
| CAS Registry No.: | 5306-85-4 | ||
| Molecular Formula: | C8H14O4 | Molecular Weight: | 174.2 |

13 C NMR
| 22.53 MHz | |
| C8 H14 O4 | 0.05 ml : 0.5 ml CDCl3 |
1H NMR
IR NEAT
RAMAN
////////

| CAS Registry No.: | 5306-85-4 | ||
| Molecular Formula: | C8H14O4 | Molecular Weight: | 174.2 |


13 C NMR
| 22.53 MHz | |
| C8 H14 O4 | 0.05 ml : 0.5 ml CDCl3 |
1H NMR
IR NEAT
RAMAN
////////
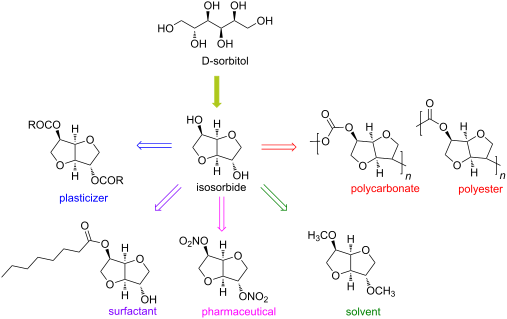
Isosorbide is a diol derived from sorbitol and obtained through dehydration reactions that has raised much interest in the literature over the past few decades. Thus, this platform chemical is a biobased alternative to a number of petrosourced molecules that can find applications in a large number of technical specialty fields, such as plasticizers, monomers, solvents or pharmaceuticals. The synthesis of isosorbide is still a technical challenge, as several competitive reactions must be simultaneously handled to promote a high molar yield and avoid side reactions, like degradation and polymerization. In this purpose, many studies have proposed innovative and varied methods with promising results. This review gives an overview of the synthesis strategies and catalysts developed to access this very attractive molecule, pointing out both the results obtained and the remaining issues connected to isosorbide synthesis.
Up to now, isosorbide has been used to access a large panel of molecules with relevant applicative properties and industrial reality (Scheme 2).12 Isosorbide dinitrate is used since several decades as vasodilator.13, 14 The dimethyl isosorbide is for example used as solvent in cosmetics15-17 and isosorbide diesters18-22 are actually industrially produced and commercialized as surfactants23-27 and PVC plasticizer28, 29 . The rigid scaffold associated to the bifunctionality of the molecule has attracted a strong interest in the field of polymers chemistry. Isosorbide and derivatives have thus been shown as suitable monomers for the industrial production of polycarbonates30, 31, polyesters32-41 or polyamides42-44, with attractive applicative properties. For example, isosorbide allows the increase of Tg, improves the scratch resistance and gives excellent optical properties to polymers. Polyesters and polycarbonates containing isosorbide have now commercial developments in food packaging, spray container, automotive, material for electronic devices … .
Conclusions
Isosorbide is a versatile platform molecule that shows key features to make it a credible alternative to petro-based products. The molecule is already available on large industrial scale (tens of thousands tons per years), which allows its development in commercial products such as active pharma ingredient, additive for cosmetic, speciality chemicals and polymers (ex: polycarbonates – polyesters). The development of more selective and higher yields syntheses of isosorbide are greatly needed to consolidate isosorbide production in view of a large expansion of its uses. Sorbitol conversion to isosorbide, relying on a starch route, is already a tough challenge. In a farther future, development of a credible path to isosorbide relying on cellulose source could even be thought of, provided that very versatile innovative catalysts will be developed in the next years. In all cases, a key issue is to develop catalysts that will avoid the massive production of “oligomeric/polymeric” by-products in order to access more sustainable processes by limiting the amounts of wastes produced during the synthesis. For this purpose, more selective homogeneous catalysts than the conventional Brønsted acids or alternative reaction conditions would be of strong interest. Selective and recyclable heterogeneous catalysts would be even more profitable as they would allow the continuous production of catalyst free isosorbide. This latter approach faces strong limitations due to the need of high reaction temperatures that often result in high amounts of side-products and the need of frequent and often tedious catalyst regeneration. Innovation concerning isosorbide synthesis is still an open field on which the design of efficient and robust catalysts, either homogeneous or heterogeneous, is a key issue. Such developments would pave the way to high scale effective processes considering altogether synthesis and purification of isosorbide.
////////////////

