
Lobeglitazone Sulfate, CKD-501
(Duvie®) Approved
Chong Kun Dang (Originator)
A dual PPARα and PPARγ agonist used to treat type 2 diabetes.

Trade Name:Duvie®MOA:Dual PPARα and PPARγ agonistIndication:Type 2 diabetes
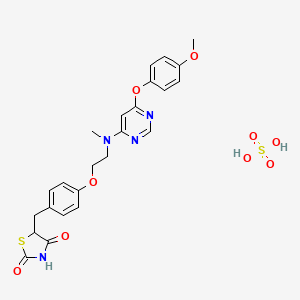
CAS No. 607723-33-1(FREE)
763108-62-9(Lobeglitazone Sulfate)
2,4-Thiazolidinedione, 5-((4-(2-((6-(4-methoxyphenoxy)-4- pyrimidinyl)methylamino)ethoxy)phenyl)methyl)-, sulfate (1:1);
Lobeglitazone (trade name Duvie, Chong Kun Dang) is an antidiabetic drug in the thiazolidinedione class of drugs. As an agonistfor both PPARα and PPARγ, it works as an insulin sensitizer by binding to the PPAR receptors in fat cells and making the cells more responsive to insulin.[3]
Lobeglitazone sulfate was approved by the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (Korea) on July 4, 2013. It was developed and marketed as Duvie® by Chong Kun Dang Corporation.
Lobeglitazone is an agonist for both PPARα and PPARγ, and it works as an insulin sensitizer by binding to the PPAR receptors in fat cells and making the cells more responsive to insulin. It is indicated as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes.
Duvie® is available as tablet for oral use, containing 0.5 mg of free Lobeglitazone. The recommended dose is 0.5 mg once daily.
Lobeglitazone which was reported in our previous works belongs to the class of potent PPARα/γ dual agonists (PPARα EC50: 0.02 μM, PPARγ EC50: 0.018 μM, rosiglitazone; PPARα EC50: >10 μM, PPARγ EC50: 0.02 μM, pioglitazone PPARα EC50: >10 μM, PPARγ EC50: 0.30 μM). Lobeglitazone has excellent pharmacokinetic properties and was shown to have more efficacious in vivo effects in KKAy mice than rosiglitazone and pioglitazone.17 Due to its outstanding pharmacokinetic profile, lobeglitazone was chosen as a promising antidiabetes drug candidate.
Medical uses
Lobeglitazone is used to assist regulation of blood glucose level of diabetes mellitus type 2 patients. It can be used alone or in combination with metformin.[4]
Lobeglitazone was approved by the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (Korea) in 2013, and the postmarketing surveillance is on progress until 2019.[4][5]
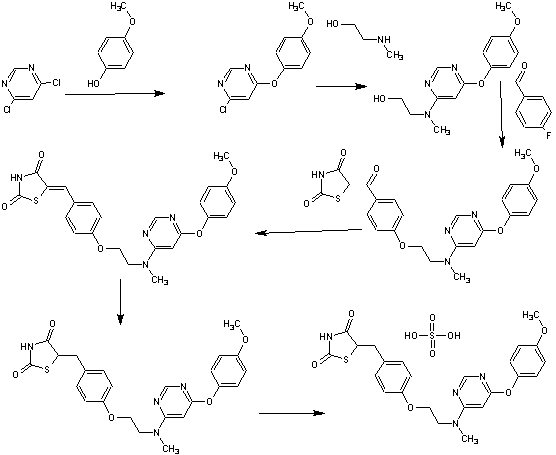
SYNTHESIS

PAPER
Org. Process Res. Dev. 2007, 11, 190-199.
Process Development and Scale-Up of PPAR α/γ Dual Agonist Lobeglitazone Sulfate (CKD-501)
http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/op060087u

