
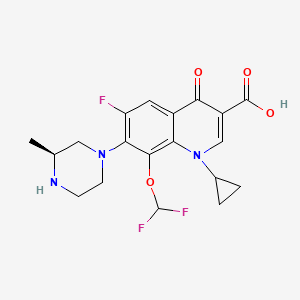
Cadrofloxacin , CS 940
3-Quinolinecarboxylic acid, 1-cyclopropyl-8-(difluoromethoxy)-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-7-[(3S)-3-methyl-1-piperazinyl]-4-oxo-, hydrochloride (1:1)
UNII-1YOQ7J9ACY; 153808-85-6; CADROFLOXACIN HYDROCHLORIDE; 1-cyclopropyl-8-(difluoromethoxy)-6-fluoro-7-[(3s)-3-methylpiperazin-1-yl]-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxylic acid;
1-cyclopropyl-8-(difluoromethoxy)-6-fluoro-7-[(3S)-3-methylpiperazin-1-yl]-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid
NDA Filed in china
| Molecular Formula: | C19H20F3N3O4 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight: | 411.37501 g/mol |
Company:HengRui (Originator), Daiichi Sankyo (Originator), UBE (Originator)
A quinolone antibiotic potentially for the treatment of bacterial infections.
![]()
Research Code CS-940
CAS No. 153808-85-6(FREE)
Cas 128427-55-4(Cadrofloxacin HCl)
HYDROCHLORIDE
| Molecular Weight | 447.84 |
| Formula | C19H20F3N3O4 • HCl |
- OriginatorSankyo; Ube Industries
- DeveloperSankyo
- ClassAntibacterials; Quinolones; Small molecules
- Mechanism of ActionType II DNA topoisomerase inhibitors
-
- 20 Jun 1996An animal study has been added to the Bacterial infections pharmacodynamics section
- 24 Mar 1995Phase-II clinical trials for Bacterial infections in Japan (PO)
Cadrofloxacin hydrochloride was studied for the treatment of bacterial infections.The compound was originally developed by UBE and Daiichi Sankyo. However, this study was discontinued. The compound currently was developed by Hengrui.
SYNTHESIS

Decarboxylation of 3,5,6-trifluoro-4- hydroxyphthalic acid (I) upon heating at 140 C in an autoclave furnished 2,4,5-trifluoro-3-hydroxybenzoic acid (II). This was converted to ethyl ester (III) by refluxing in EtOH in the presence of H2SO4. Condensation of (III) with chlorodifluoromethane and NaH in hot DMF produced the corresponding difluoromethyl ether, and subsequent basic hydrolysis of the ethyl ester yielded 3- (difluoromethoxy) -2, 4,5-trifluorobenzoic acid (IV). Alternatively, acid (II) was converted to acid chloride with SOCl2 and subsequently condensed with ammonia to give amide (V). After formation of the difluoromethyl ether (VI) under similar conditions as above, acid (IV) was obtained by diazotization of the amide function of (VI) in hot sulfuric acid. The difluoromethoxy acid (IV) was also prepared by direct alkylation of hydroxy acid (II) with chlorodifluoromethane in the presence of NaOH in hot DMF. acid (IV) was activated as the corresponding acid chloride (VII) with SOCl2. Condensation of acid chloride (VII) with the magnesium salt of diethyl malonate gave rise to the benzoylmalonate (VIII). Further decarbethoxylation of (VIII) by heating in the presence of p-toluenesulfonic acid yielded keto ester (IX). This was condensed with triethyl orthoformate in the presence of Ac2O to give the ethoxyacrylate (X), which was converted to enamine (XII) by treatment with cyclopropylamine (XI). The target quinolone system (XIII) was then obtained by intramolecular cyclization of (XII) in the presence of NaH. Then, ethyl ester (XII) cleavage using boron trifluoride etherate provided the key quinolonecarboxylic acid boron chelate (XIV)
| Patent ID | Date | Patent Title |
|---|---|---|
| US2011159049 | 2011-06-30 | PHARMACEUTICAL COMPOSITION |
| US2010330165 | 2010-12-30 | USE OF CHEMOTHERAPEUTIC AGENTS |
| US2007196504 | 2007-08-23 | PHARMACEUTICAL COMPOSITION |
| US2007197501 | 2007-08-23 | Use Of Chemotherapeutic Agents |
| US2007148235 | 2007-06-28 | PHARMACEUTICAL COMPOSITION |
| US2005152975 | 2005-07-14 | Pharmaceutical composition |
| US2004022848 | 2004-02-05 | Medicinal composition |
| US2003045544 | 2003-03-06 | Use of chemotherapeutic agents |
//////CS 940, Quinolone antibiotic , CADROFLOXACIN, NDA
CC1CN(CCN1)C2=C(C=C3C(=C2OC(F)F)N(C=C(C3=O)C(=O)O)C4CC4)F














Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.