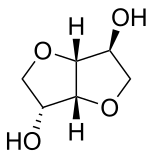
Isosorbide is a heterocyclic compound that is derived from glucose. Isosorbide and its two isomers, namely isoidide and isomannide, are 1,4:3,6-dianhydrohexitols. It is a white solid that is prepared from the double dehydration of sorbitol. Isosorbide is a non-toxic diolproduced from biobased feedstocks, that is biodegradable and thermally stable. It is used in medicine and has been touted as a potential biofeedstock.
Hydrogenation of glucose gives sorbitol. Isosorbide is obtained by double dehydration of sorbitol:
An intermediate in the dehydration is the monocycle sorbitan.[1]
Isosorbide is used as a diuretic, mainly to treat hydrocephalus, and is also used to treat glaucoma.[2] Other medications are derived from isosorbide, including isosorbide dinitrate and isosorbide mononitrate, are used to treat angina pectoris. Other isosorbide-based medicines are used as osmotic diuretics and for treatment of esophageal varices. Like other nitric oxide donors (see biological functions of nitric oxide), these drugs lower portal pressure by vasodilation and decreasing cardiac output. Isosorbide dinitrate and hydralazineare the two components of the anti-hypertensive drug isosorbide dinitrate/hydralazine (Bidil).
Isosorbide is also used as a building block for bio based polymers such as polyesters.[3]
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
D-Isosorbide; 1,4:3,6-Dianhydro-D-sorbitol; 1,4-Dianhydrosorbitol
|
|
| Identifiers | |
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.010.449 |
| KEGG | |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| Properties | |
| C6H10O4 | |
| Molar mass | 146.14 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Highly hygroscopic white flakes |
| Density | 1.30 at 25 °C |
| Melting point | 62.5 to 63 °C (144.5 to 145.4 °F; 335.6 to 336.1 K) |
| Boiling point | 160 °C (320 °F; 433 K) at 10 mmHg |
| in water (>850 g/L), alcoholsand ketones | |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
|
|
From the net
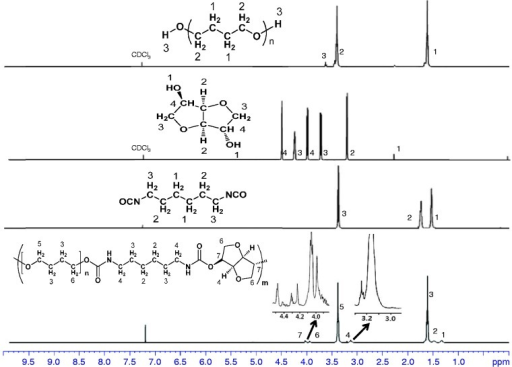
1H Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectra of PTMG, isosorbide, HDI, and polyurethane.HDI: hexamethylene diisocyanate; PTMG: poly(tetramethylene glycol).
REF
http://www.rsc.org/suppdata/gc/c4/c4gc01822b/c4gc01822b1.pdf
Synthesis of five- and six-membered heterocycles by dimethyl carbonate with catalytic amount of nitrogen bicyclic bases
http://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2015/gc/c4gc01822b#!divAbstract
F. Aricò, a,*S. Evaristoa and P. Tundoa,*
Catalytic amount of a nitrogen bicyclic base, i.e., DABCO, DBU and TBD is effective for the one-pot synthesis of heterocycles from 1,4-, 1,5-diols and 1,4-bifunctional compounds via dimethyl carbonate chemistry under neat conditions. Nitrogen bicyclic bases, that previously showed to enhance the reactivity of DMC in methoxycarbonylation reaction by BAc2 mechanism, are herein used for the first time as efficient catalysts for cyclization reaction encompassing both BAc2 and BAl2 pathways. This synthetic procedure was also applied to a large scale synthesis of cyclic sugars isosorbide and isomannide starting from D-sorbitol and D-mannitol, respectively. The resulting anhydro sugar alcohols were obtained as pure crystalline compounds that did not require any further purification or crystallization.
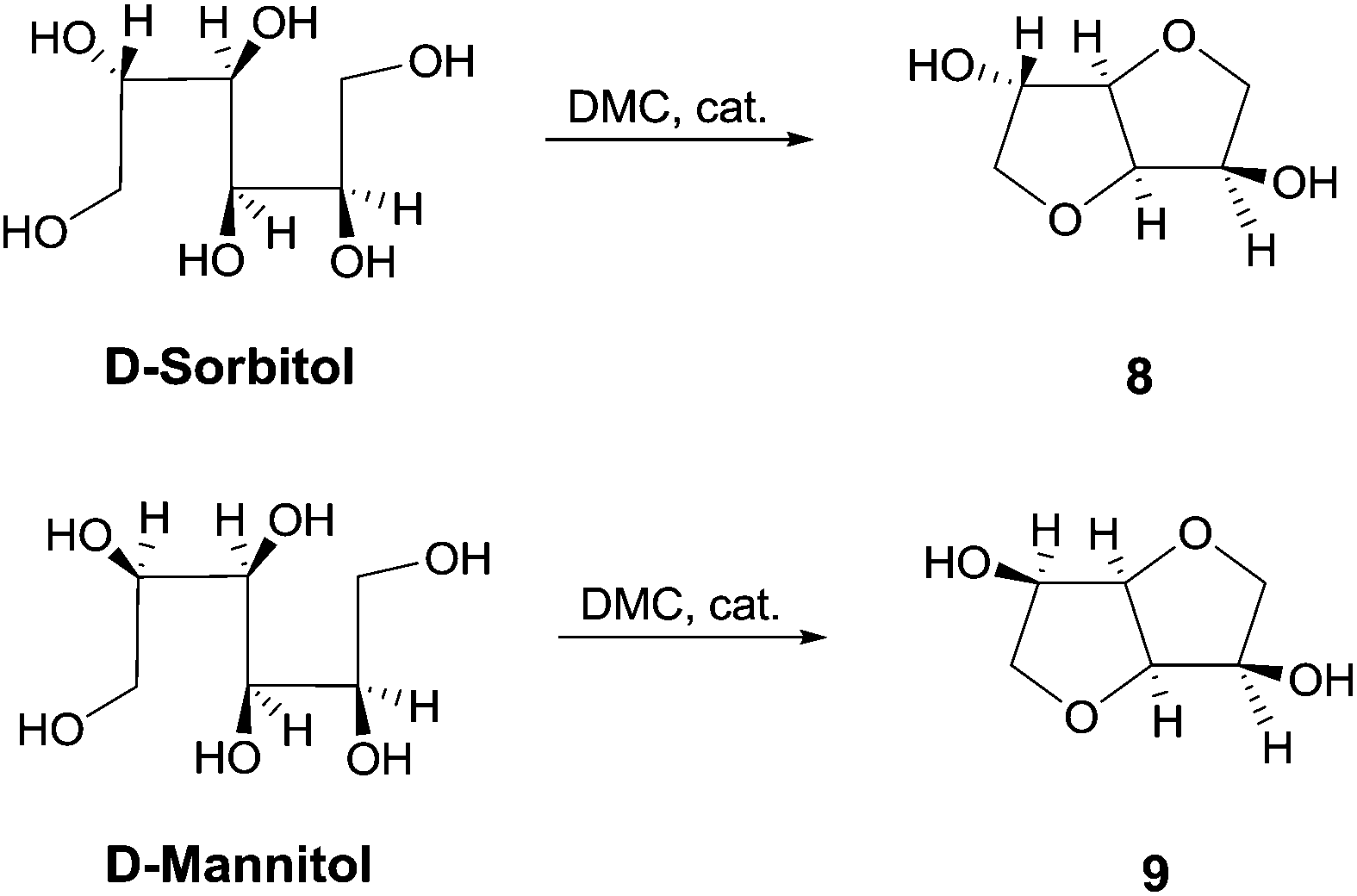
Larger scale synthesis of isosorbide: In a round bottom flask equipped with a reflux condenser, D-sorbitol (0.05 mol, 1.00 mol. eq.), DMC (0.44 mol, 8.00 mol. eq.), DBU (2.70 mmol, 0.05 mol. eq.) and MeOH (20.00 mL) were heated at reflux while stirring. The progress of the reaction was monitored by NMR. After 48 hours the reaction was stopped, cooled at room temperature and the mixture was filtered over Gooch n°4. Finally, DMC was evaporated under vacuum and the product was obtained as pure in 98% yield (7.90 g, 0.05 mol). Characterization data were consistent with those obtained for the commercially available compound.
File:Isosorbide dinitrate synthesis.png


