READ
ANTHONY MELVIN CRASTO
 DRUG APPROVALS BY DR ANTHONY MELVIN CRASTO …..FOR BLOG HOME CLICK HERE
DRUG APPROVALS BY DR ANTHONY MELVIN CRASTO …..FOR BLOG HOME CLICK HERE
 amcrasto@gmail.com
amcrasto@gmail.com
CALL +919323115463 INDIA
//////////////
READ
ANTHONY MELVIN CRASTO
 DRUG APPROVALS BY DR ANTHONY MELVIN CRASTO …..FOR BLOG HOME CLICK HERE
DRUG APPROVALS BY DR ANTHONY MELVIN CRASTO …..FOR BLOG HOME CLICK HERE
CALL +919323115463 INDIA
//////////////
Conventional enantioselective preparative chromatographic separation using columns packed with chiral stationary phase is characterized by a 50% yield constraint. Racemization of the undesired enantiomer and recycling the formed mixture is an attractive option to tackle this limit. To implement this concept, potential is seen in particular in applying enzymes immobilized in a second fixed bed. However, the identification of suitable operating conditions and the direct connection of a chromatographic column and an enzymatic reactor is not trivial. The paper presents results of an experimental study applying jointly a batch-wise operated chiral Chirobiotic T column to resolve the two enantiomers of mandelic acid (MA) and a mandelate racemase immobilized on Eupergit CM. The general concept could be successfully demonstrated over several cycles focusing on the provision of (S)-MA. A mathematical model was developed in order to illustrate essential process features and to quantitatively describe the coupled separation and racemization processes. The key ingredients of this model, namely, the adsorption isotherms of the two enantiomers on the chiral column and the rate of racemization in the enzymatic reactor, were determined experimentally. The potential of applying the model for further process optimization and generalization is indicated.
Combination of Enantioselective Preparative Chromatography and Racemization: Experimental Demonstration and Model-Based Process Optimization
link https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.oprd.8b00254


Dr. Katarzyna Wrzosek
Max-Planck Institute for Dynamics of Complex Technical System, Physical and Chemical Foundations of Process Engineering, 39106 Magdeburg, Germany
*E-mail: wrzosek@mpi-magdeburg.mpg.de.
M. Sc. Isabel Harriehausen
Prof. Dr.-Ing. Andreas Seidel-Morgenstern
Magdeburg, Germany


Grüne Zitadelle Von Magdeburg


Magdeburg Cathedral
READ
ANTHONY MELVIN CRASTO
 DRUG APPROVALS BY DR ANTHONY MELVIN CRASTO …..FOR BLOG HOME CLICK HERE
DRUG APPROVALS BY DR ANTHONY MELVIN CRASTO …..FOR BLOG HOME CLICK HERE
CALL +919323115463 INDIA
///////////////enantioselective chromatography, enzymatic reactor, equilibrium dispersion model, mandelate racemase, racemization