A scaleable synthetic route to the potent PPARα/γ dual agonistic agent, lobeglitazone (1), used for the treatment of type-2 diabetes was developed. The synthetic pathway comprises an effective five-step synthesis. This process involves a consecutive synthesis of the intermediate, pyrimidinyl aminoalcohol (6), from the commercially available 4,6-dichloropyrimidine (3) without the isolation of pyrimidinyl phenoxy ether (4). Significant improvements were also made in the regioselective 1,4-reduction of the intermediate, benzylidene-2,4-thiazolidinedione (10), using Hantzsch dihydropyridine ester (HEH) with silica gel as an acid catalyst. The sulfate salt form of lobeglitazone was selected as a candidate compound for further preclinical and clinical study. More than 2 kg of lobeglitazone sulfate (CKD-501, 2) was prepared in 98.5% purity after the GMP batch. Overall yield of 2 was improved to 52% from 17% of the original medicinal chemistry route.
Silica gel TLC Rf = 0.35 (detection: iodine char chamber, ninhydrin solution, developing solvents: CH2Cl2/MeOH, 20:1); mp 111.4 °C; IR (KBr) ν 3437, 3037, 2937, 2775, 1751, 1698, 1648, 1610, 1503, 1439, 1301, 1246, 1215, 1183 cm-1; 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 3.09 (m, 4H), 3.29 (m, 1H), 3.76 (s, 3H), 3.97 (m, 2H), 4.14 (m, 2H), 4.86 (m, 1H), 6.06 (bs, 1H), 6.86 (m, 2H), 7.00 (m, 2H), 7.13 (m, 4H), 8.30 (s, 1H), 11.99 (s, NH); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 37.1, 38.2, 53.7, 53.8, 56.3, 62.2, 65.8, 86.0, 115.1, 116.0, 123.0, 129.8, 131.2, 145.7, 153.4, 157.9, 158.1, 161.1, 166.5, 172.4, 172.5, 176.3, 176.5; MS (ESI)m/z (M + 1) 481.5; Anal. Calcd for C24H26N4O9S2: C, 49.82; H, 4.53; N, 9.68; S, 11.08. Found: C, 49.85; H, 4.57; N, 9.75; S, 11.15.
PATENT
References
- Lee JH, Noh CK, Yim CS, Jeong YS, Ahn SH, Lee W, Kim DD, Chung SJ. (2015). “Kinetics of the Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and Excretion of Lobeglitazone, a Novel Activator of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Gamma in Rats.”.Journal of Pharmaceutical sciences 104 (9): 3049–3059.doi:10.1002/jps.24378. PMID 25648999.
- Kim JW, Kim JR, Yi S, Shin KH, Shin HS, Yoon SH, Cho JY, Kim DH, Shin SG, Jang IJ, Yu KS. (2011). “Tolerability and pharmacokinetics of lobeglitazone (CKD-501), a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ agonist: a single- and multiple-dose, double-blind, randomized control study in healthy male Korean subjects.”. Clinical therapeutics 33 (11): 1819–1830.doi:10.1016/j.clinthera.2011.09.023. PMID 22047812.
- Lee JH, Woo YA, Hwang IC, Kim CY, Kim DD, Shim CK, Chung SJ. (2009). “Quantification of CKD-501, lobeglitazone, in rat plasma using a liquid-chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry method and its applications to pharmacokinetic studies.”. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis 50 (5): 872–877.doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2009.06.003. PMID 19577404.
- “MFDS permission information of Duvie Tablet 0.5mg”(Release of Information). Ministry of Food and Drug Safety. Retrieved2014-10-23.
- “국내개발 20번째 신약‘듀비에정’허가(20th new drug developed in Korea ‘Duvie Tablet’ was approved)”. Chong Kun Dang press release. 2013-07-04. Retrieved 2014-10-23.
 |
|
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
|---|---|
|
5-[(4-[2-([6-(4-Methoxyphenoxy)pyrimidin-4-yl]-methylamino)ethoxy]phenyl)methyl]-1,3-thiazolidine-2,4-dione
|
|
| Clinical data | |
| Trade names | Duvie |
| Routes of administration |
Oral |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | >99%[1] |
| Metabolism | liver (CYP2C9, 2C19, and 1A2)[1] |
| Biological half-life | 7.8–9.8 hours[2] |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | 607723-33-1 |
| PubChem | CID 9826451 |
| DrugBank | DB09198 |
| ChemSpider | 8002194 |
| Synonyms | CKD-501 |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | C24H24N4O5S |
| Molar mass | 480.53616 g/mol |
///Lobeglitazone Sulfate, CKD-501, Duvie®, Approved KOREA, Chong Kun Dang, A dual PPARα and PPARγ agonist , type 2 diabetes.
CN(CCOC1=CC=C(C=C1)CC2C(=O)NC(=O)S2)C3=CC(=NC=N3)OC4=CC=C(C=C4)OC.OS(=O)(=O)O














Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.