A fully continuous-flow diazotization–hydrolysis protocol has been developed for the preparation of p-cresol. This process started from the diazotization of p-toluidine to form diazonium intermediate. The reaction was then quenched by urea and subsequently followed by a hydrolysis to give the final product p-cresol. Three types of byproducts were initially found in this reaction sequence. After an optimization of reaction conditions (based on impurity analysis), side reactions were eminently inhibited, and a total yield up to 91% were ultimately obtained with a productivity of 388 g/h. The continuous-flow methodology was used to avoid accumulation of the highly energetic and potentially explosive diazonium salt to realize the safe preparation for p-cresol.
. 1H NMR (400 MHz, (CD3)2SO) δ/ppm: 9.06 (br s, 1H, −OH), 6.94 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 6.62 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 2.17 (s, 3H, −CH3).
13C NMR (CDCl3) δ/ppm: 153.0, 129.9, 115.1, 20.5.
Literature data:(3b) 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3) δ/ppm: 7.03 (d, J = 8.2 Hz, 2H), 6.73 (dd, J = 8.2, 2.0 Hz, 2H), 4.75 (s, 1H, OH), 2.27 (s, 3H, CH3).
13C NMR (CDCl3) δ/ppm: 153.2, 130.2, 115.2, 20.6.
3(b) Taniguchi, T.; Imoto, M.; Takeda, M.; Nakai, T.; Mihara, M.; Iwai, T.; Ito, T.; Mizuno, T.; Nomoto, A.; Ogawa, A. Heteroat. Chem. 2015, 26, 411– 416 DOI: 10.1002/hc.21275
http://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/acs.oprd.7b00250
NMR PREDICT
 |
|
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| 79-44-7 | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.099 |
| PubChem | 6598 |
| Properties | |
| C3H6ClNO | |
Dimethylcarbamoyl Chloride

Mechanisms for the Formation of Dimethylcarbamoyl Chloride
Thionyl chloride is the most common reagent in process chemistry for the conversion of a carboxylic acid to an acid chloride. One of the primary factors is cost, since the reagent is inexpensive and represents one of the most cost-efficient ways of preparing acid chlorides. However, one disadvantage of thionyl chloride is the potential formation of dimethylcarbamoyl chloride, a known carcinogen in animal models, when used in combination with DMF as catalyst.
Dimethylcarbamoyl chloride is a reagent for transferring a dimethylcarbonyl group to alcoholic or phenolic hydroxyl groups forming dimethyl carbamates, usually having pharmacological or pesticidal activities. Because of its high toxicity and its carcinogenic properties shown in animal experiments and presumably also in humans,[1] dimethylcarbamoyl chloride can only be used under stringent safety precautions.
The production of dimethylcarbamoyl chloride from phosgene and dimethylamine (DMA) was reported as early as 1879 (reported as “Dimethylharnstoffchlorid” – dimethylurea chloride).[2]
Dimethylcarbamoyl chloride can be produced in high yields (90%) at 275 °C by reacting phosgene with gaseous dimethylamine in a flow reactor.[3] To suppress the formation of ureas excessive phosgene is used (in a 3:1 ratio).
The reaction can also be carried out at the laboratory scale with diphosgene or triphosgene and a aqueous dimethylamine solution in the two-phase system benzene+xylene/water in a stirred reactor with sodium hydroxide as an acid scavenger. However, considerably lower yields (56%) are achieved due to the hydrolysis sensitivity of dimethylcarbamoyl chloride .[4]
Dimethylcarbamoyl chloride is also formed (together with methyl chloride) when reacting phosgene with trimethylamine.[5]
A more recent process is based on dimethylamine chloride, which is converted practically quantitatively to dimethylcarbamoyl chloride on a palladium catalyst under pressure with carbon monoxide at room temperature.[6]
Dicarbamoyl chloride can also be formed in small amounts (0-20 ppm) from dimethylformamide (DMF) in the Vilsmeier-Haack reaction[7] or when DMF is used as a catalyst in the reaction of carboxylic acids with thionyl chloride to the corresponding carboxylic acid chlorides.[8]
The tendency towards dicarbamoyl chloride formation depends on the chlorination reagent (thionyl chloride> oxalyl chloride> phosphorus oxychloride) and is higher in the presence of a base. However, dicarbamoyl chloride hydrolyses very quickly to dimethylamine, hydrochloric acid and carbon dioxide (with a half-life of about 6 minutes at 0 °C) so that less than 3 ppm of dicarbamoyl chloride are found in the Vilsmeier product after aqueous work-up.[9]
Dimethylcarbamoyl chloride is a clear, colorless, corrosive and flammable liquid with a pungent odor and a tear-penetrating effect, which decomposes rapidly in water.[10]Because of its unpleasant, toxic, mutagenic and carcinogenic properties[11][12] it has to be used under extreme precautions.
Dimethylcarbamoyl chloride behaves like an acid chloride whose chlorine atom can be exchanged for other nucleophiles. Therefore, it reacts with alcohols, phenols and oximes to the corresponding N, N-dimethylcarbamates, with thiols to thiolourethanes, with amines and hydroxylamine to substituted ureas, and with imidazoles and triazoles to carbamoylazoles.[13]
Dimethylcarbamoyl chloride is less reactive and less selective to substrates with multiple nucleophilic centers than conventional acid chlorides.
Unsaturated conjugated aldehydes such as (2E)-butenal react with dimethylcarbamoyl chloride forming dienyl carbamates, which can be used as dienes in Diels-Alder reactions.[14]
Alkali metal carboxylates react with dimethylcarbamoyl chloride forming the corresponding dimethylamides. Dimethylcarbamoyl chloride reacts with anhydrous sodium carbonate[15] or with excess dimethylamine to tetramethylurea.[16]
The reaction of dimethylcarbamoyl chloride with DMF forms tetramethylformamidinium[17] chloride which is a major intermediate in the preparation of tris(dimethylamino)methane, a reagent for the introduction of enamine functions in conjunction with activated methylene groups[18] and the preparation of amidines.[19]
Dimethylcarbamoyl chloride is a starting material for the insecticide class of the dimethyl carbamates[20] which act as inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase, including dimetilane,[21]and the related compounds isolane, pirimicarb and triazamate.
The quaternary ammonium compounds neostigmine[22] finds pharmaceutical applications as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. It is obtained from 3-dimethylaminophenol and dimethylcarbamoyl chloride and subsequent quaternization with methyl bromide or dimethyl sulfate[23]
and pyridostigmine, which is obtainable from 3-hydroxypyridine and dimethylcarbamoyl chloride and subsequent reaction with methyl bromide.[24]
Dimethylcarbamoyl chloride is also used in the synthesis of the benzodiazepine camazepam.[25]

