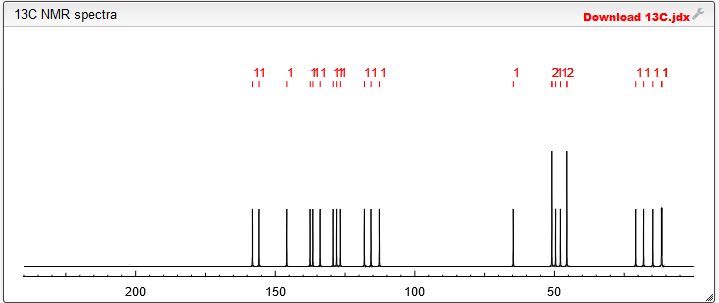
13C NMR PREDICT
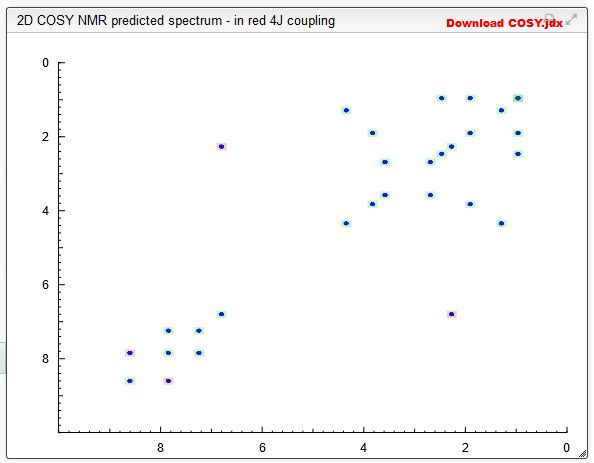
COSY PREDICT
| CN1552714A * | Jun 6, 2003 | Dec 8, 2004 | 天津倍方科技发展有限公司 | 2-substituted benzyl-5,7-dihydrocarbyl-3,7-dihydro pyrroline [2,3-d] pyromidine-4-one derivative ,its preparation and medicinal use |
| CN102970965A * | Apr 4, 2011 | Mar 13, 2013 | Sk化学公司 | Composition containing PDE5 inhibitor for relieving skin wrinkles |
| WO2007067570A1 * | Dec 5, 2006 | Jun 14, 2007 | Biomarin Pharmaceutical Inc. | Methods and compositions for the treatment of disease |
//////////yonkenafil, Phase 2, Erectile dysfunction , phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) inhibitor, Tasly Pharmaceutical Group; Yangtze River Pharmaceutical Group
Cc4cn(CCC)c1c4N/C(=N\C1=O)c2cc(ccc2OCC)S(=O)(=O)N3CCN(CC3)CC
Gisadenafil


















 Chidamide (Epidaza) is an
Chidamide (Epidaza) is an 










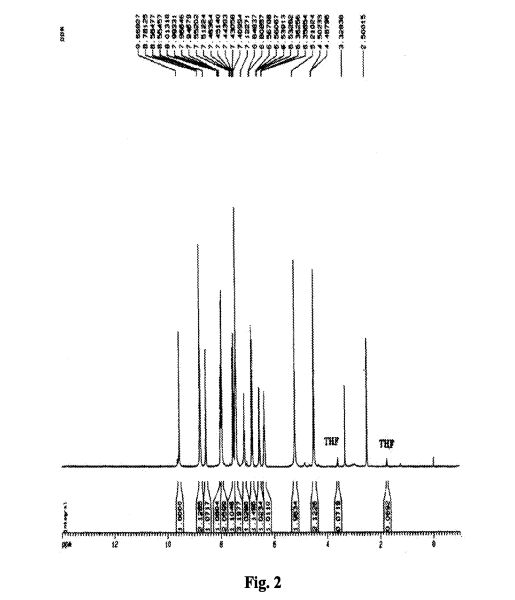
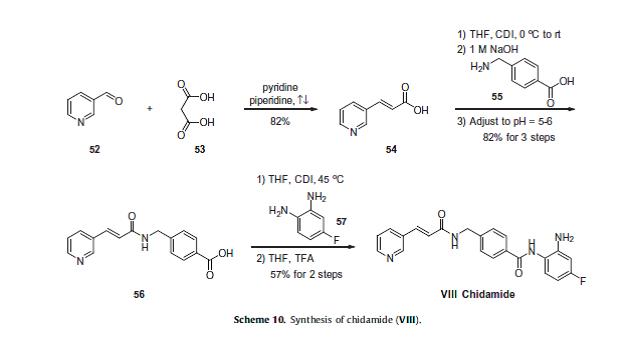
 To a suspension of 0.29 g (1.78 mmol) of N, N’-carbonyldiimidazole in tetrahydrofunan (15 ml) is added 0.50 g (1.78 mmol) of 4-[N-(Pyridn-3-ylacryloyl)aminomethyl]benzoic acid, followed by stirring at 45°C for 1 hour. After cooling, the reaction mixture is added to a separately prepared tetrahydrofunan (10 ml) solution including 0.28 g (2.22 mmol) of 4-fluoro-1,2-phenylenediamine and 0.20 g (1.78 mmol) of trifluoroacetic acid at room temperature. After reaction at room temperature for 24 hours, the deposited white solid is collected by filtration, washed with tetrahydrofunan, and then dried to give the title compound (0.40 g, 57%). 1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6): δppm: 4.49 (2H, d), 4.84 (2H, br.s), 6.60 (IH, t), 6.80 (2H, m), 6.96 (IH, t), 7.18 (IH, d), 7.42 (2H, d), 7.52 (IH, d), 7.95 (2H, d), 8.02 (IH, d), 8.56 (IH, d), 8.72 (IH, br. t), 8.78 (IH, s), 9.60 (IH, br.s). IR (KBr) cm“1: 3310, 1655, 1631, 1524, 1305, 750. HRMS calcd for C22Hι9N4O2F: 390.4170. Found: 390.4172. MA calcd for C22Hι9N4O2F: C, 67.68%; H, 4.40%; N, 14.35. Found: C, 67.52%; H, 4.38%; N, 14.42%.
To a suspension of 0.29 g (1.78 mmol) of N, N’-carbonyldiimidazole in tetrahydrofunan (15 ml) is added 0.50 g (1.78 mmol) of 4-[N-(Pyridn-3-ylacryloyl)aminomethyl]benzoic acid, followed by stirring at 45°C for 1 hour. After cooling, the reaction mixture is added to a separately prepared tetrahydrofunan (10 ml) solution including 0.28 g (2.22 mmol) of 4-fluoro-1,2-phenylenediamine and 0.20 g (1.78 mmol) of trifluoroacetic acid at room temperature. After reaction at room temperature for 24 hours, the deposited white solid is collected by filtration, washed with tetrahydrofunan, and then dried to give the title compound (0.40 g, 57%). 1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6): δppm: 4.49 (2H, d), 4.84 (2H, br.s), 6.60 (IH, t), 6.80 (2H, m), 6.96 (IH, t), 7.18 (IH, d), 7.42 (2H, d), 7.52 (IH, d), 7.95 (2H, d), 8.02 (IH, d), 8.56 (IH, d), 8.72 (IH, br. t), 8.78 (IH, s), 9.60 (IH, br.s). IR (KBr) cm“1: 3310, 1655, 1631, 1524, 1305, 750. HRMS calcd for C22Hι9N4O2F: 390.4170. Found: 390.4172. MA calcd for C22Hι9N4O2F: C, 67.68%; H, 4.40%; N, 14.35. Found: C, 67.52%; H, 4.38%; N, 14.42%.