Established in 1996, Orochem Technologies Inc. started as a Biotech and Chromatography company to manufacture unique Sample Prep Technology “Products” for the Bioanalysis, Drug Discovery, and the Genomics and Proteomics markets.
Established in 1996, Orochem Technologies Inc. started as a Biotech and Chromatography company to manufacture unique Sample Prep Technology Products for the Bioanalysis, Drug Discovery, and the Genomics and Proteomics markets. Backed with unique expertise in high throughput formats, membranes and surface chemistries, Orochem was one of the first companies to translate the concept of pre-filters from single to high throughput formats, a concept now widely implemented for sample prep plates in the biotech and analytical markets. In the year 2001 Orochem manufactured the first commercially available Protein Crash and Precipitation 96-well plate for Bioanalytical processes. By the year 2006, with the acquisition of Column Engineering Inc, Orochem evolved to become a “full-service” provider for silica manufacturing utilized for analytical and preparatory chromatography. Orochem invests heavily into R&D in-house and owns strong intellectual property in stationary phases for achiral and Chiral Chromatography.
Orochem’s is globally recognized as an organization that conceives, develops, and installs some of the most technologically viable solutions for “highest purities” for industrial or “metric ton” scale purification for API’s, nutritional supplements, fatty acids, and specialty sugars. Orochem provides Simulated Moving Bed (SMB) Chromatography technology for the laboratory scale, pilot scale and large-scale purification of commercially viable molecules for its customers around the world. Orochem’s products and services for Simulated Moving Bed Chromatography include Synthesis and manufacture of stationary phases “tailored for specific separations”, a uniquely engineered SMB system and the installation and commissioning of the SMB systems at customer sites with well-trained Orochem technical service engineers.
Orochem owns several manufacturing facilities around the world. The Naperville, Illinois, USA site has about 84,000 square feet of manufacturing area where most of the Membrane Filter Plates, Silica manufacturing, Silica bonding, Solid Phase Extraction products and HPLC Columns are manufactured. Orochem India, Mumbai has 20,000 square feet facility and manufactures Sample prep products for the Discovery & Clinical Research organizations in Asia. Simulated Moving Bed chromatography systems are designed, built and assembled completely at our US locations in Naperville in Illinois.
USA (HQ)
Orochem Technologies Inc.
630 210 8300
630 210 8315
info@orochem.com
340 Shuman Blvd., Naperville, 60563, IL.
(1S,4R)-2-(4-Methoxybenzoyl)bicyclo[2.2.2]octa-2,5-diene (3a) Yellow liquid (25.2 mg, 95% yield):
1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3) 1.39 (s, 4H, alkyl), 3.77-3.80 (m, 1H, alkyl), 3.85 (s, 3H, OMe), 4.36 (d, J = 5.4 Hz, 1H, alkyl), 6.36 (dd, J = 6.0, 6.0 Hz, 1H, vinyl), 6.46 (dd, J = 6.0, 6.0 Hz, 1H, vinyl), 6.88-6.91 (m, 3H, vinyl + arom.), 7.67 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 2H, arom.);
13C{1H} NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3) = 24.7, 24.8, 37.1, 38.2, 55.4, 113.3, 130.8, 131.5, 133.2, 135.1, 146.5, 147.7, 162.6, 192.3;
HRMS (ESI-TOF) m/z calculated for C16H16NaO2 [M+Na]+ 263.1048, found 263.1036;
FT-IR (neat, cm-1 ) 1033, 1174, 1255, 1354, 1600, 1637, 1730, 2870, 2957, 3054.
Optical Rotation: []D 26 +39.9 (c 2.52, CHCl3) for an enantiomerically enriched sample of 94% ee.
HPLC analysis (column, CHIRALPAK AD-3, hexane/2-propanol = 98/2, flow rate 1.0 mL/min, 20 C, detection UV 250 nm light); tR of major-isomer 20.7
////////////////
(1S,4R)-2-(4-Methoxybenzoyl)bicyclo[2.2.2]octa-2,5-diene
Sodium aluminate is presented as a highly active heterogeneous catalyst that is able to convert a range of alcohols into the corresponding unsymmetrical carbonate esters by reaction with dimethyl carbonate. Preparing NaAlO2 via spray drying boosts the basic properties and the activity of the catalyst.
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.oprd.8b00333
/////////////https://pubs.acs.org/doi/suppl/10.1021/acs.oprd.8b00333/suppl_file/op8b00333_si_001.pdf
carboxymethylation, dimethyl carbonate, mixed carbonate esters, sodium aluminate,
 Conferred prestigious award at event ABP News Presents Healthcare Leadership Awards 26th November, 2018 at Taj Lands End, Mumbai India
Conferred prestigious award at event ABP News Presents Healthcare Leadership Awards 26th November, 2018 at Taj Lands End, Mumbai India
Dedicated to Shobha Crasto Aishal crasto Lionel crasto
Service to education is service to humanity
Society recognises efforts done towards it
/////////////award, event ABP News, Healthcare, Leadership, 26th, November, 2018, Taj Lands End, Mumbai, India, education, anthony crasto

Here we describe an efficient and cost-effective chemoenzymatic synthesis of the β-lactamase inhibitor avibactam starting from commercially available ethyl 5-hydroxypicolinate hydrochloride. Avibactam was synthesized in 10 steps with an overall yield of 23.9%. The synthetic route features a novel lipase-catalyzed resolution step during the preparation of (2S,5S)-ethyl 5-hydroxypiperidine-2-carboxylate, a valuable precursor of the key intermediate ethyl (2S,5R)-5-((benzyloxy)amino)piperidine-2-carboxylate. Our synthetic route was used to produce 400 g of avibactam sodium salt.
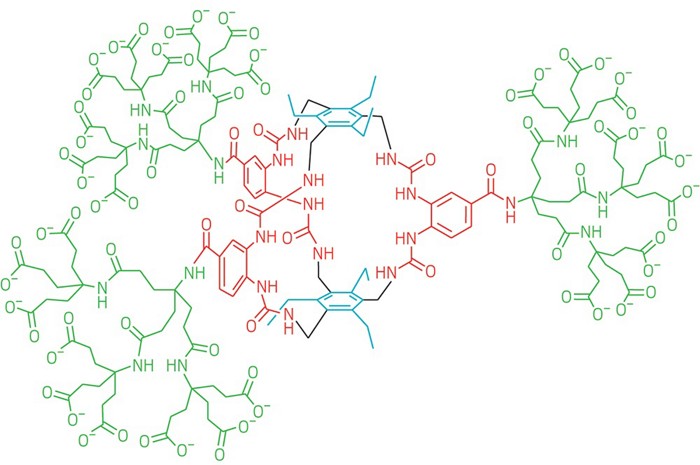
It’s a receptor that binds glucose strongly and with the highest selectivity yet. Could help with #diabetes treatment: http://ow.ly/EPzn30mDYjf
Read all at
I have an exciting news which I want to share today.
Couple of days ago, I was browsing on the internet to see if we can buy ready stock of Chemicals online, especially from Indian Suppliers.
I was surprised to see that there is one stunning B2B Marketplace which is specially meant for ready stock of Chemicals in India.
Carbanio (www.carbanio.com) is showing promising future for all Indian Suppliers which helps them not only buy Chemicals within India, but also to Sell Chemicals. They are no registration charges and no charges to publish Chemical products. Hope they are going to launch internationally very soon which will boost exports from India.
This is really a great news for everyone who would like to generate more revenue by selling online. Online sales will not only help you in increasing revenue, but also will enable you to do business 24*7. In addition, you will also receive new requirements from their Buyers which will help you in scaling your business and portfolio.
To know more about the selling benefits, visit https://www.carbanio.com/sell-on-carbanio
Those who wish to buy, the biggest benefit of this platform is you can buy ready stock and get it delivered at your doorstep with assured Purity and Quality. I see there are huge discounts offered by their registered Sellers, which will be a cost benefit factor.
Another plus point in this site is, you can post your Chemical requirements in case if that is not available on the platform, they will help you in sourcing it for you!