13c NMR


RAMAN

/////////////
We have reported herein a catalyst-free 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition of C,N-cyclic azomethine imines and 3-nitroindoles by which a series of five-ring-fused tetrahydroisoquinolines featuring an indoline scaffold were obtained as single diastereomers in moderate to high yields without any additives under mild conditions. Moreover, the current method provides a novel and convenient approach for the efficient incorporation of two biologically important scaffolds (tetrahydroisoquinoline and indoline).
DOI: 10.1039/C6GC02517J
“ALL FOR DRUGS” CATERS TO EDUCATION GLOBALLY, No commercial exploits are done or advertisements added by me. This article is a compilation for educational purposes only.
P.S. : The views expressed are my personal and in no-way suggest the views of the professional body or the company that I represent
A methodology for chemical routes development and evaluation on the basis of data-mining is presented. A section of the Reaxys database was converted into a network, which was used to plan hypothetical synthesis routes to convert a bio-waste feedstock, limonene, to a bulk intermediate, benzoic acid. The route evaluation considered process conditions and used multiple indicators, including exergy, E-factor, solvent score, reaction reliability and route redox efficiency, in a multi-criteria environmental sustainability evaluation. The proposed methodology is the first route evaluation based on data mining, explicitly using reaction conditions, and is amenable to full automation.
In the field of process and synthetic chemistry ‘clean synthesis’ has become one of the standard criteria for good, commercially viable synthesis routes. As a result synthetic and process chemists must be equipped with adequate methodologies for quantification of ‘cleanness’ or ‘greenness’ of alternative routes at the early phases of the development cycle. These new criteria, and the traditional criteria of cost, security of supply, health and safety (H&S), and risk, provide a balanced picture of sustainability of a future technology. Thus, there are two separate aspects to process chemistry: developing the chemistry and the process, and evaluating the overall process, which must occur in parallel. Evaluation of the proposed routes requires data. As data science rapidly evolves, chemistry will inevitably use more of the new tools of data mining and data analysis to automate the routine tasks, such as evaluation of process metrics. In this paper we show some initial results in automation of process evaluation based on deep data mining of process chemistry and multi-criteria decision making.
The evaluation of greenness is a mature field, with a large number of published and standardised approaches, of which many are adopted by industry. 1 However, all published methods are highly case-specific and rather labour-intensive. In the field of synthetic routes development one of the most exciting new areas is the potential for automation of synthesis planning using data mining.2 What has never been attempted before is to automate route generation and evaluation in a coherent methodology, which would aid process development at the early, data-lean, stages. For this we show how to automatically generate process options using a network representation of a section of Reaxys database,3 followed by their screening using multi-criteria decision making, see Fig. 1. As the methods mature and become commercially available, such integration and automation will produce significant savings of time, and would deliver a far more detailed view of the competing synthesis route options than is generally possible at the early stages of design.
To date, obtaining the data, assembling the network and finding potential synthesis routes can already be carried out in a fully automated fashion. Due to issues around data availability the connection to the analysis of the routes still has to be initiated manually, involving a data curation step. The subsequent analysis and multi-criteria decision making have been largely automated in this study. To our knowledge this is the first example of the analysis of synthesis routes generated from the network representation of Reaxys obtained through datamining, using reaction conditions and process data.
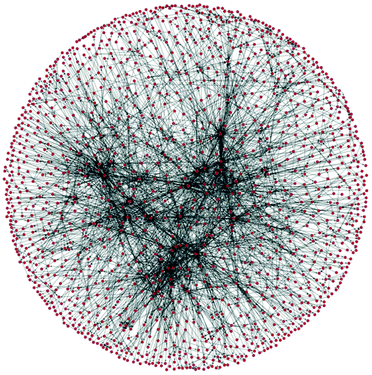
| Fig. 2 A section of a network of organic chemistry. Dots are species and arrows represent reactions. |
DOI: 10.1039/C6GC02482C, http://pubs.rsc.org/en/Content/ArticleLanding/2017/GC/C6GC02482C?utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=pub-GC-vol-19-issue-1&utm_source=toc-alert#!divAbstract
Professor of Sustainable Reaction Engineering
Fellow of Wolfson College
Catalytic Reaction Engineering
Sustainable Chemical Technologies
Office Phone: 330141