.png)





1521-3773/asset/olalertbanner.jpg?v=1&s=0c0a7bae38bad177497650f0bc0083504684f4fa)
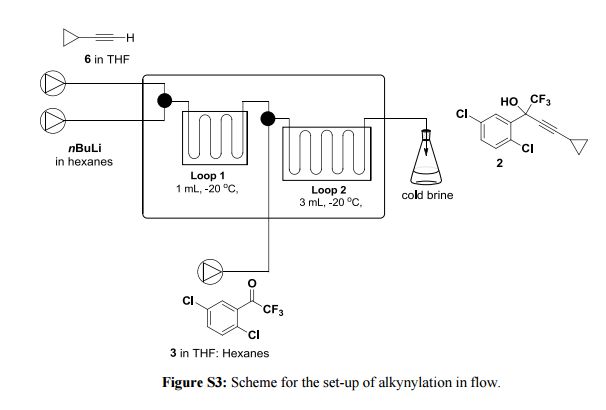
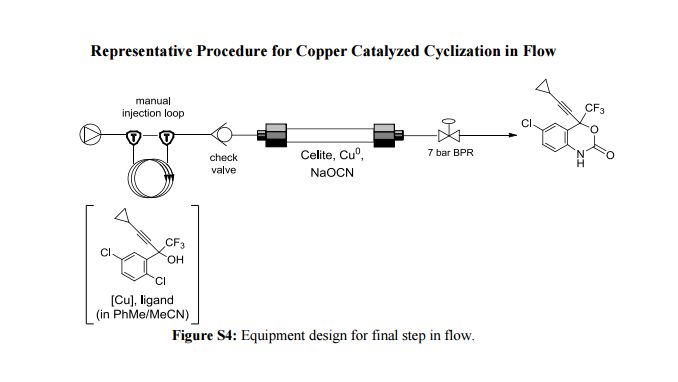



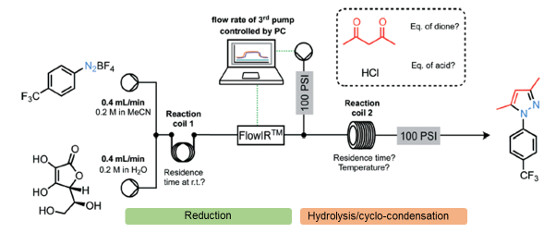
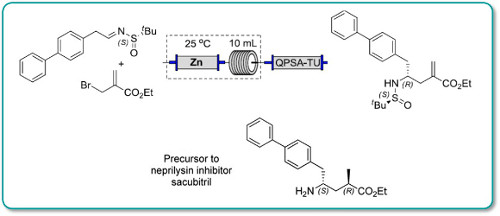
























 .
.


 ENTECAVIR, BARACLUDE
ENTECAVIR, BARACLUDE




 Rilpivirine
Rilpivirine Elbasvir
Elbasvir Quetiapine
Quetiapine