To know more about the buying benefits, visit https://www.carbanio.com/buyer
For free registration, please visit https://www.carbanio.com/register
In case if you still want to know more, you can get in touch with them via businesssupport@carbanio.com

The control of pharmaceutical impurities is currently a critical issue to the pharmaceutical industry. Structure elucidation of pharmaceutical impurities is an important part of the drug product development process. Impurities can have unwanted pharmacological or toxicological effects that seriously impact product quality and patient safety. Potential sources and mechanisms of impurity formation are discussed for both drugs. The International Conference on Harmonization (ICH) has formulated a workable guideline regarding the control of impurities. In this review, a description of different types and origins of impurities in relation to ICH guidelines and, degradation routes, including specific examples, are presented. The article further discusses measures regarding the control of impurities in pharmaceuticals substance and drug product applications.
Impurities in pharmaceuticals are the unwanted chemicals that remain with the active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), or develop during formulation, or upon aging of both API and formulated APIs to medicines. The presence of these unwanted chemicals even in small amounts may influence the efficacy and safety of the pharmaceutical products.
According to ICH, an impurity in a drug substance is defined as-“any component of the new drug substance that is not the chemical entity defined as the new drug substance”. There is an ever increasing interest in impurities present in APIs recently, not only purity profile but also impurity profile has become essential as per various regulatory requirements. The presence of the unwanted chemicals, even in small amount, may influence the efficacy and safety of the pharmaceutical products.
“In the pharmaceutical world, an impurity is considered as any other organic material, besides the drug substance, or ingredients, arise out of synthesis or unwanted chemicals that remains with API’s”
The control of pharmaceutical impurities is currently a critical issue to the pharmaceutical industry. The International Conference on Harmonization (ICH) has formulated a workable guideline regarding the control of impurities.
CLASSIFICATIONS OF IMPURITIES:
Impurities have been named differently or classified as per the ICH guidelines as follows:
A] Common names
1. By-products
2. Degradation products
3. Interaction products
4. Intermediates
5. Penultimate intermediates
6. Related products
7. Transformation products
B] United State Pharmacopeia
The United States Pharmacopoeia (USP) classifies impurities in various sections:
1. Impurities in Official Articles
2. Ordinary Impurities
3. Organic Volatile Impurities
C] ICH Terminology
According to ICH guidelines, impurities in the drug substance produced by chemical synthesis can broadly be classified into following three categories –
1. Organic Impurities (Process and Drug related)
2. Inorganic Impurities
3. Residual Solvents
Organic impurities may arise during the manufacturing process and or storage of the drug substance may be identified or unidentified, volatile or non-volatile, and may include
1. Starting materials or intermediates
2. By-products
3. Degradation products
Impurities are found in API’s unless, a proper care is taken in every step involved throughout the multi-step synthesis for example; in paracetamol bulk, there is a limit test for p-aminophenol, which could be a starting material for one manufacturer or be an intermediate for the others. Impurities can also be formed by degradation of the end product during manufacturing of the bulk drugs.
The degradation of penicillin and cephalosporin are well-known examples of degradation products. The presence of a β-lactam ring as well as that of an a-amino in the C6 or C7 side chain plays a critical role in their degradation.
4. ICH Harmonised Tripartite Guideline Q3A(R): Impurities in New Drug Substances; International Conference on Harmonization: Geneva, 2002.
5. Mishra, B.; Thakur, A.; Mahata, P. P. Pharmaceutical Impurities: A Review. Int. J. Pharm. Chem.2015, 5 (7), 232– 239
6 International Conference on Harmonisation (ICH) Guidelines; Q8, Pharmaceutical Development, 2005; Q9, Quality Risk Management, 2006.
7 Ganzer, W. R.; Materna, J. A.; Mitchell, M. B.; Wall, L. K. Pharm. Technol. 2005, July 2) 1–12.
8 Nasr, M. Drug Information Association Annual Meeting, Philadelphia, PA, June 19, 2006; Pharmaceutical Quality Assessment System (PQAS) in the 21st Century, 2006.
/////