MChem in Biochemistry, Novosibirsk State University, 1994
PhD in Chemical Engineering, University of Bath, 2000
Boreskov Institute of Catalysis, Novosibirsk, Russia (1994-1997)
University of Bath, Department of Chemical Engineering, Research Officer (1997-2000)
University of Bath, Department of Chemical Engineering, Lecturer-SL-Reader (2000-2009)
University of Warwick, School of Engineering, Professor of Engineering (2009-2013)
Our group is developing cleaner manufacturing processes within chemical and chemistry using industries. We are mainly focusing on liquid- and multi-phase catalytic and biochemical processes. Within the group we have pursued projects on developing functional materials for catalysts, adsorbents and reactors, design of multi-functional intensive reactors, modelling of reaction kinetics and integrated processes, linking reaction kinetics with computational fluid dynamics (CFD) and linking process modelling with life cycle assessment (LCA), integration of reactions and separation.
Public funding:
The group is currently involved in an EU project ‘RECOBA’ (http://www.spire2030.eu/recoba/), in which our group collaborates with Materials and Electronic Engineering at Cambridge to work on innovative measurement techniques for monitoring processes under reaction conditions.
We are involved in the EPSRC project on developing novel routes to platform and functional molecules from waste terpenes, led by University of Bath.
We are involved in “Dial a Molecule 2” network funded by EPSRC.
Keywords
|
J. Zakrzhewski, A.P. Smalley, M. Kabeshov, A. Lapkin, M. Gaunt, Continuous flow synthesis and derivatization of aziridines via palladium-catalyzed C(sp3)-H activation, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 55 (2016) 8878-8883.
P. Yaseneva, P. Hodgson, J. Zakrzewski, S. Falss, R.E. Meadows, A.A. Lapkin, Continuous flow Buchwald-Hartwig amination of a pharmaceutical intermediate, React. Chem. Eng., 1 (2016) 229-238.
P. Yaseneva, D. Plaza, X. Fan, K. Loponov, A. Lapkin, Synthesis of the antimalarial API artemether in a flow reactor, Catal. Today, 239 (2015) 90-96.
N. Peremezhney, E. Hines, A. Lapkin, C. Connaughton, Combining Gaussian processes, mutual information and a generic algorithm for multi-targeted optimisation of expensive-to-evaluate functions, Engineering Optimisation, 46 (2014) 1593-1607.
P. Yaseneva, C.F. Marti, E. Palomares, X. Fan, T. Morgan,P.S. Perez, M. Ronning, F. Huang,T. Yuranova, L. Kiwi-Minsker, S. Derrouiche, A.A. Lapkin, Efficient reduction of bromates using carbon nanofibre supported catalysts: experimental and a comparative life cycle assessment study, Chem. Eng. J., 248 (2014) 230-241
K.N. Loponov, J. Lopes, M. Barlog, E.V. Astrova, A.V. Malkov, A.A. Lapkin, Optimization of a Scalable Photochemical Reactor for Reactions with Singlet Oxygen, Org.Process Res.Dev., 18 (2014) 1443-1454.
X. Fan, V. Sans, P. Yaseneva, D. Plaza, J.M.J. Williams, A.A. Lapkin, Facile Stoichiometric Reductions in Flow: an Example of Artemisinin, Org.Process Res.Dev., 16 (2012) 1039-1042.
M.V. Sotenko, M. Rebros, V.S. Sans, K.N. Loponov, M.G. Davidson, G. Stephens, A.A. Lapkin, Tandem transformation of glycerol to esters, J. Biotechnol., 162 (2012) 390-397.
A.A. Lapkin, A. Voutchkova, P. Anastas, A conceptual framework for description of complexity in intensive chemical processes, Chem. Eng. Processing. Process intensification, 50 (2011) 1027-1034.
Lapkin, A., Peters, M., Greiner, L., Chemat, S., Leonhard, K., Liauw, M. A. and Leitner, W., Screening of new solvents for artemisinin extraction process using ab-initio methodology, Green Chem., 12 (2010) 241-251.
Lapkin, A. A. and Plucinski, P. K., Engineering factors for efficient flow processes in chemical industries, in Chemical reactions and processes under flow conditions, pp. 1- 43, Eds: Luis, S. V. and Garcia-Verdugo, E., Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge, 2010.
Iwan, A., Stephenson, H., Ketchie, W. C. and Lapkin, A. A., High temperature sequestration of CO2 using lithium zirconates, Chem. Eng. J., 146 (2009) 249-258.
Constable, D. J. C., Jimenez-Gonzalez, C. and Lapkin A., ‘Process metrics’, in Green chemistry metrics: measuring and monitoring sustainable processes, pp. 228- 247, Eds.: Lapkin, A. and Constable, D. J. C., Wiley-Blackwell, Chichester, 2008.
L.Torrente-Murciano, A.Lapkin, D.V. Bavykin, F.C. Walsh, K. Wilson, Highly selective Pd/titanate nanotubes catalysts for the double bond migration reaction, J. Catal., 245 (2007) 270-276.
A. Lapkin, P. Plucinski, Comparative assessment of technologies for extraction of artemisinin, J. Natural Prod., 69 (2006) 1653-1664.
D.V. Bavykin, A.A. Lapkin, S.T. Kolaczkowski, P.K. Plucinski, Selective oxidation of alcohols in a continuous multifunctional reactor: ruthenium oxide catalysed oxidation of benzyl alcohol, Applied Catal. A: General, 288 (2005) 165-174.

