
ORM 10921
UNII-D26C95A960; D26C95A960; ORM-12741; ORM12741; ORM 12741; ORM-10921;
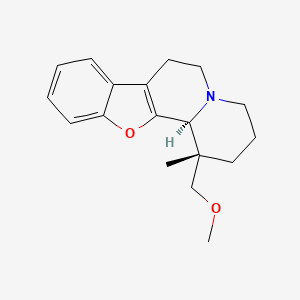
(1S,12bS)-1-(Methoxymethyl)-1-methyl-2,3,4,6,7,12b-hexahydro-1H-[1]benzofuro[2,3-a]quinolizine
(1S,12bS)-1-(methoxymethyl)-1-methyl-2,3,4,6,7,12b-hexahydro-[1]benzofuro[2,3-a]quinolizine
285.38, C18 H23 N O2
cas 610782-82-6
| Belle David Din, Reija Jokela, Arto Tolvanen,Antti Haapalinna, Arto Karjalainen, Jukka Sallinen, Jari Ratilainen | |
| Applicant | Orion Corporation |


David Din Belle
Senior research scientist at Orion Corporation
https://fi.linkedin.com/in/david-din-belle-a2594115

Jari Ratilainen
https://fi.linkedin.com/in/jari-ratilainen-6a566218

https://fi.linkedin.com/in/reija-jokela-06499a1a
The basic drug substance candidate ORM10921 (MW = 285.38),
IUPAC name [1R*,12bR*)-(−)-1,3,4,6,7,12b-hexahydro-1-methoxymethyl-1-methyl-2H-benzofuro [2,3-a]quinolizine],
and its hydrochloric salt were synthesized by Orion Pharma, Finland.
The absolute configuration was assigned by optical rotation and later by single-crystal X-ray diffraction (see Supporting Information). The optical purity of the material was >97%.
- Originator Juvantia Pharma (CEASED); Orion
- Class Neuropsychotherapeutics
- Mechanism of Action Alpha 2c adrenergic receptor antagonists
Highest Development Phases
- Discontinued Major depressive disorder; Schizophrenia
Most Recent Events
- 10 May 2006 Discontinued – Phase-I for Schizophrenia in Finland (unspecified route)
- 10 May 2006 Discontinued – Preclinical for Depression in Finland (unspecified route)
- 15 Nov 2002 Preclinical trials in Schizophrenia in Finland (unspecified route)

Figure 1: Chemical structure of the study compound. Molecular Formula: C18H23NO2 · HCl · ½ H2O; Molecular Weights: 285.39 (free base), 321.85 (hydrochloride) 330.86 (hydrochloride hemihydrate). ORM-10921 · HCl is a single stereoisomer with the (1R*,12bR*) configuration.
The alpha adrenergic receptors can be divided on a pharmacological basis into alphal- and alpha2-adrenoceptors, which can both be further divided into subtypes. Three genetically encoded subtypes, namely alpha2A-, alpha2B- and alpha2C-adrenoceptors, have been discovered in human. Accordingly, alpha2- adrenoceptors in humans have been subdivided into three pharmacological subtypes known as alpha2A-, alpha2B- and alpha2C-adrenoceptors. A fourth, pharmacologically defined subtype, alpha2D, is known in rodents and in some other mammals, and it corresponds to the genetically defined alpha2A-adrenoceptors.
The alpha2-adrenoceptor subtypes have distinct tissue distributions and functional roles. For instance, while alpha2A-adrenoceptors are widely expressed in various tissues, alpha2C-adrenoceptors are concentrated in the CNS, and they appear to play a role in the modulation of specific CNS-mediated behavioural and physiological responses. Compounds that are non-specific to any of the above-mentioned alpha2 subtypes, and compounds that are specific to certain alpha2 subtypes, are already known. For example, atipamezole is a non-specific alpha2 antagonist. Atipamezole has been described in, for example, EP-A-183 492 (cf. p.13, compound XV) and Haapalinna, A. et al., Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 356 (1997) 570-582. U.S. Patent No. 5,902,807 describes compounds that are selective antagonists for the alpha2C subtype and may be used in the treatment of mental illness, e.g. mental disturbance induced by stress. Such compounds include, for example, MK-912 and BAM- 1303. Furthermore, WO-A-99 28300 discloses substituted imidazole derivatives having agonist-like activity for alpha2B- or 2B/2C-adrenoceptors. hi addition, WO 01/64645 relates to derivatives of quinoline useful as alpha2 antagonists, as well as to selective alpha2C antagonist agents. The disclosures of all documents cited above in this paragraph are incorporated by reference herein.
Several arylquinolizine derivatives and related compounds have been described in the literature, some of which possess valuable pharmaceutical effects. For example, U.S. Patents No. 4,806,545 and 4,044,012 describe 1,1-disubstituted indolo[2,3-«]quinolizidines useful as vasodilators and antihypoxic agents. Further, substituted arylquinolizine derivatives, described for example in U.S. Patent No. 4,686,226 possessing alpha2-adrenoceptor antagonistic activity are useful for example as antidepressant, antihypertensive, or antidiabetic agents or platelet aggregation inhibitors. In addition, U.S. Patent No. 3,492,303 relates to indolo[2,3- α]quinolizidines useful as central nervous system depressants.
PATENT
WO 2003082866
https://www.google.com/patents/WO2003082866A1?cl=en
///////////
CC1(CCCN2C1C3=C(CC2)C4=CC=CC=C4O3)COC













Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.