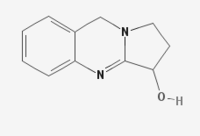
Vasicine (peganine) is a quinazoline alkaloid. It is the active compound of Justicia adhatoda, after which the chemical is named.
Vasicine has been compared to theophylline both in vitro and in vivo.[1] It has also been studied in combination with the related alkaloid vasicinone. Both the alkaloids in combination (1:1) showed pronounced bronchodilatory activity in vivo and in vitro.[2] Both alkaloids are also respiratory stimulants.[2] Vasicine has a cardiac–depressant effect, while vasicinone is a weak cardiac stimulant; the effect can be normalized by combining the alkaloids.[2][3] Vasicine is reported to have a uterine stimulant effect.[3]
Vasicine
Synonym Peganine
Biological Sources It is obtained from the leaves of Adhatoda vasica (L.) Nees (Acanthaceae) (Malabar Nut, Adotodai, Paveltia); and the seeds of Peganum harmala L. (Rutaceae) (Harmel, Syrian Rue, African Rue).
Chemical Structure
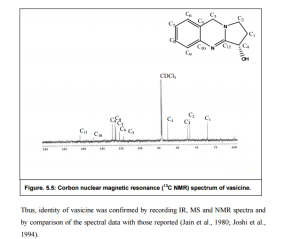
1, 2, 3, 9-Tetrahydropyrrolo [2, 1-b] quinazoline-3-ol; (C11H12N2O).
Isolation It is isolated from the leaves of Adhatoda vasica* and also from the seeds of Peganum harmala** by adopting the standard methods of isolation described earlier in this chapter.
Characteristic Features
dl-Form: 1. It is obtained as needles from ethanol having mp 210°C.
- It sublimes on being subjected to high vacuum.
- It is soluble in acetone, alcohol, chloroform; and slightly soluble in water, ether and
benzene.
l-Form: 1. It is obtained as needles from ethanol with mp 212°C.
- Its specific rotation [α ]D14-2540(C = 2.4 in CHCl3); [α ]D14–14 62° (C = 2.4 in ethanol).
Note: In dilute HCl it is obtained as its dextrorotatory form.
Identification Tests
- Hydrochloride dihydrate derivative is obtained as needles having mp 208°C (dry).
- Hydroiodide dihydrate derivative is formed as needles with mp 195°C (dry).
- Methiodide derivative is obtained as needles from methanol having mp 187°C.
- Acetyl vasicine derivative (C11H11N2O COCH3) is formed as crystals having mp 123°C and bp0.01 230-240°C.
Uses
- It is mostly used as an expectorant and bronchodilator.
- It also shows oxytocic properties very similar to those exhibited by oxytocin and methyl ergometrine.
- Vasicine also shows abortifacient action which is due to the release of prostaglandins.
Biosynthesis of Vasicine Various studies in Peganum harmala have evidently revealed vasicine (peganine) to be derived from the anthranilic acid, while the remaining portion of the structure comprising of a pyrrolidine ring provided by ornithine. The probable mechanism of vasicine skeleton may be explained by virtue of the nucleophilic attack from the N-atom present in anthranilate upon the pyrrolidinium cation, ultimately followed by amide formation. However, interestingly this pathway is not being adopted in Justicia adhatoda.

Vasaka
http://www.himalayawellness.com/products/pharmaceuticals/vasaka.htm
Effective respiratory care
Vasaka (Malabar Nut Tree/Adhatoda zeylanica) is well known in Ayurveda for its beneficial effects in respiratory ailments, particularly as an expectorant in bronchitis. The leaves, flowers, fruits and roots are used extensively for treating cold, cough, whooping-cough, chronic bronchitis and asthma.
Vasaka grows throughout India, up to an altitude of 1,300 meters.
Active constituents:
Vasaka contains the pyrroquinazoline alkaloids, including vasicine, vasicol and vasinone along with other minor constituents. Vasicine and vasinone are the major bioactive constituents of Vasaka which have bronchodilatory and antitussive properties.
The alkaloids present in the plant show significant protection against allergen-induced bronchial obstruction.
Herb Functions:
Respiratory care: Vasaka exhibits anti-inflammatory, antitussive and bronchodilatory action which eases congestion and coughing by helping loosen and thin mucus in airways. Vasaka relieves dyspnea by dilating the airways and improves overall lung functions. The herb is an excellent supportive therapy for symptomatic relief in tuberculosis and pulmonary infections.
Indications
- Productive cough
- Bronchitis
- Bronchial asthma
Contraindications:
None
Recommended dose:
One capsule, twice a day or as directed by your physician
Composition:
Each capsule contains 250mg extract of Vasaka
Note: Since Himalaya’s Pure Herbs are in capsule form, some children below 14 years may find it difficult to swallow them. For this reason, Pure Herbs are recommended for children ages 14 and above.
The information on this page is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice. Do not use this information to diagnose or treat your problem without consulting your doctor.
http://kumarncsirihbt.weebly.com/publications.html

Adhatoda Vasica (Justicia Adhatoda) – Malabar Nut, Vasa, Vasaka …
Presentation “Herbal drugs for health Herbal drugs for health …
References
- Nepali, Kunal; Sharma, Sahil; Ojha, Ritu; Dhar, Kanaya Lal (2012). “Vasicine and structurally related quinazolines”. Medicinal Chemistry Research 22 (1): 1–15. doi:10.1007/s00044-012-0002-5. ISSN 1054-2523.
- Avula, B.; et al. (2008). “Quantitative determination of vasicine and vasicinone in Adhatoda vasica by high performance capillary electrophoresis” (PDF). Die Pharmazie – An International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 63 (1): 20–22. doi:10.1691/ph.2008.7175.
- ^ Jump up to:a b Rajani, M; Soni, S; Anandjiwala, Sheetal; Patel, G (2008). “Validation of different methods of preparation of Adhatoda vasica leaf juice by quantification of total alkaloids and vasicine”. Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 70 (1): 36. doi:10.4103/0250-474X.40329.ISSN 0250-474X.
 |
|
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1,2,3,9-Tetrahydropyrrolo[2,1-b]quinazolin-3-ol
|
|
| Other names
Peganine
|
|
| Identifiers | |
| 6159-56-4 | |
| Jmol interactive 3D | Image |
| PubChem | 72610 |
| Properties | |
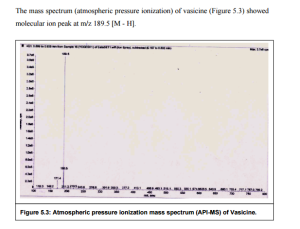
| C11H12N2O | |
| Molar mass | 188.23 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 210 °C (410 °F; 483 K) |
| Solubility in acetone, alcohol, chloroform | Soluble |
//////














Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.