////////automation, chemical process, route selection, data mining
The design, development, and scale up of a continuous iridium-catalyzed homogeneous high pressure reductive amination reaction to produce 6, the penultimate intermediate in Lilly’s CETP inhibitor evacetrapib, is described. The scope of this report involves initial batch chemistry screening at milligram scale through the development process leading to full-scale production in manufacturing under GMP conditions. Key aspects in this process include a description of drivers for developing a continuous process over existing well-defined batch approaches, manufacturing setup, and approaches toward key quality and regulatory questions such as batch definition, the use of process analytics, start up and shutdown waste, “in control” versus “at steady state”, lot genealogy and deviation boundaries, fluctuations, and diverting. The fully developed continuous reaction operated for 24 days during a primary stability campaign and produced over 2 MT of the penultimate intermediate in 95% yield after batch workup, crystallization, and isolation.

ACS Editors’ Choice – This is an open access article published under an ACS AuthorChoice License, which permits copying and redistribution of the article or any adaptations for non-commercial purposes.

Continuous flow Doebner–Miller synthesis of different quinaldines from respective anilines is demonstrated using sulfuric acid as a homogeneous catalyst. The extent of reaction was monitored for various parameters, namely, temperature, residence time, mole ratio of sulfuric acid to substrate, mole ratio of crotonaldehyde to substrate, and so forth. Continuous stirred reactors in series were used as a preferred configuration for this rection that generates byproduct in the form of sticky solid material. The approach has been extended for six different anilines, and the results are compared with batch reactions. Continuous stirred reactors in series with distributed dosing of crotonaldehyde facilitated a continuous flow reaction with lower byproduct formation, increased yields, and continuous workup and is a scalable approach.




