DOI: 10.1039/C6RE00059B, Paper
 Open Access
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence.
This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence.Self-optimising flow reactors combine online analysis with evolutionary feedback algorithms to rapidly achieve optimum conditions.
Self-optimisation of the final stage in the synthesis of EGFR kinase inhibitor AZD9291 using an automated flow reactor
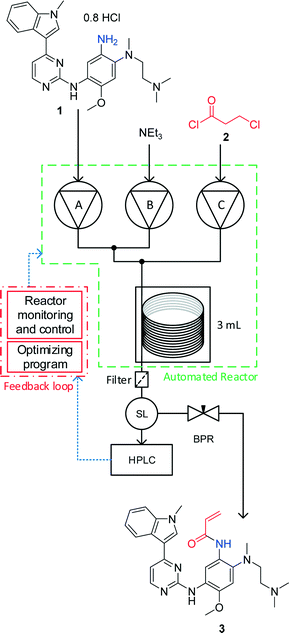
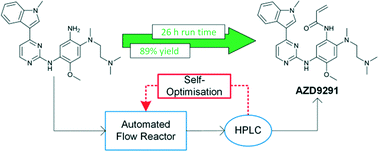
Self-optimising flow reactors combine online analysis with evolutionary feedback algorithms to rapidly achieve optimum conditions. This technique has been applied to the final bond-forming step in the synthesis of AZD9291, an irreversible epidermal growth factor receptor kinase inhibitor developed by AstraZeneca. A four parameter optimisation of a telescoped amide coupling followed by an elimination reaction was achieved using at-line high performance liquid chromatography. Optimisations were initially carried out on a model compound (2,4-dimethoxyaniline) and the data used to track the formation of various impurities and ultimately propose a mechanism for their formation. Our protocol could then be applied to the optimisation of the 2-step telescoped reaction to synthesise AZD9291 in 89% yield.
Self-optimisation of the final stage in the synthesis of EGFR kinase inhibitor AZD9291 using an automated flow reactor
E-mail: r.a.bourne@leeds.ac.uk
DOI: 10.1039/C6RE00059B
http://pubs.rsc.org/en/Content/ArticleLanding/2016/RE/C6RE00059B#!divAbstract
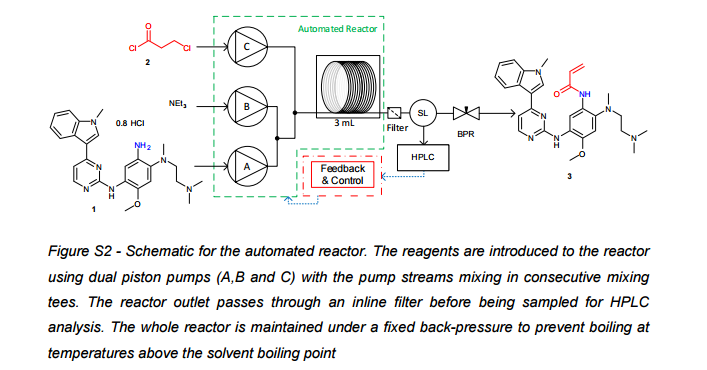
| Scheme 1 Synthesis of the model acrylamide 6 via the β-chloroamide 5 intermediate. |
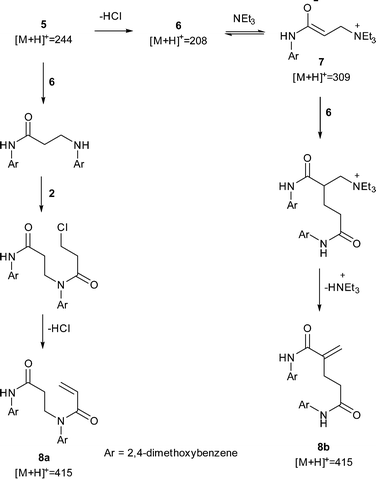
| Scheme 2 Proposed mechanisms to dimers 8a and 8b. The observation of a peak corresponding to 7suggested a Rauhut–Currier mechanism to 8b but subsequent LC-MS-MS analysis showed the major dimer to most likely be 8a. All observed peaks from offline LC-MS are displayed. |
///////Self-optimisation, synthesis, EGFR kinase inhibitor, AZD9291, automated flow reactor













Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.