Dr. Amol A. Kulkarni is a Scientist in the Chemical Engineering Division at the National Chemical Laboratory. He did his B. Chem. Eng. (1998), M. Chem. Eng (2000) and Ph.D. in chemical engineering (2003) all from the University Dept. of Chem. Technology (UDCT, Mumbai). In 2004 he worked at the Max Planck Institute-Magdeburg (Germany) as a Alexander von Humboldt Research Fellow. At NCL he is driving a research program on the design of microreactors and exploring their applications for continuous syntheses including of nanoparticles. He has been awarded with the Max-Planck-Visiting Fellowship from the Max-Planck-Society, Munich for 2008-2011. His research areas include: (i) design and applications of microreactors, (ii) design of multiphase reactors, (iii) experimental and computational fluid dynamics, and (iv) nonlinear dynamics of coupled systems. He is an active member of Initiative for Research and Innovation in Science (IRIS) supported by Intel’s Education Initiative to organize National Science Fair and popularize science in India.
///////////Continuous Flow, Doebner–Miller Reaction, Isolation, Continuous Stirred Tank Reactors, chemical engeineering, process, Amol A. Kulkarni, ncl, pune
Sreeni Labs Private Limited, Hyderabad, India is ready to take up challenging synthesis projects from your preclinical and clinical development and supply from few grams to multi-kilo quantities. Sreeni Labs has proven route scouting ability to design and develop innovative, cost effective, scalable routes by using readily available and inexpensive starting materials. The selected route will be further developed into a robust process and demonstrate on kilo gram scale and produce 100’s of kilos of in a relatively short time.
Accelerate your early development at competitive price by taking your route selection, process development and material supply challenges (gram scale to kilogram scale) to Sreeni Labs…………
WEBSITE………. https://sreenilabs.com/
Sreeni Labs based in Hyderabad, India is working with various global customers and solving variety of challenging synthesis problems. Their customer base ranges from USA, Canada, India and Europe. Sreeni labs Managing Director, Dr. Sreenivasa Reddy Mundla has worked at Procter & Gamble Pharmaceuticals and Eli Lilly based in USA.
The main strength of Sreeni Labs is in the design, development of innovative and highly economical synthetic routes and development of a selected route into a robust process followed by production of quality product from 100 grams to 100s of kg scale. Sreeni Labs main motto is adding value in everything they do.
They have helped number of customers from virtual biotech, big pharma, specialty chemicals, catalog companies, and academic researchers and drug developers, solar energy researchers at universities and institutions by successfully developing highly economical and simple chemistry routes to number of products that were made either by very lengthy synthetic routes or by using highly dangerous reagents and Suzuki coupling steps. They are able to supply materials from gram scale to multi kilo scale in a relatively short time by developing very short and efficient synthetic routes to a number of advanced intermediates, specialty chemicals, APIs and reference compounds. They also helped customers by drastically reducing number of steps, telescoping few steps into a single pot. For some projects, Sreeni Labs was able to develop simple chemistry and avoided use of palladium & expensive ligands. They always begin the project with end in the mind and design simple chemistry and also use readily available or easy to prepare starting materials in their design of synthetic routes
Over the years, Sreeni labs has successfully made a variety of products ranging from few mg to several kilogram scale. Sreeni labs has plenty of experience in making small select libraries of compounds, carbocyclic compounds like complex terpenoids, retinal derivatives, alkaloids, and heterocyclic compounds like multi substituted beta carbolines, pyridines, quinolines, quinolones, imidazoles, aminoimidazoles, quinoxalines, indoles, benzimidazoles, thiazoles, oxazoles, isoxazoles, carbazoles, benzothiazoles, azapines, benzazpines, natural and unnatural aminoacids, tetrapeptides, substituted oligomers of thiophenes and fused thiophenes, RAFT reagents, isocyanates, variety of ligands, heteroaryl, biaryl, triaryl compounds, process impurities and metabolites.
Sreeni Labs is Looking for any potential opportunities where people need development of cost effective scalable routes followed by quick scale up to produce quality products in the pharmaceutical & specialty chemicals area. They can also take up custom synthesis and scale up of medchem analogues and building blocks. They have flexible business model that will be in sink with customers. One can test their abilities & capabilities by giving couple of PO based (fee for service) projects.
Some of the compounds prepared by Sreeni labs;
See presentation below
LINK ON SLIDESHARE
Managing Director at Sreeni Labs Private Limited
QUOTE………….
One virtual biotech company customer from USA, through a common friend approached Sreeni Labs and told that they are buying a tetrapeptide from Bachem on mg scale at a very high price and requested us to see if we can make 5g. We accepted the challenge and developed solution phase chemistry and delivered 6g and also the process procedures in 10 weeks time. The customer told that they are using same procedures with very minor modifications and produced the tetrapeptide ip to 100kg scale as the molecule is in Phase III.
One East coast customer in our first meeting told that they are working with 4 CROs of which two are in India and two are in China and politely asked why they should work with Sreeni Labs. We told that give us a project where your CROs failed to deliver and we will give a quote and work on it. You pay us only if we deliver and you satisfy with the data. They immediately gave us a project to make 1.5g and we delivered 2g product in 9 weeks. After receiving product and the data, the customer was extremely happy as their previous CRO couldn’t deliver even a milligram in four months with 3 FTEs.
One Midwest biotech company was struggling to remove palladium from final API as they were doing a Suzuki coupling with a very expensive aryl pinacol borane and bromo pyridine derivative with an expensive ligand and relatively large amount of palldium acetate. The cost of final step catalyst, ligand and the palladium scavenging resin were making the project not viable even though the product is generating excellent data in the clinic. At this point we signed an FTE agreement with them and in four months time, we were able to design and develop a non suzuki route based on acid base chemistry and made 15g of API and compared the analytical data and purity with the Suzuki route API. This solved all three problems and the customer was very pleased with the outcome.
One big pharma customer from east coast, wrote a structure of chemical intermediate on a paper napkin in our first meeting and asked us to see if we can make it. We told that we can make it and in less than 3 weeks time we made a gram sample and shared the analytical data. The customer was very pleased and asked us to make 500g. We delivered in 4 weeks and in the next three months we supplied 25kg of the same product.
Through a common friend reference, a European customer from a an academic institute, sent us an email requesting us to quote for 20mg of a compound with compound number mentioned in J. med. chem. paper. It is a polycyclic compound with four contiguous stereogenic centers. We gave a quote and delivered 35 mg of product with full analytical data which was more pure than the published in literature. Later on we made 8g and 6g of the same product.
One West coast customer approached us through a common friend’s reference and told that they need to improve the chemistry of an advanced intermediate for their next campaign. At that time they are planning to make 15kg of that intermediate and purchased 50kg of starting raw material for $250,000. They also put five FTEs at a CRO for 5 months to optimize the remaining 5 steps wherein they are using LAH, Sodium azide, palladium catalyst and a column chromatography. We requested the customer not to purchase the 50kg raw material, and offered that we will make the 15kg for the price of raw material through a new route in less than three months time. You pay us only after we deliver 15 kg material. The customer didn’t want to take a chance with their timeline as they didn’t work with us before but requested us to develop the chemistry. In 7 weeks time, we developed a very simple four step route for their advanced intermediate and made 50g. We used very inexpensive and readily available starting material. Our route gave three solid intermediates and completely eliminated chromatographic purifications.
One of my former colleague introduced an academic group in midwest and brought us a medchem project requiring synthesis of 65 challenging polyene compounds on 100mg scale. We designed synthetic routes and successfully prepared 60 compounds in a 15 month time.
UNQUOTE…………
The man behind Seeni labs is Dr.Sreenivasa Reddy Mundla

Managing Director at Sreeni Labs Private Limited
Sreeni Labs Private Limited
Road No:12, Plot No:24,25,26
Links
LINKEDIN https://in.linkedin.com/in/sreenivasa-reddy-10b5876
FACEBOOK https://www.facebook.com/sreenivasa.mundla
RESEARCHGATE https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Sreenivasa_Mundla/info
EMAIL mundlasr@hotmail.com, Info@sreenilabs.com, Sreeni@sreenilabs.com
Dr. Sreenivasa Mundla Reddy
Dr. M. Sreenivasa Reddy obtained Ph.D from University of Hyderabad under the direction Prof Professor Goverdhan Mehta in 1992. From 1992-1994, he was a post doctoral fellow at University of Wisconsin in Professor Jame Cook’s lab. From 1994 to 2000, worked at Chemical process R&D at Procter & Gamble Pharmaceuticals (P&G). From 2001 to 2007 worked at Global Chemical Process R&D at Eli Lilly and Company in Indianapolis.
In 2007 resigned to his job and founded Sreeni Labs based in Hyderabad, Telangana, India and started working with various global customers and solving various challenging synthesis problems.
The main strength of Sreeni Labs is in the design, development of a novel chemical route and its development into a robust process followed by production of quality product from 100 grams to 100’s of kg scale.
They have helped number of customers by successfully developing highly economical simple chemistry routes to number of products that were made by Suzuki coupling. they are able to shorten the route by drastically reducing number of steps, avoiding use of palladium & expensive ligands. they always use readily available or easy to prepare starting materials in their design of synthetic routes.
Sreeni Labs is Looking for any potential opportunities where people need development of cost effective scalable routes followed by quick scale up to produce quality products in the pharmaceutical & specialty chemicals area. They have flexible business model that will be in sink with customers. One can test their abilities & capabilities by giving PO based projects
August 2007 – Present (8 years 11 months)
Sreeni Labs Profile

March 2001 – August 2007 (6 years 6 months)

July 1994 – February 2001 (6 years 8 months)


With Sreenivasa Mundla, Narahara sastry, Ram Kishan Rao, Jagadeesh Bharatam, Jagadish Gunjur and Jagadish Bharatham.
PUBLICATIONS
Jianye Zhang · Zhiqian Dong · Sreenivasa Reddy Mundla · X Eric Hu · William Seibel ·Ruben Papoian · Krzysztof Palczewski · Marcin Golczak
Article: ChemInform Abstract: Regioselective Synthesis of 4Halo ortho-Dinitrobenzene Derivative
Aug 2010 · ChemInform
Hong-yu Li · William T. McMillen · Charles R. Heap · Denis J. McCann · Lei Yan · Robert M. Campbell · Sreenivasa R. Mundla · Chi-Hsin R. King · Elizabeth A. Dierks · Bryan D. Anderson · Karen S. Britt · Karen L. Huss
Apr 2008 · Journal of Medicinal Chemistry
Hong-yu Li · Yan Wang · William T. McMillen · Arindam Chatterjee · John E. Toth ·Sreenivasa R. Mundla · Matthew Voss · Robert D. Boyer · J. Scott Sawyer
Feb 2008 · ChemInform
Hong-yu Li · Yan Wang · William T. McMillen · Arindam Chatterjee · John E. Toth ·Sreenivasa R. Mundla · Matthew Voss · Robert D. Boyer · J. Scott Sawyer
Nov 2007 · Tetrahedron
Hong-yu Li · Yan Wang · Charles R Heap · Chi-Hsin R King · Sreenivasa R Mundla · Matthew Voss · David K Clawson · Lei Yan · Robert M Campbell · Bryan D Anderson · Jill R Wagner ·Karen Britt · Ku X Lu · William T McMillen · Jonathan M Yingling
Apr 2006 · Journal of Medicinal Chemistry
Hui Cao · Sreenivasa R. Mundla · James M. Cook
Aug 2003 · Tetrahedron Letters
Article: ChemInform Abstract: A New Method for the Synthesis of 2,6-Dinitro and 2Halo6-nitrostyrenes
Nov 2000 · ChemInform
Article: ChemInform Abstract: A Novel Method for the Efficient Synthesis of 2-Arylamino-2-imidazolines
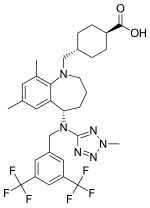
TGF-β inhibitors
The present invention provides 2-(6-methyl-pyridin-2-yl)-3-[6-amido-quinolin-4-yl) -5,6-dihydro-4H-pyrrolo[1,2-b]pyrazole monohydrate, i.e., Formula I.
EXAMPLE 1 Preparation of 2-(6-methyl-pyridin-2-yl)-3-[6-amido-quinolin-4-yl-5,6-dihydro-4H -pyrrolo[1,2-b]pyrazole monohydrate
Galunisertib
1H NMR (CDCl3): δ=9.0 ppm (d, 4.4 Hz, 1H); 8.23-8.19 ppm (m, 2H); 8.315 ppm (dd, 1.9 Hz, 8.9 Hz, 1H); 7.455 ppm (d, 4.4 Hz, 1H); 7.364 ppm (t, 7.7 Hz, 1H); 7.086 ppm (d, 8.0 Hz, 1H); 6.969 ppm (d, 7.7 Hz, 1H); 6.022 ppm (m, 1H); 5.497 ppm (m, 1H); 4.419 ppm (t, 7.3 Hz, 2H); 2.999 ppm (m, 2H); 2.770 ppm (p, 7.2 Hz, 7.4 Hz, 2H); 2.306 ppm (s, 3H); 1.817 ppm (m, 2H). MS ES+: 370.2; Exact: 369.16
ABOVE MOLECULE IS
https://newdrugapprovals.org/2016/05/04/galunisertib/
Galunisertib
Phase III
A TGF-beta receptor type-1 inhibitor potentially for the treatment of myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) and solid tumours.
LY-2157299
CAS No.700874-72-2
READ MY PRESENTATION ON
KEYWORDS Sreenivasa Mundla Reddy, Managing Director, Sreeni Labs Private Limited, Hyderabad, Telangana, India, new, economical, scalable routes, early clinical drug development stages, Custom synthesis, custom manufacturing, drug discovery, PHASE 1, PHASE 2, PHASE 3, API, drugs, medicines

Synthesis of Biaryls through Nickel-Catalyzed Suzuki–Miyaura Coupling of Amides by Carbon–Nitrogen Bond Cleavage (pages 6959–6963)Shicheng Shi, Guangrong Meng and Prof. Dr. Michal Szostak
Version of Record online: 21 APR 2016 | DOI: 10.1002/anie.201601914
Breaking and making: The first nickel-catalyzed Suzuki–Miyaura coupling of amides for the synthesis of biaryl compounds through N−C amide bond cleavage is reported. The reaction tolerates a wide range of sensitive and electronically diverse substituents on both coupling partners.
1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.70 (s, 4 H), 7.61 (d, J = 7.3 Hz, 2 H), 7.48 (t, J = 7.6 Hz, 2 H), 7.42 (t, J = 7.3 Hz, 1 H).
13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3) δ 144.87, 139.92, 129.48 (q, J F = 32.5 Hz), 129.13, 128.32, 127.56, 127.42, 125.83 (q, J F = 3.8 Hz), 124.46 (q, J F = 270.0 Hz).
//////Nickel-Catalyzed, Decarbonylative Suzuki–Miyaura Coupling, Amides, Biaryls